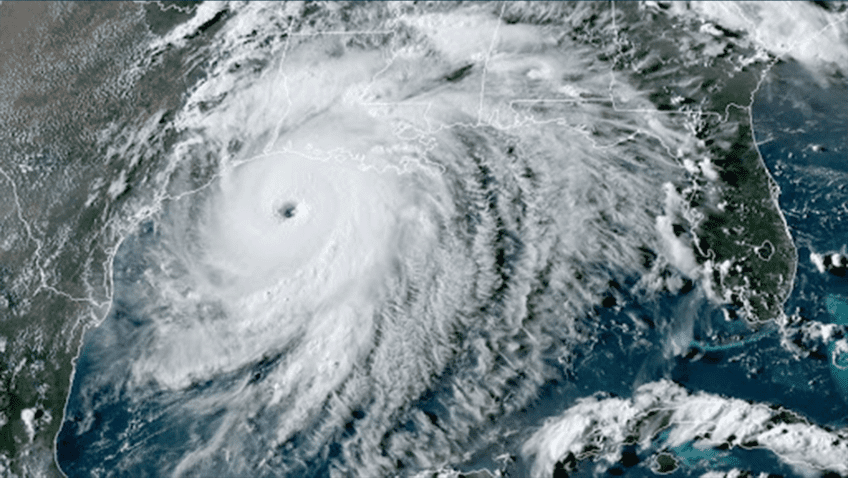
In the wake of hurricanes: satellites and robots reveal an altered biogeochemical landscape
On August 30, 2023, Hurricane Idalia made landfall as a major Hurricane in Florida’s Big Bend after meandering through the northwestern Caribbean and intensifying over the warm waters of the Gulf of America. In its aftermath, damage on land was immediately visible, but observations from satellites and ocean-going robots revealed that the ocean was also […]