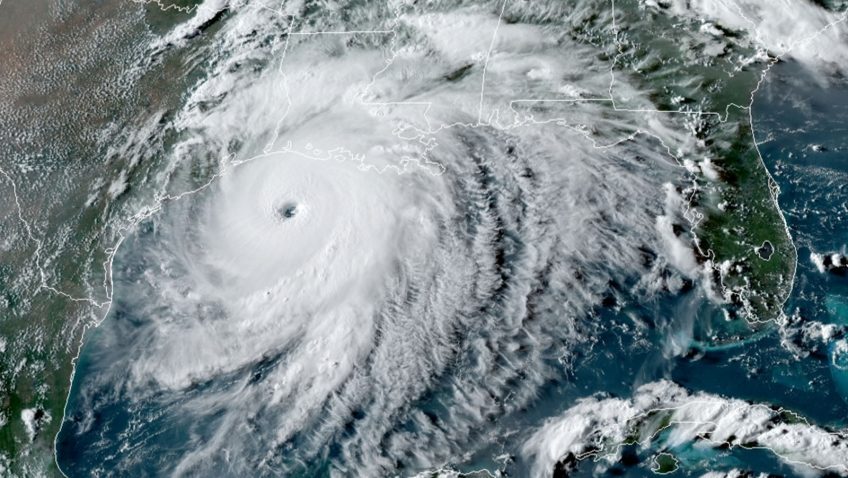
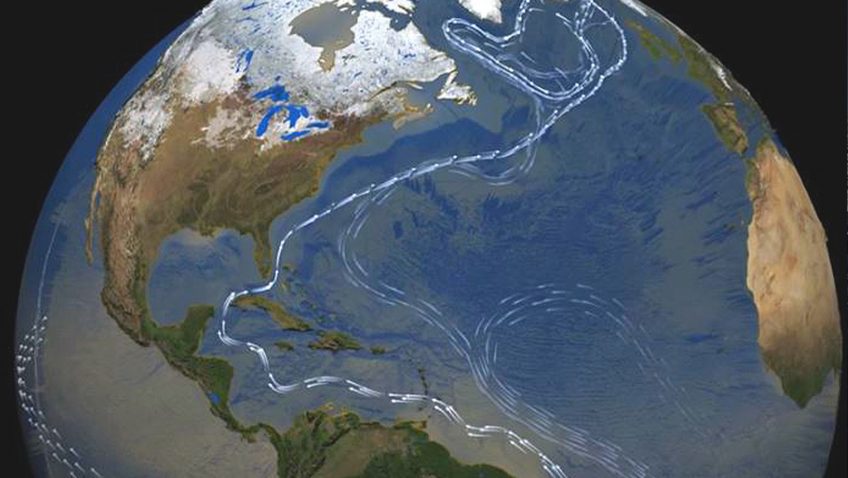
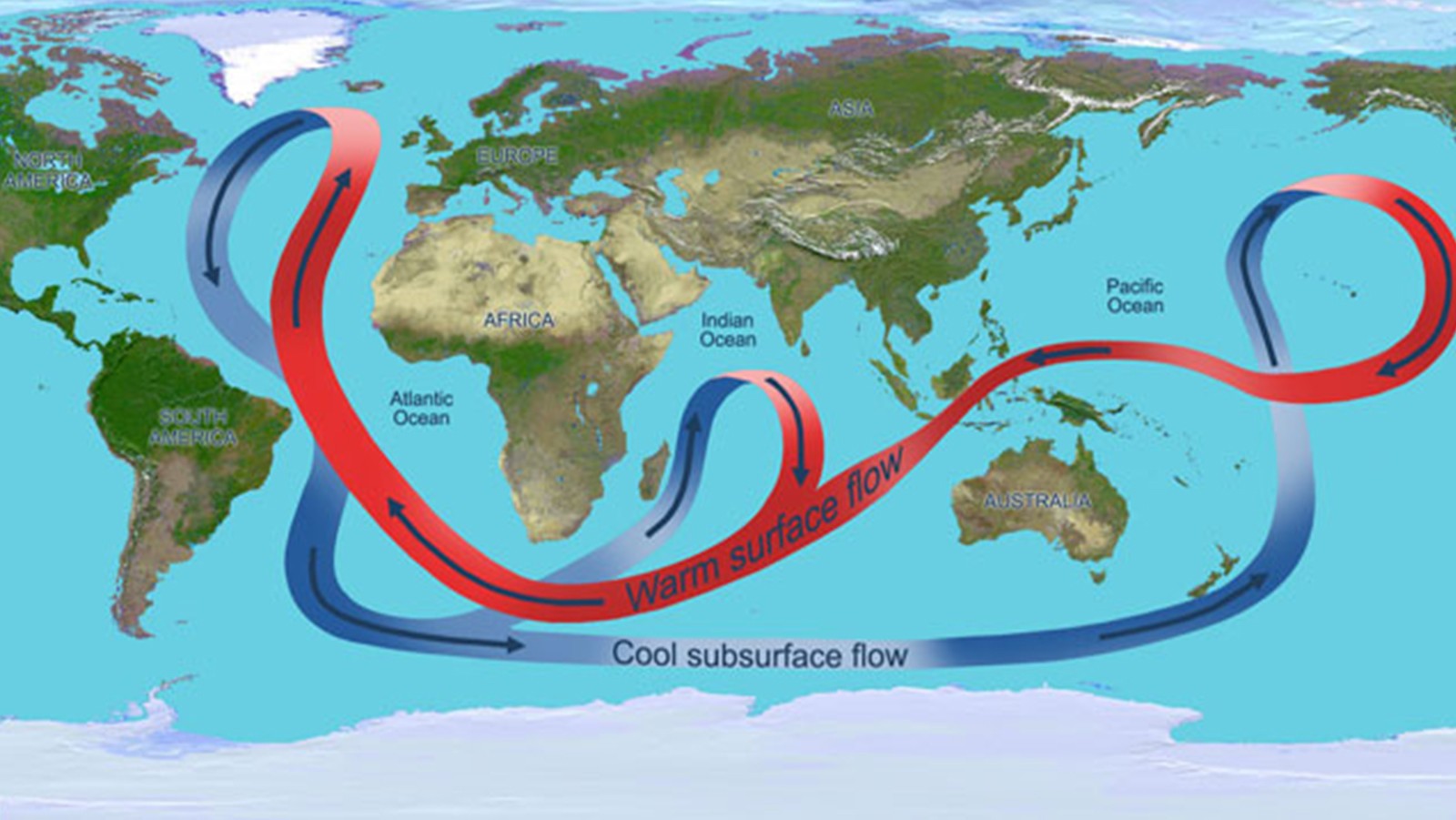
Deep Ocean Warming Continues into the Vema Channel
In a recent study published in American Geophysical Union (AGU), scientists at NOAA’s Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML) contributed to an international study that confirmed warming trends and the possibility of increased rates of warming in one of the deepest channels of the Southwest Atlantic ocean, the Vema Channel.