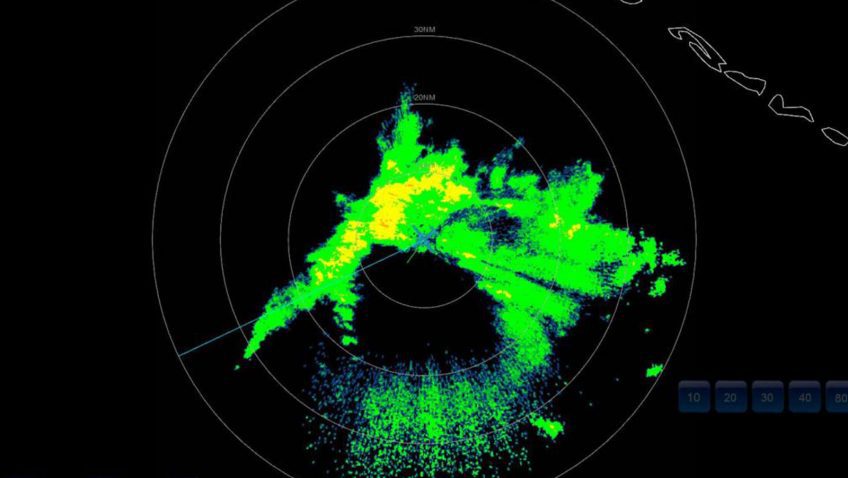
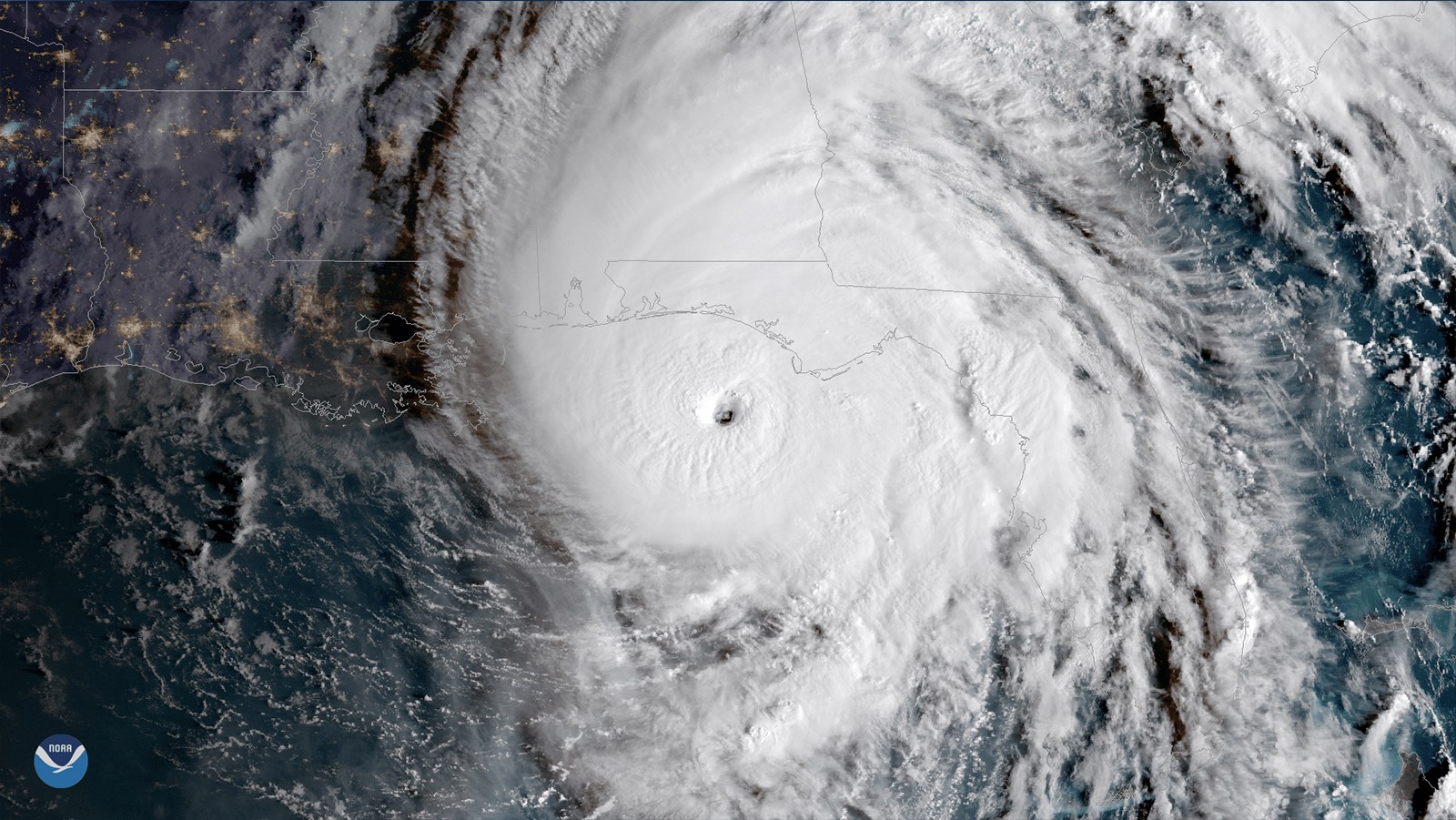
Ocean Drone Sails into Category 4 Hurricane Sam
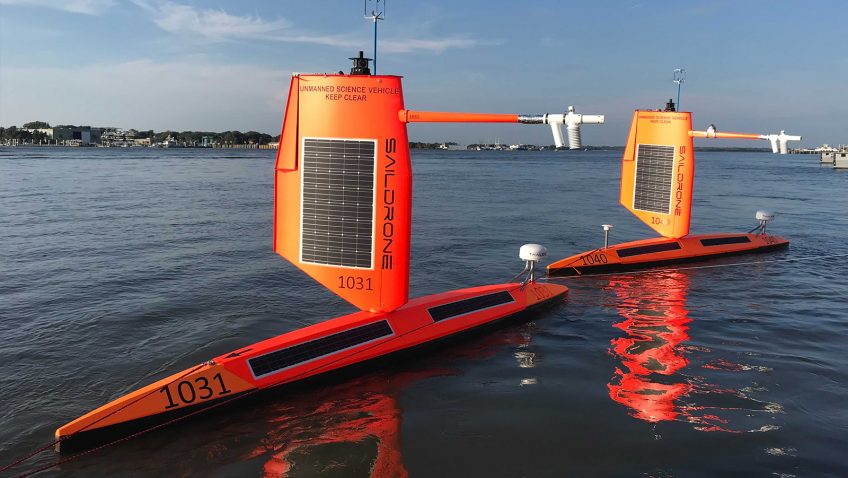
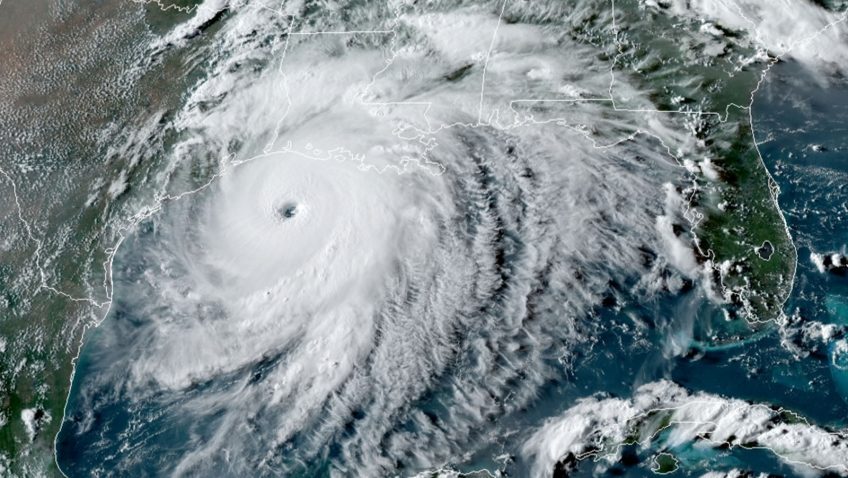
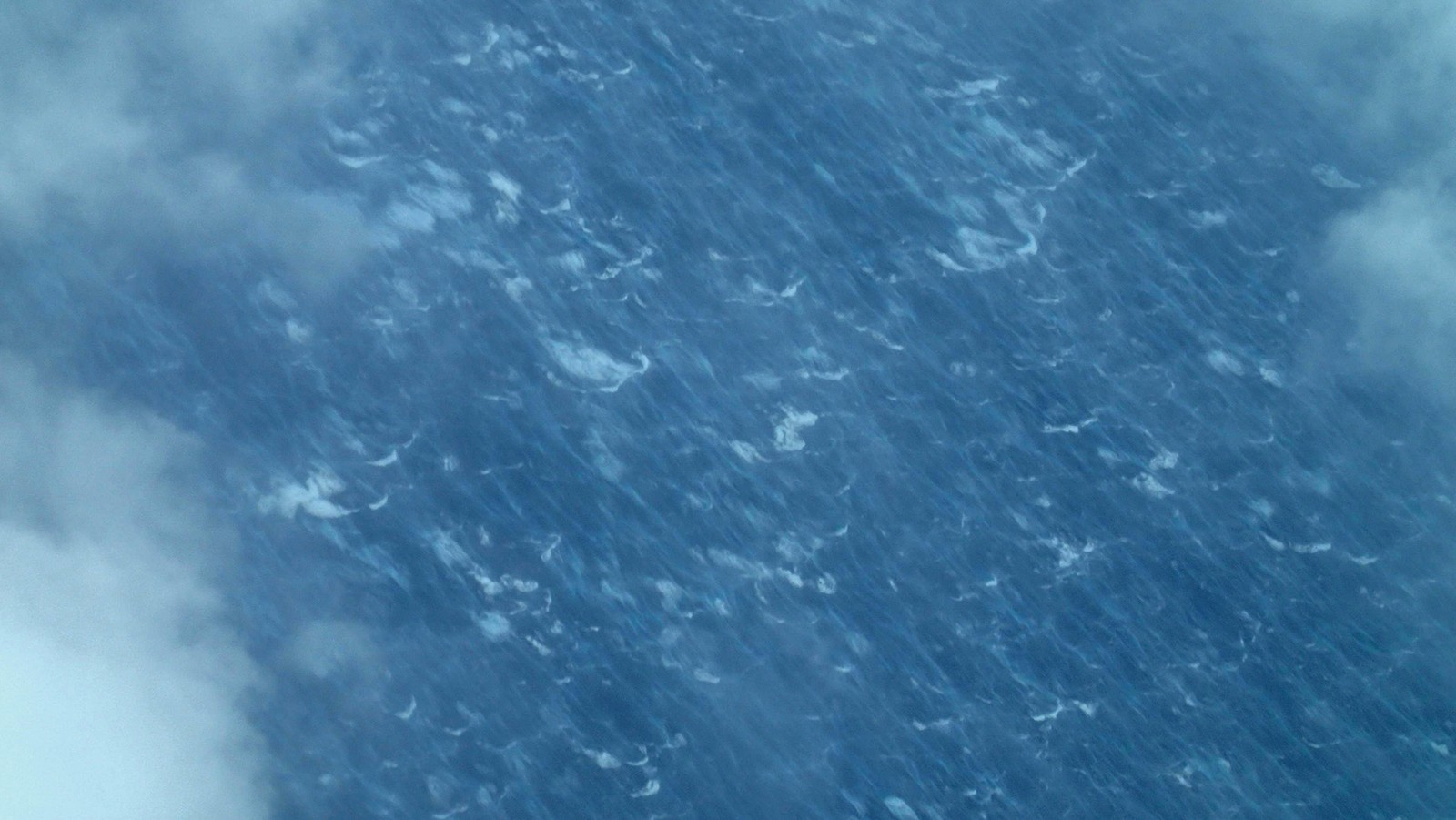
For the first time ever, Saildrone Inc. and NOAA have used an uncrewed surface vehicle to collect oceanic and atmospheric data from inside the eye of a hurricane. On September 30th, 2021 saildrone 1045 travelled directly into Category 4 Hurricane Sam.