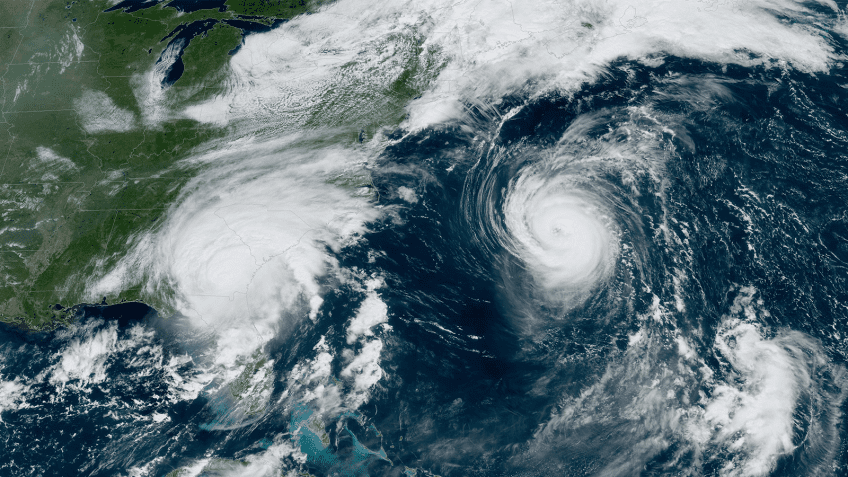
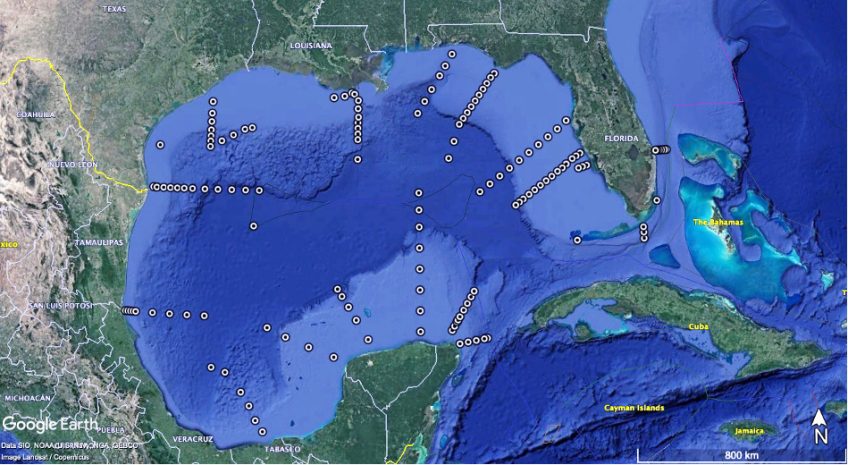
NOAA’s Multi-Faceted Hurricane Data Collection Efforts Provide a Detailed View of Hurricanes Franklin and Idalia
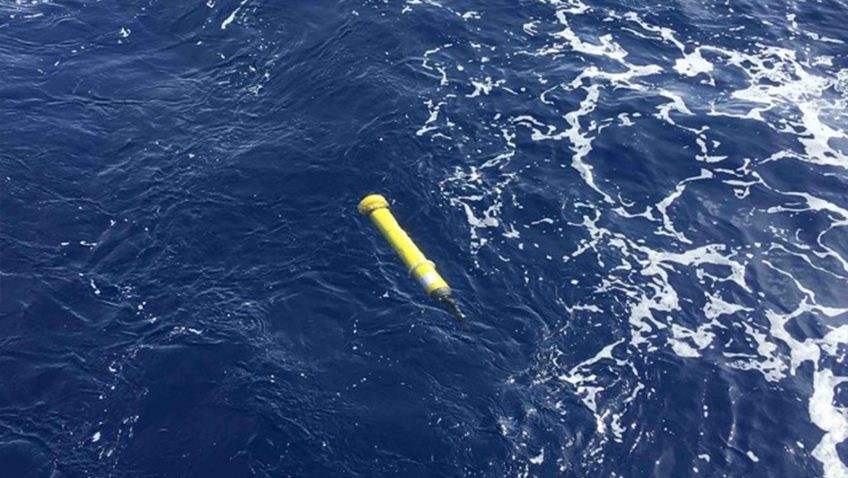
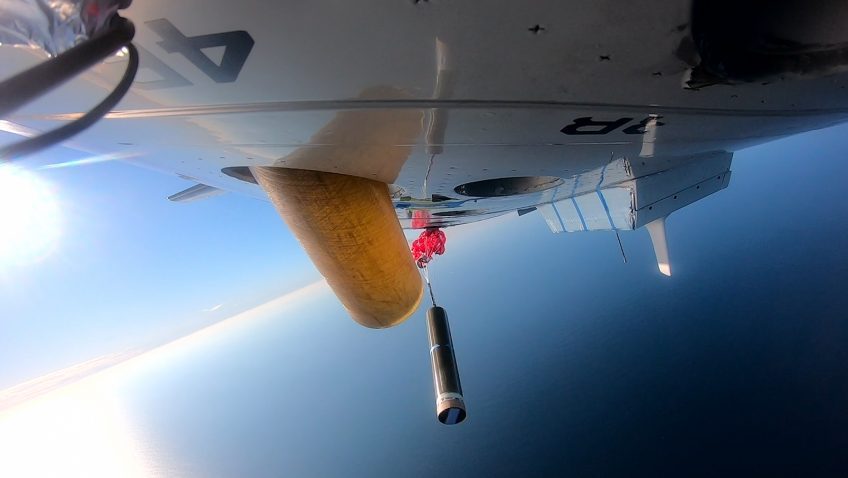
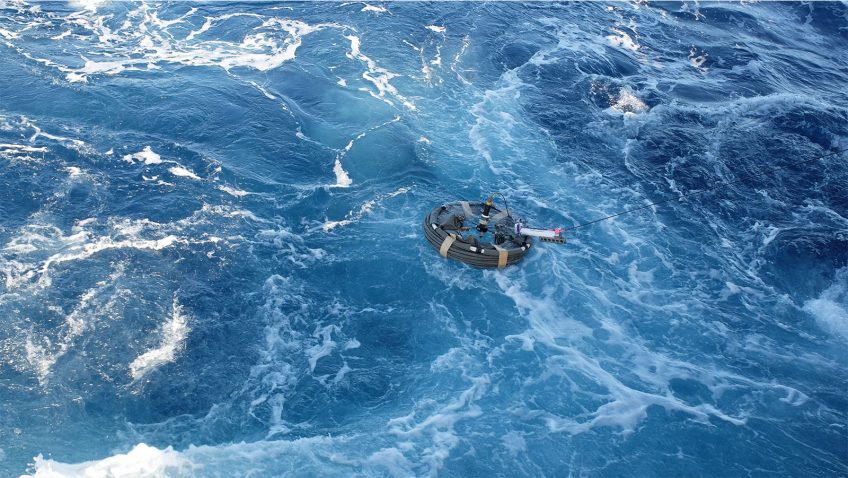
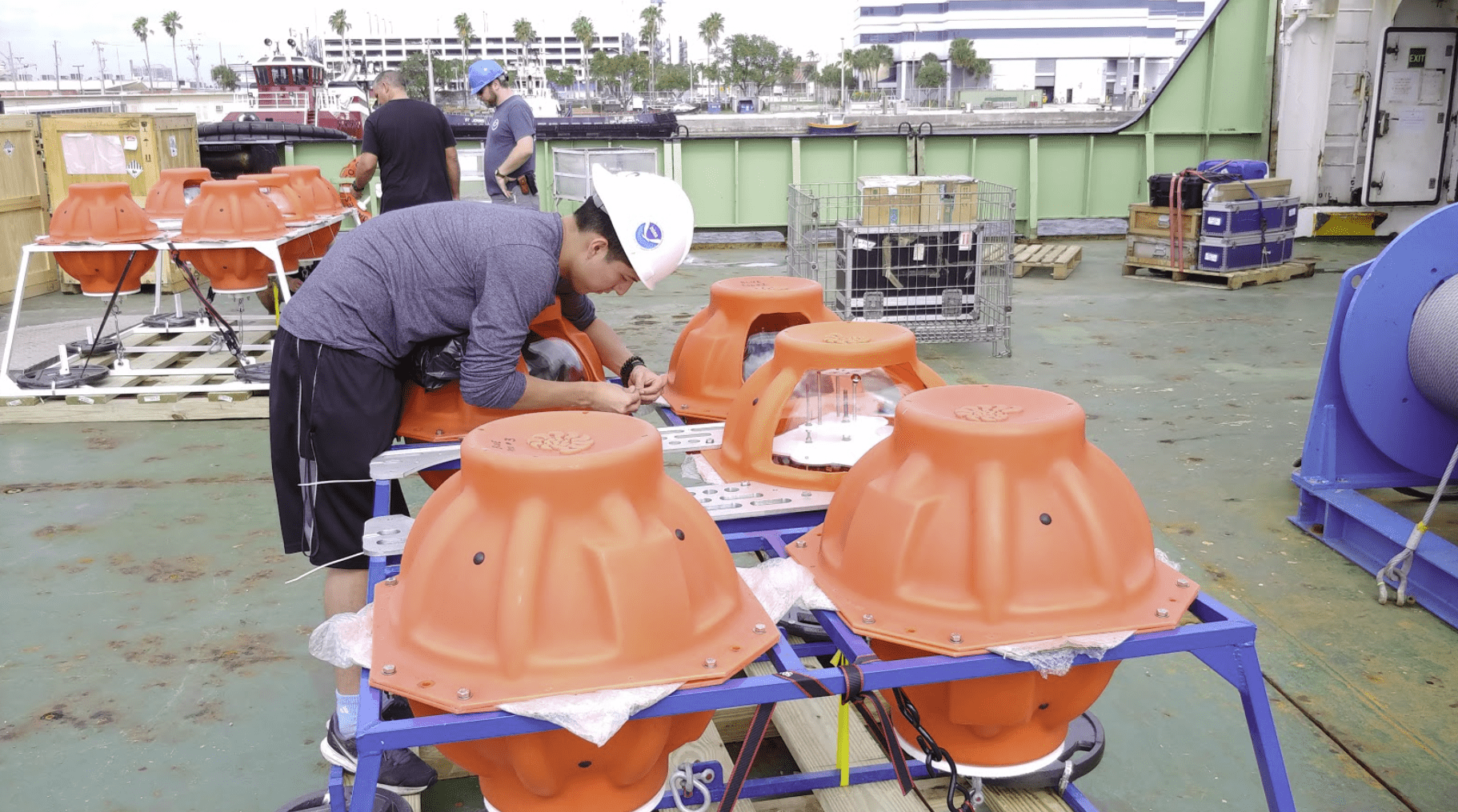
As Hurricanes Franklin and Idalia strengthened in late August, NOAA scientists collected critical data from the air, sea surface, and underwater to enhance forecasts and increase scientific knowledge. In less than two weeks, a fleet of strategically placed oceanographic instruments gathered temperature, salinity, and surface wind speed data, while NOAA’s Hurricane Hunter aircraft repeatedly flew […]