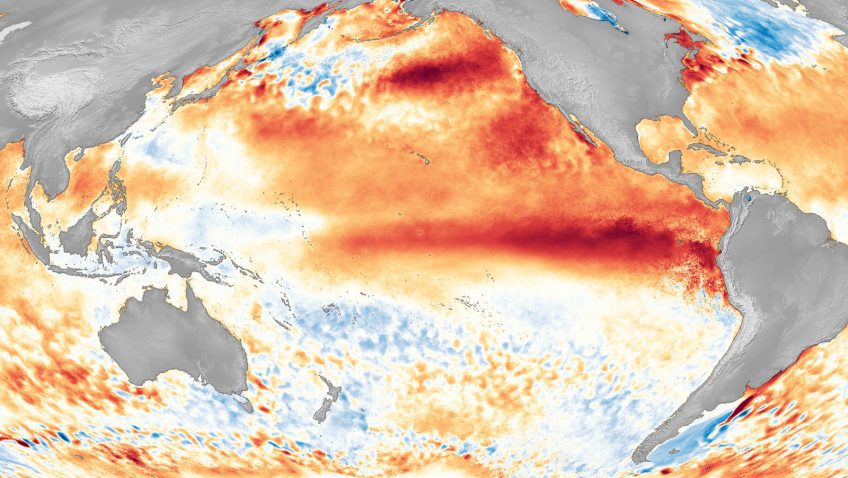
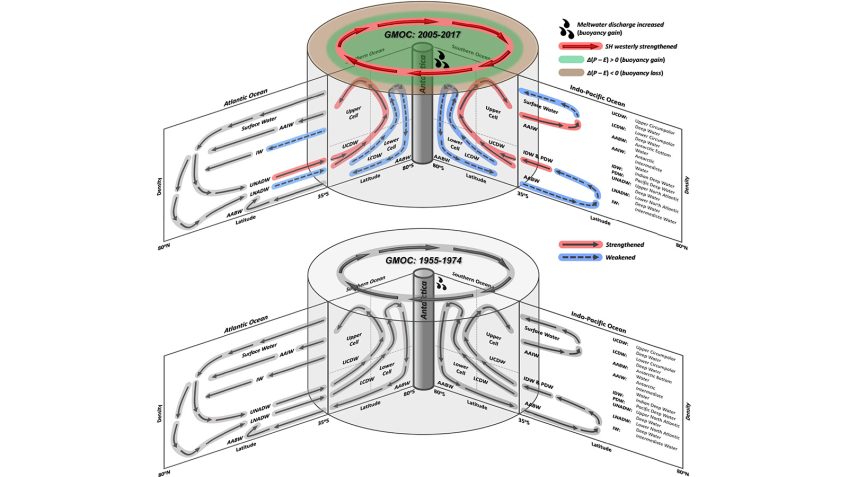
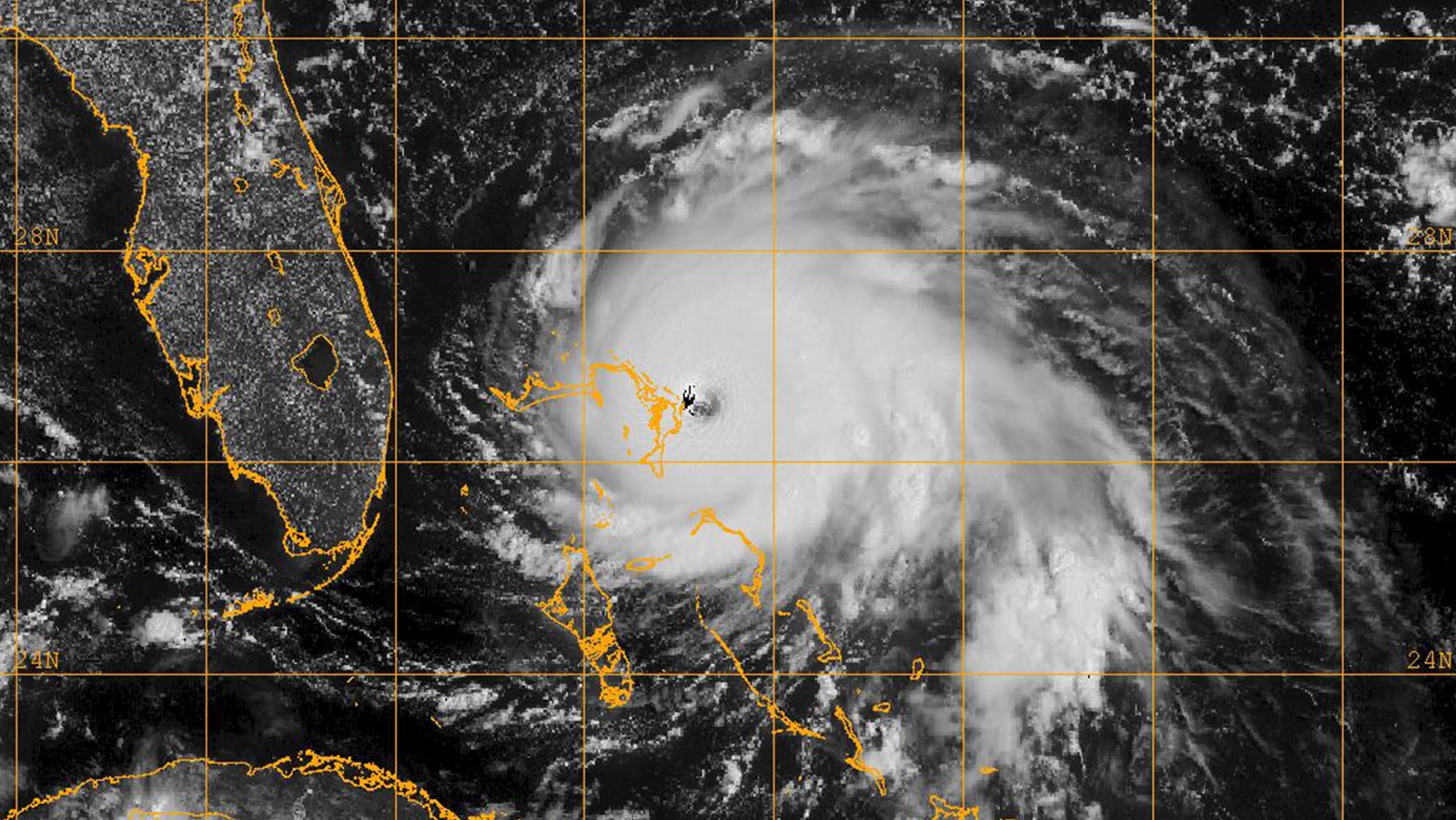
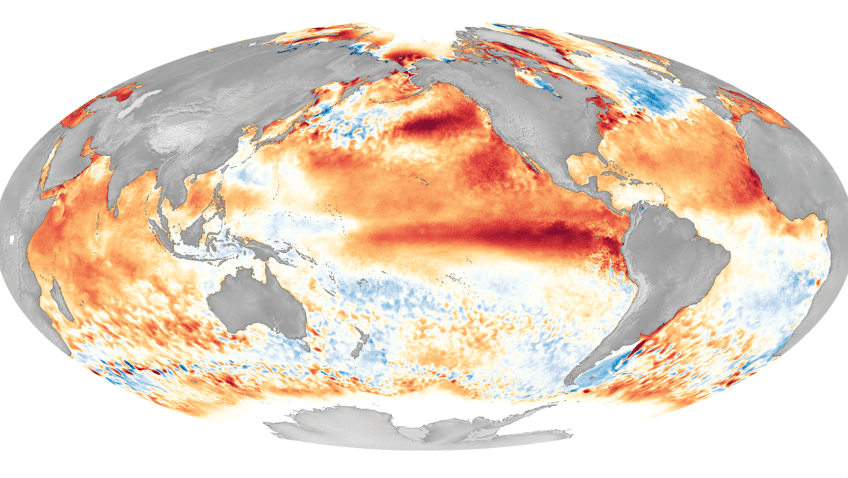
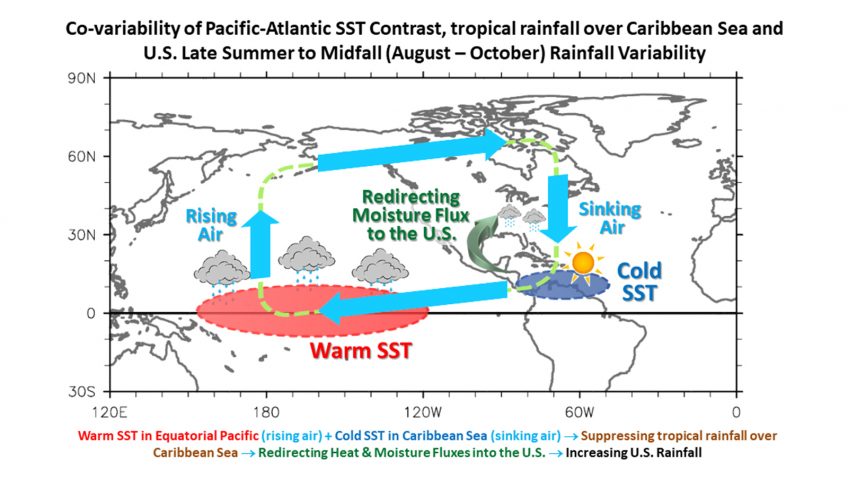
The Growing Impact of ENSO on U.S. Extreme Drought and Flood Events
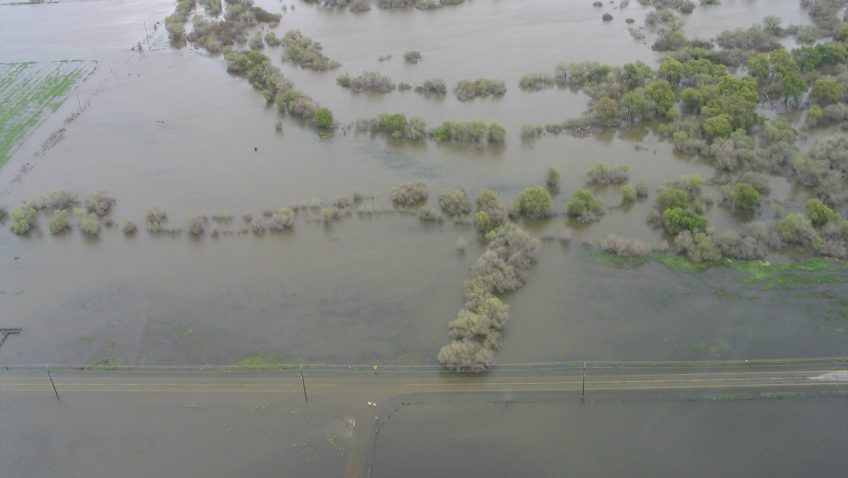
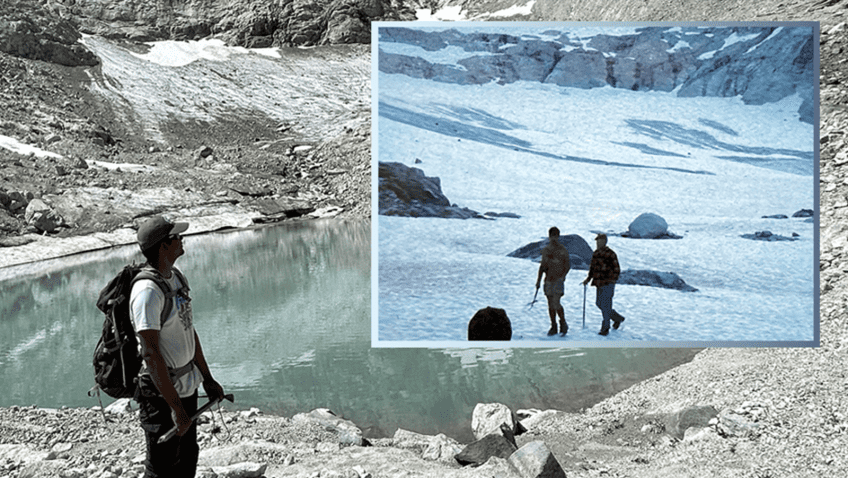
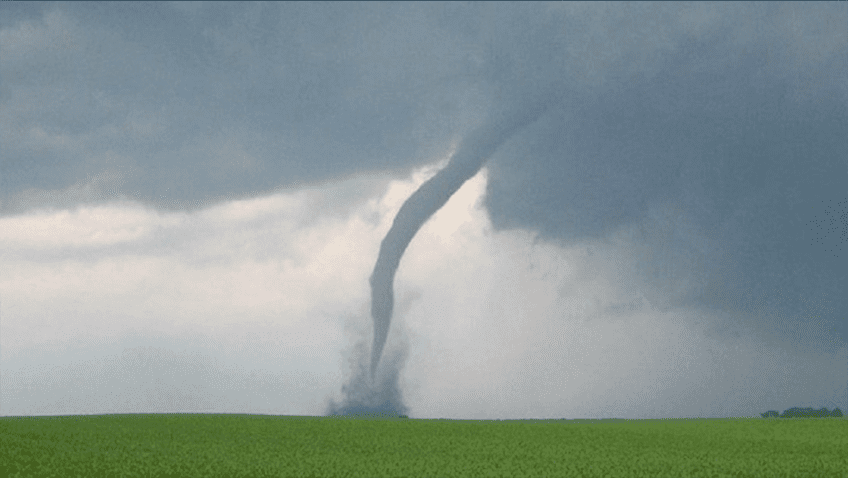
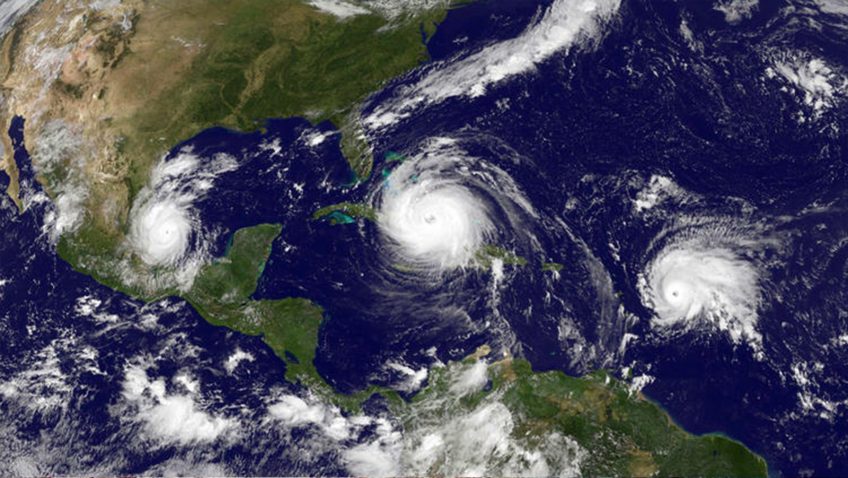
Extreme hydroclimate events, such as droughts, floods, and heavy rainfall, account for a substantial portion of weather-related disasters in the United States, leading to significant socio-economic losses involving agriculture, water resources, and public health, among others. For instance, from 1980 to 2024, droughts were responsible for approximately $368 billion in economic losses for the United […]