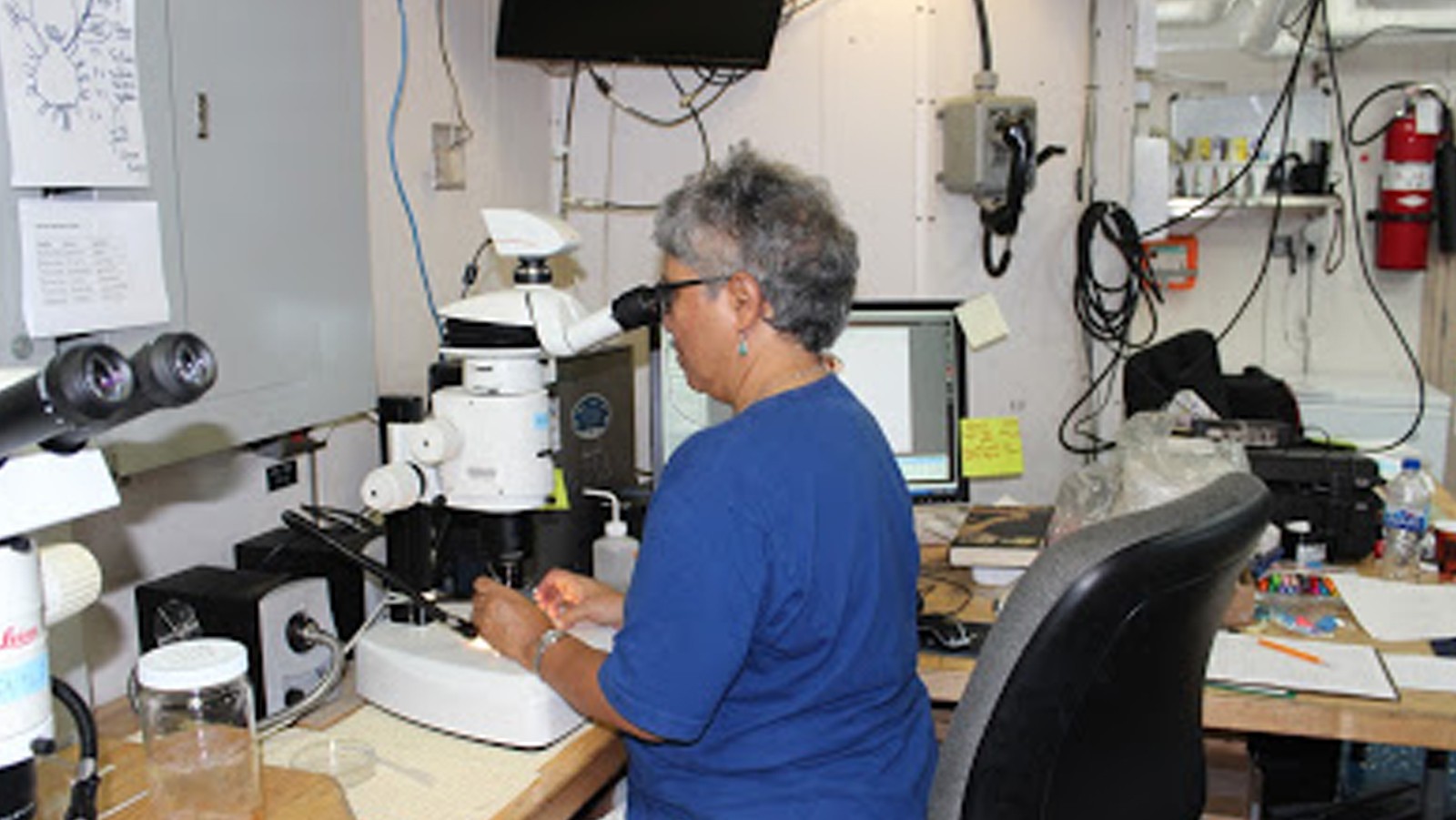
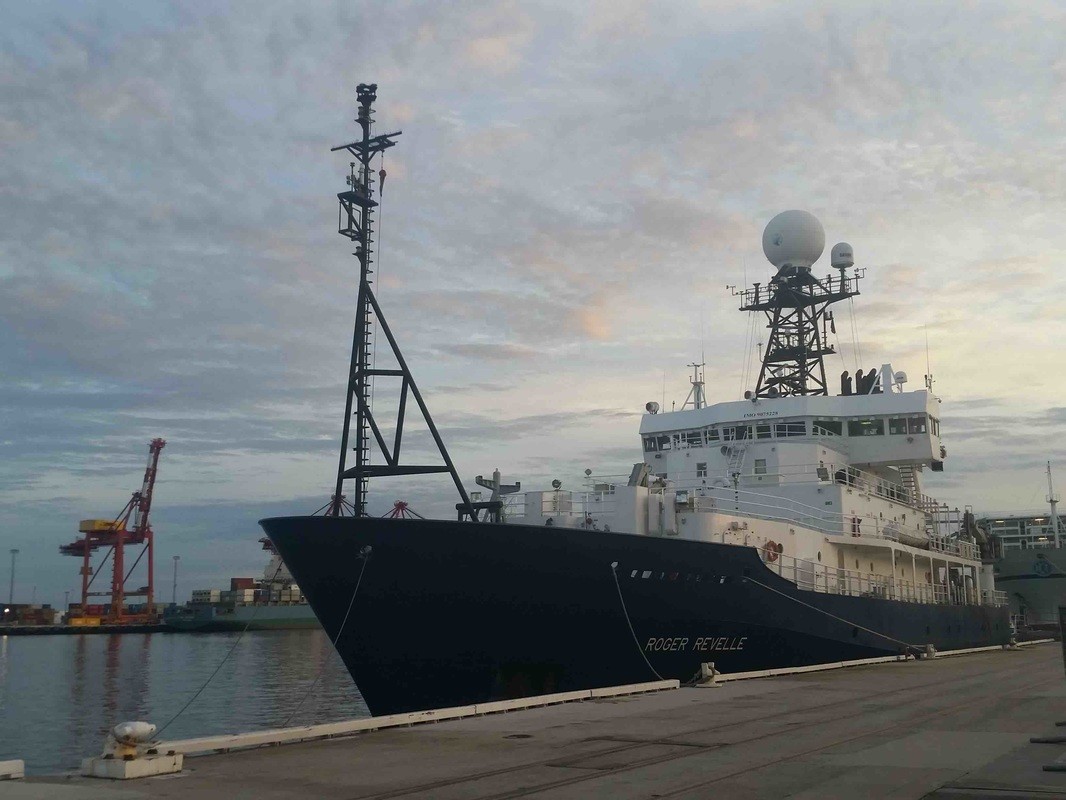
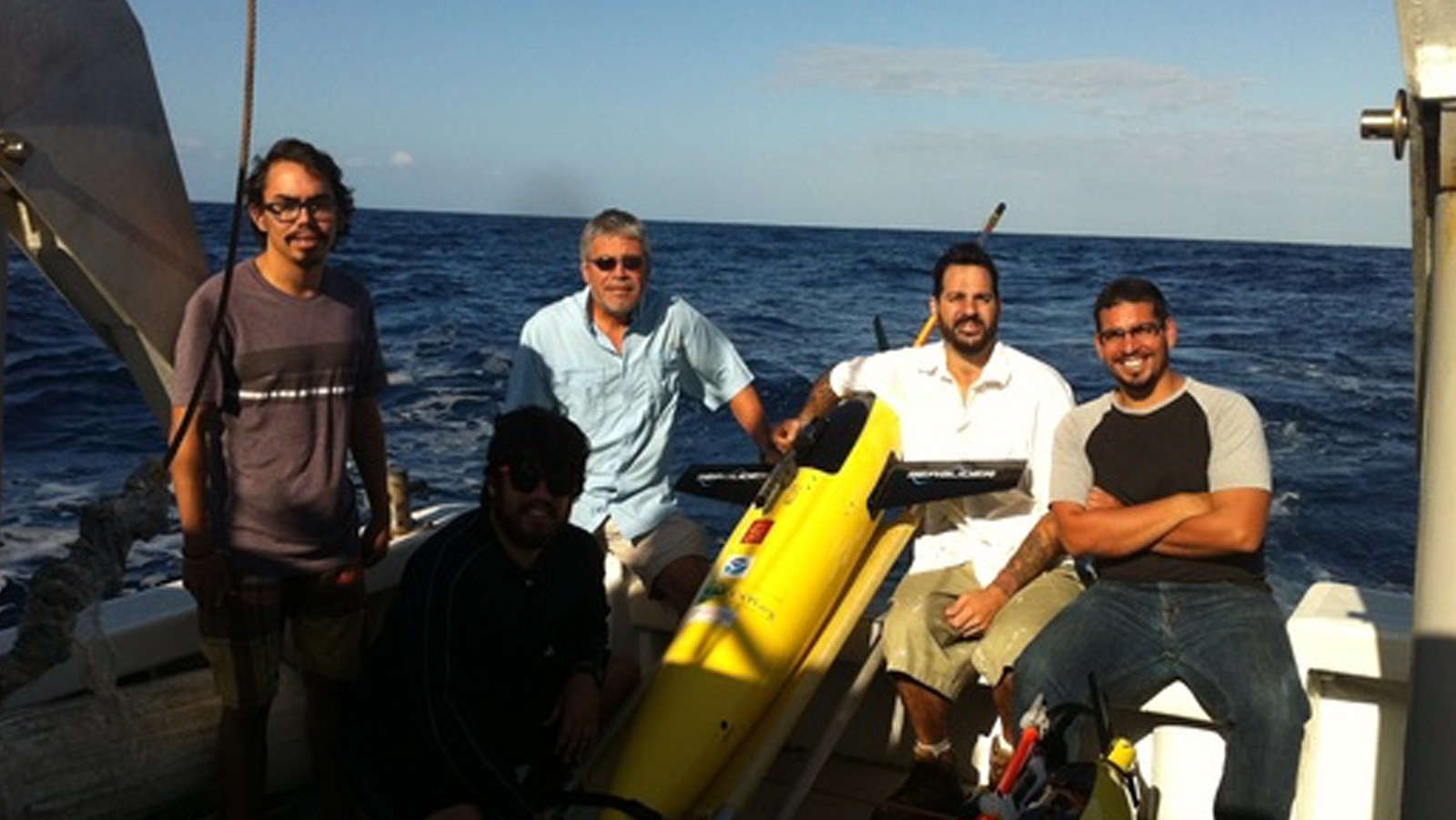
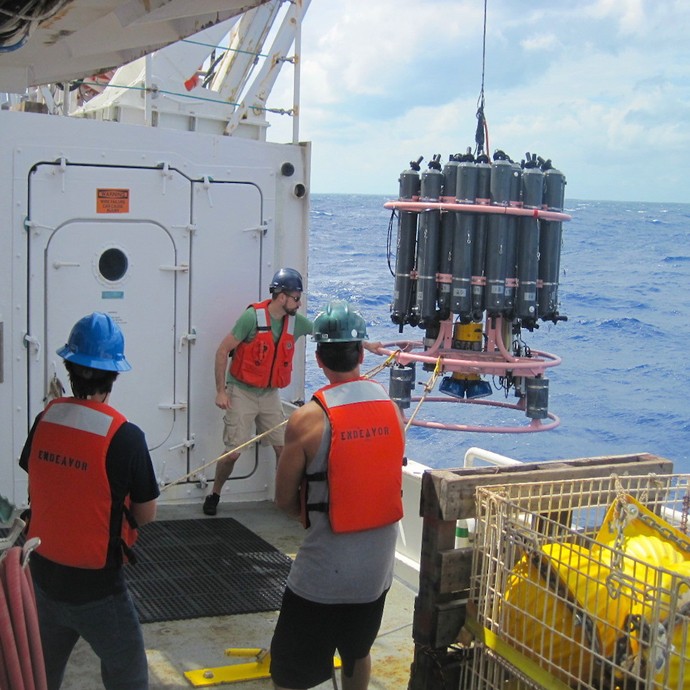
During the months of March and April, AOML joined an international team of oceanographers to actively sample the Indian Ocean in support of the Global Ocean Ship-Based Hydrographic Investigation Program (GO-SHIP), an initiative to measure and investigate the ocean basins from coast to coast and from top to bottom. Aboard the R/V Roger Revelle, the team transected the Indian Ocean from the Antarctic northward into the Bay of Bengal, collecting seawater samples at 113 stations as part of a multi-decadal effort to measure various ocean properties, including temperature, salinity, nutrients, carbon and other gases.