Underwater Gliders Retrieved After Successful Second Mission
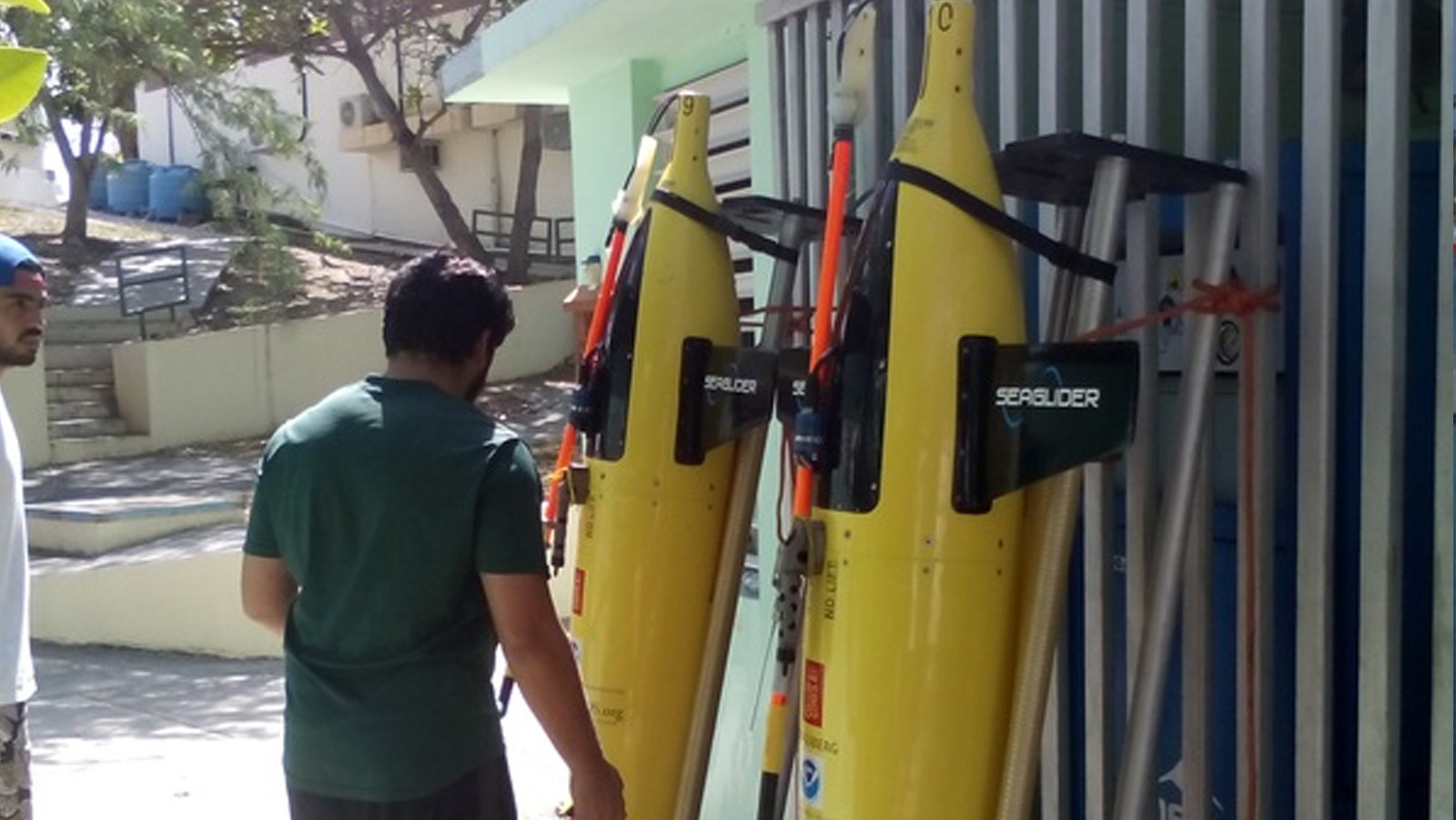
On April 27th, AOML physical oceanographers partnered with the University of Puerto Rico to successfully recover two underwater gliders from the Caribbean Sea aboard the R/V La Sultana of the University of Puerto Rico Mayaguez. The gliders successfully transected a region in the eastern Caribbean providing approximately 3000 profile observations of temperature, salinity, oxygen, and surface as well as depth-average current velocities.