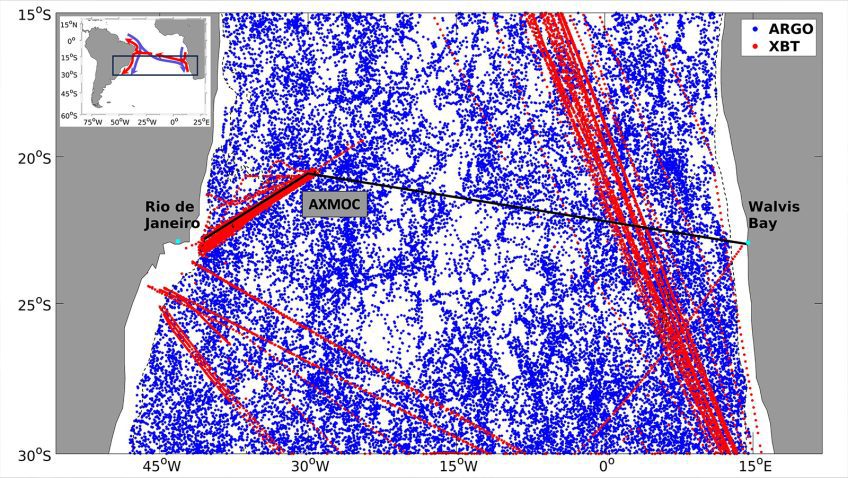
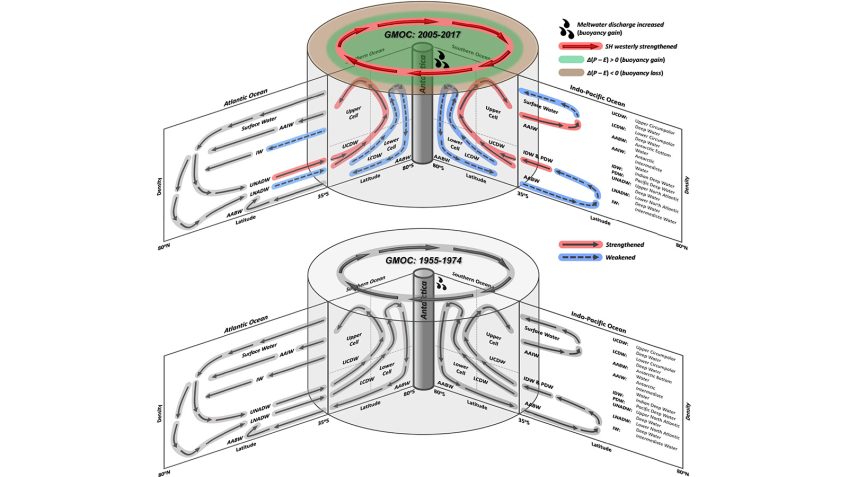
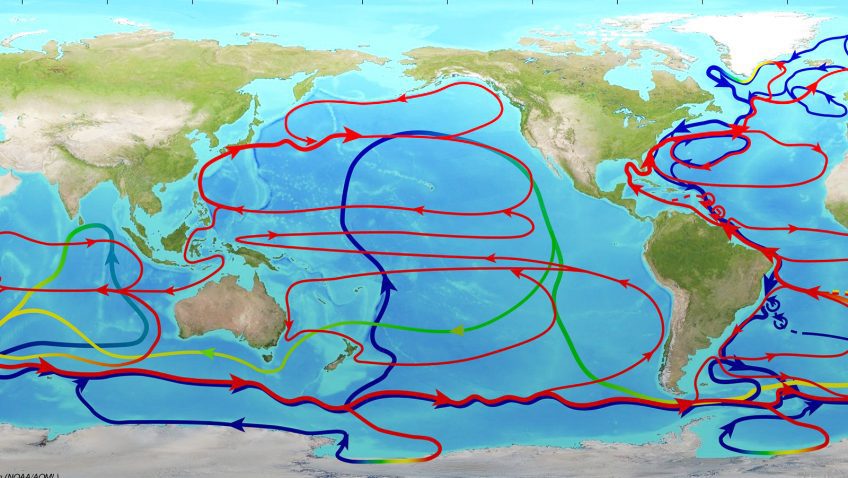
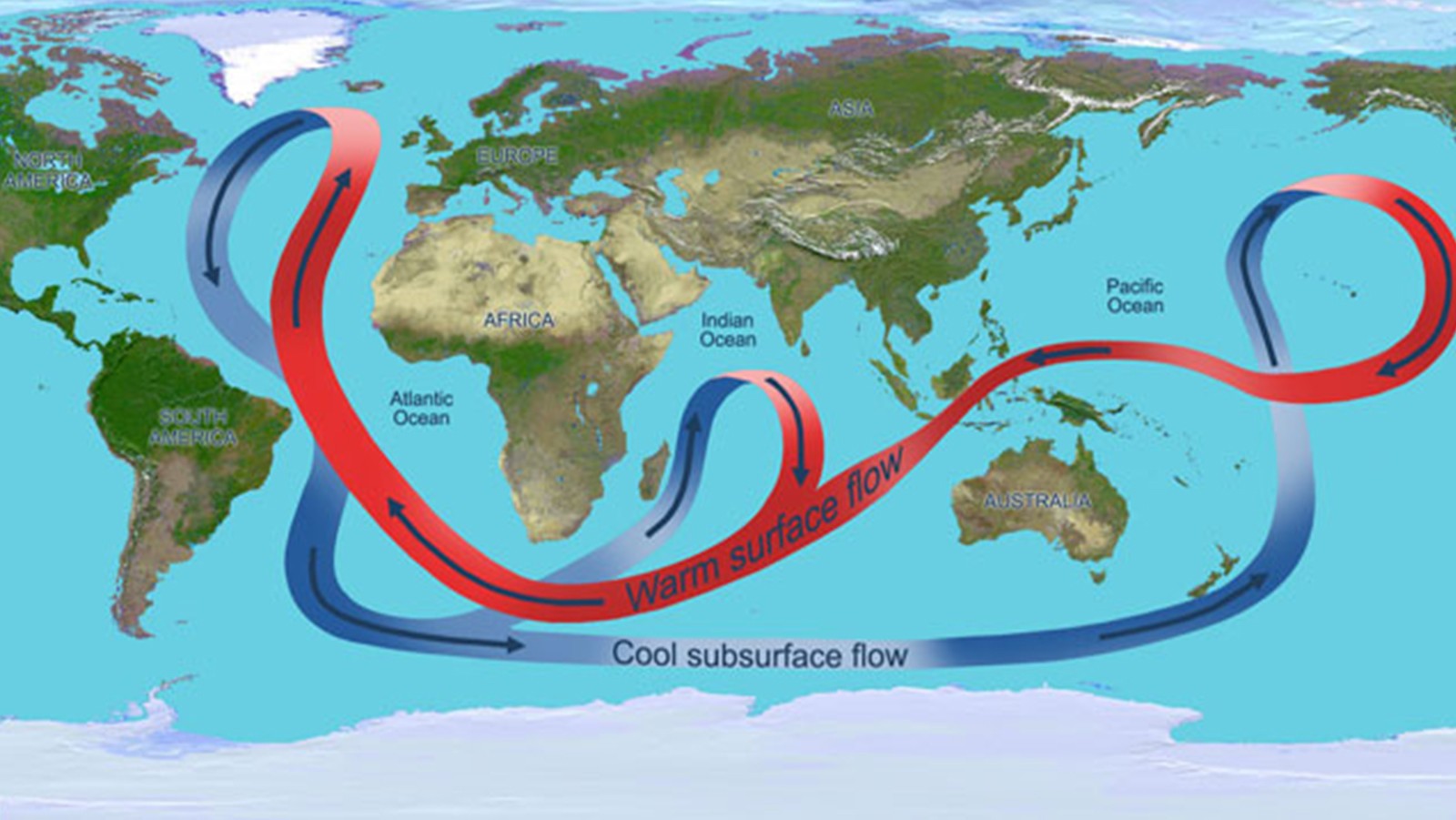
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation is weakening in the deep sea of the North Atlantic Ocean, study finds
Just in! A new study, which analyzed mooring observations and hydrographic data, found the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) abyssal limb in the North Atlantic has weakened over the past two decades contributing to sea level rise in the region.