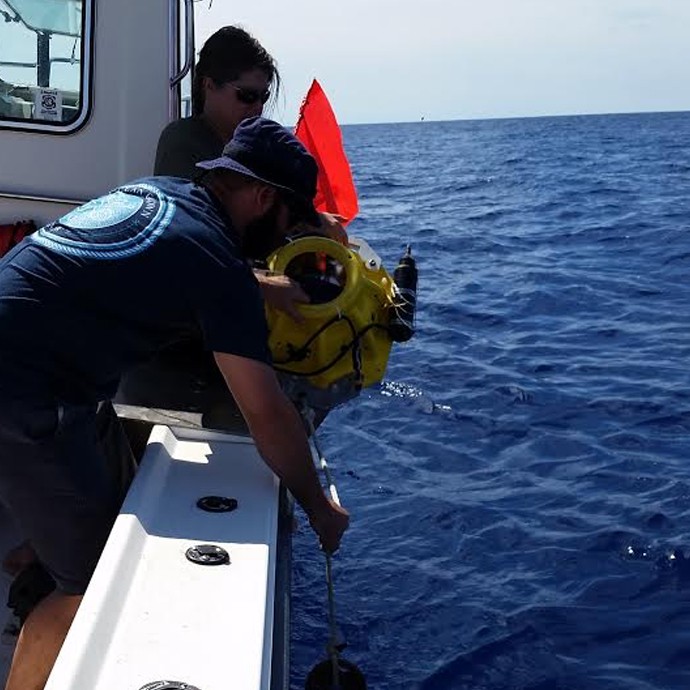
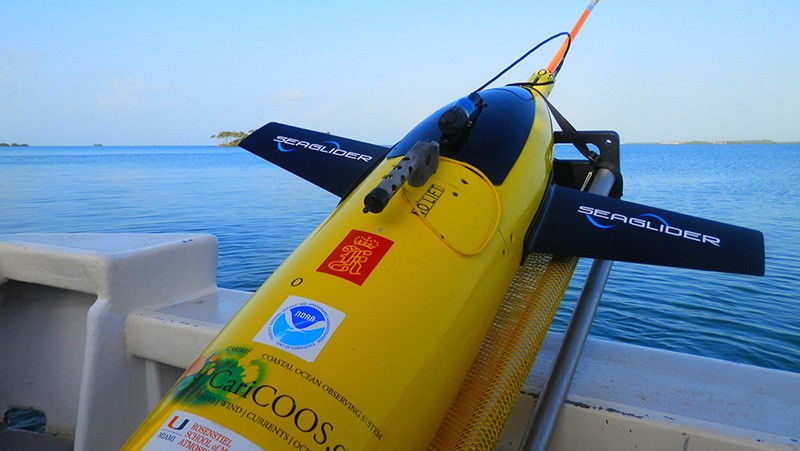
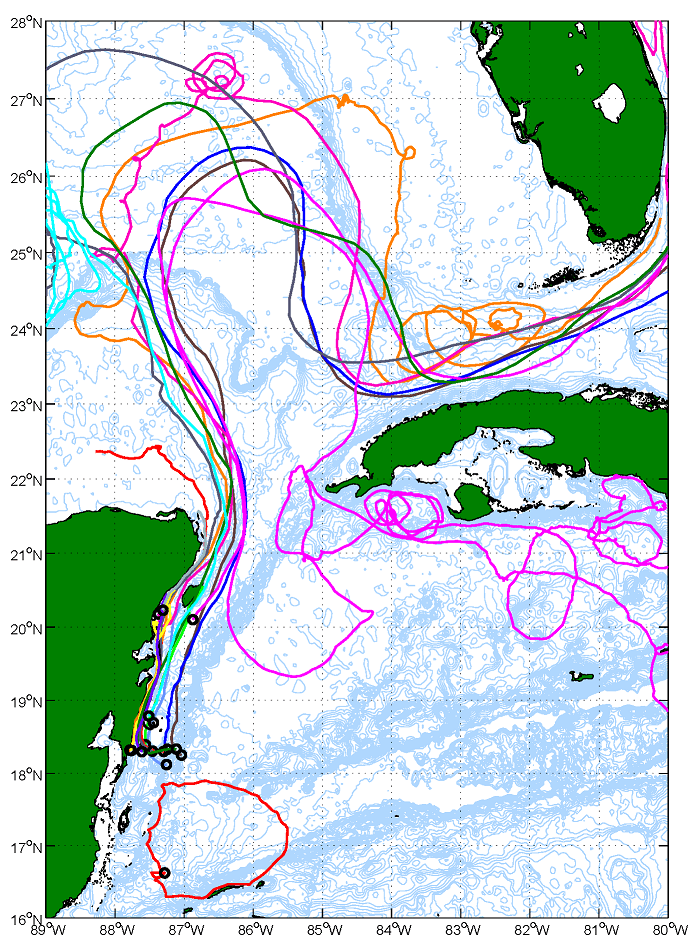
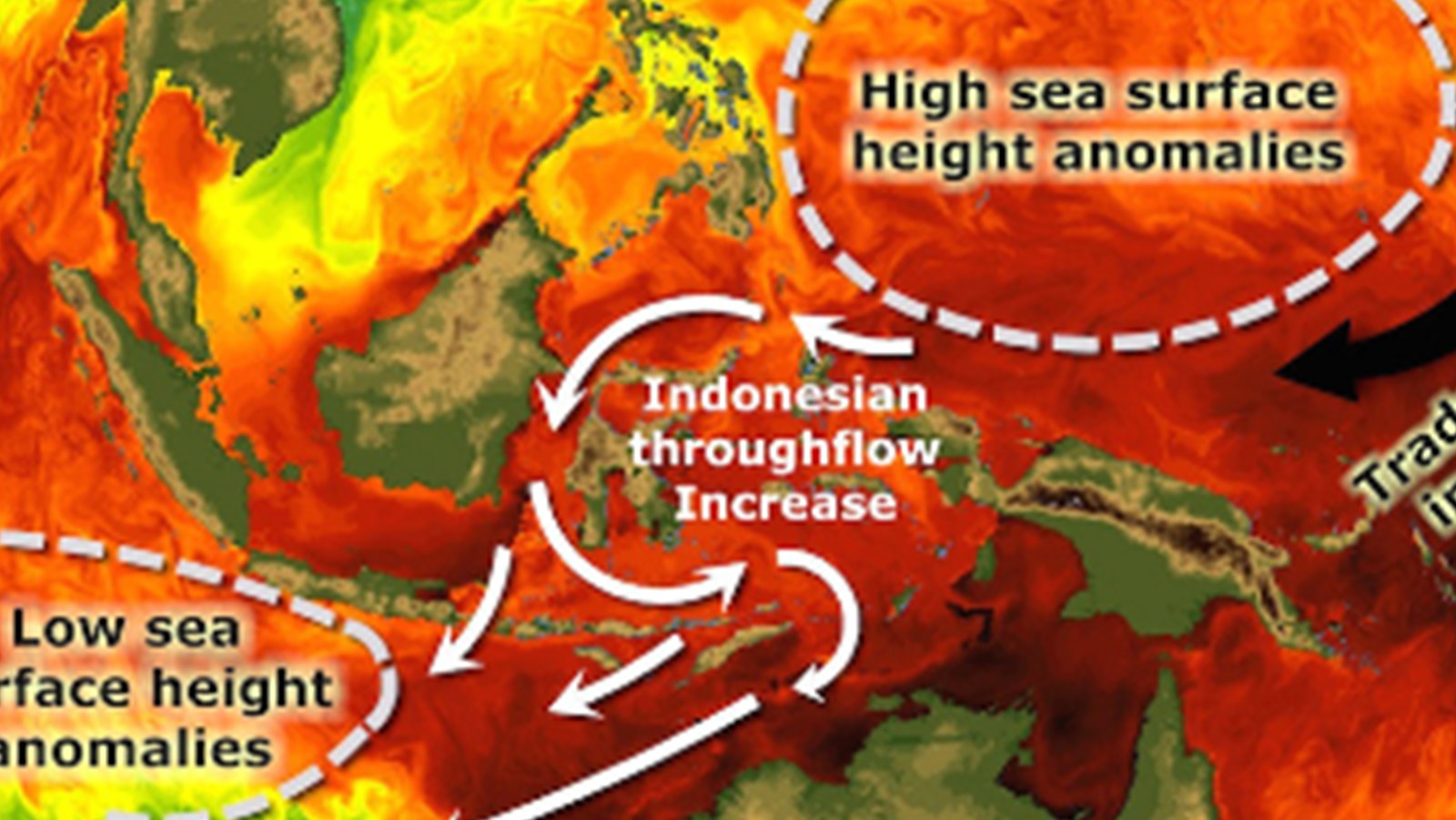
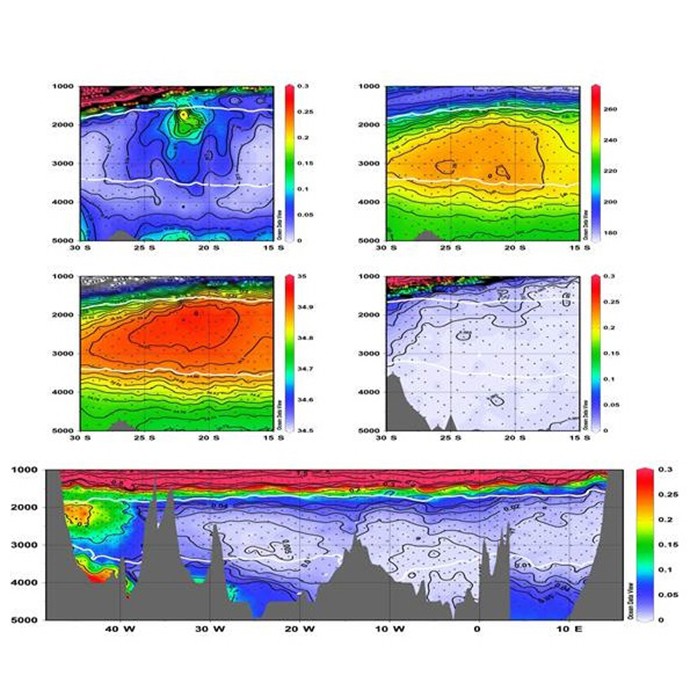
On July 14th, 2015, AOML physical oceanographers deployed one of two sea gliders in the Caribbean from the University of Puerto Rico’s R/V La Sultana. The third deployment will continue the project’s mission to gather important data in the Caribbean and Tropical North Atlantic Ocean to help with hurricane intensity forecasting and provide valuable information about the role the ocean plays in tropical cyclone development. What’s new for this mission? For the first time, the gliders will collect ocean current velocity profiles in addition to the real-time temperature, salinity, and oxygen data. AOML scientists also equipped the glider with an improved battery which will allow the glider to record more profile measurements. The second of the two gliders will be deployed in the Tropical North Atlantic in the upcoming weeks.