AOML Scientists Tackle one of the Most Challenging Problems in U.S. Seasonal Rainfall Prediction
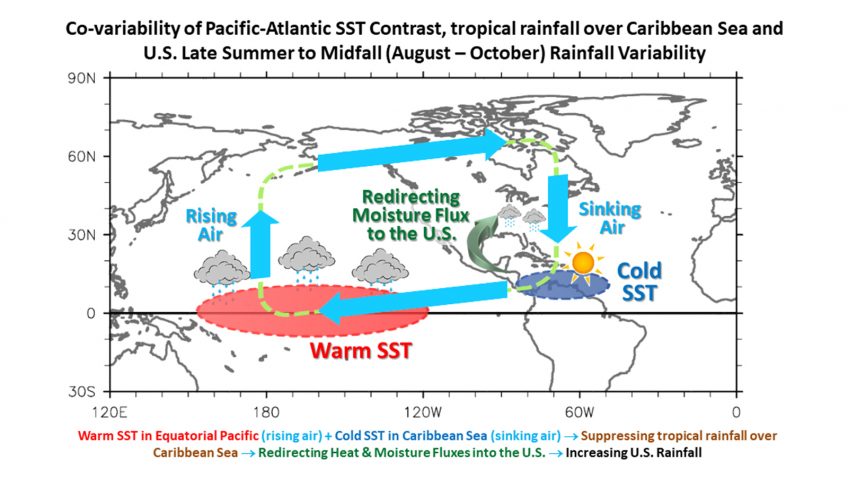
In a recent article published in Geophysical Research Letters, AOML and CIMAS scientists investigated U.S. rainfall variability, focusing on the late summer to mid-fall (August-October) season. The main goal of the study was to identify potential predictors of U.S. precipitation during August-October and to explore the underlying physical mechanisms.