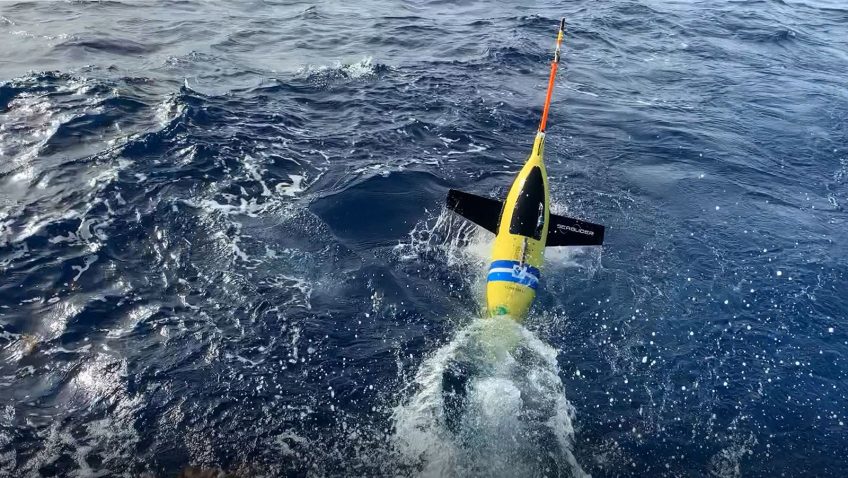
Hurricane Gliders Return Home from 2020 Season
NOAA’s hurricane gliders are returning home after a successful journey during the 2020 hurricane season. These gliders were deployed off the coasts of Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, the U.S. Virgin Islands, the Gulf of Mexico, and the eastern U.S. to collect data for scientists to use to improve the accuracy of hurricane forecast models.