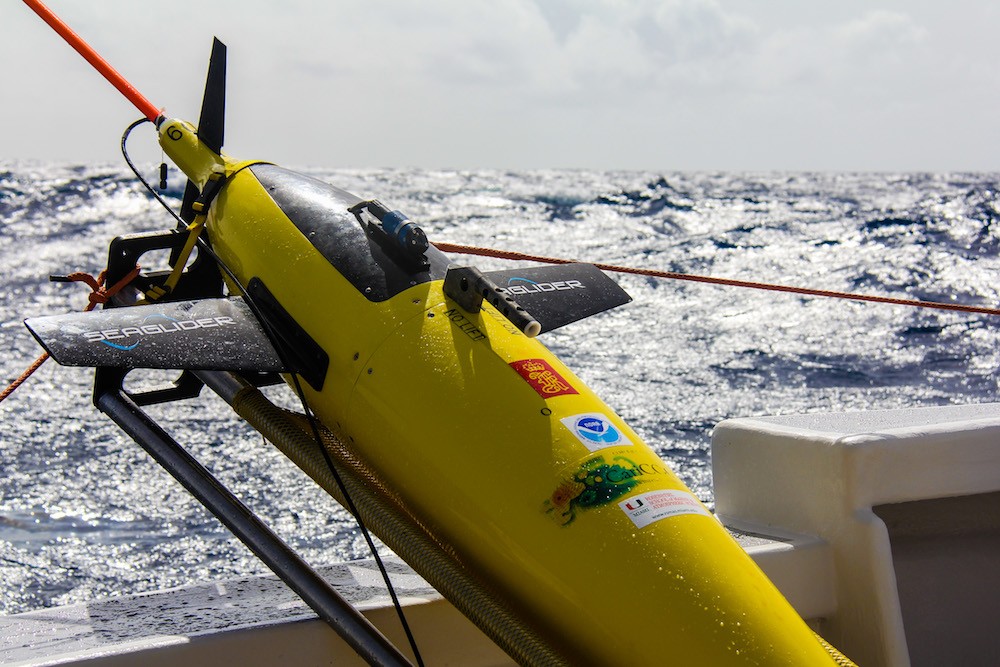
Underwater Glider Data Improved Intensity Forecasts of Hurricane Gonzalo
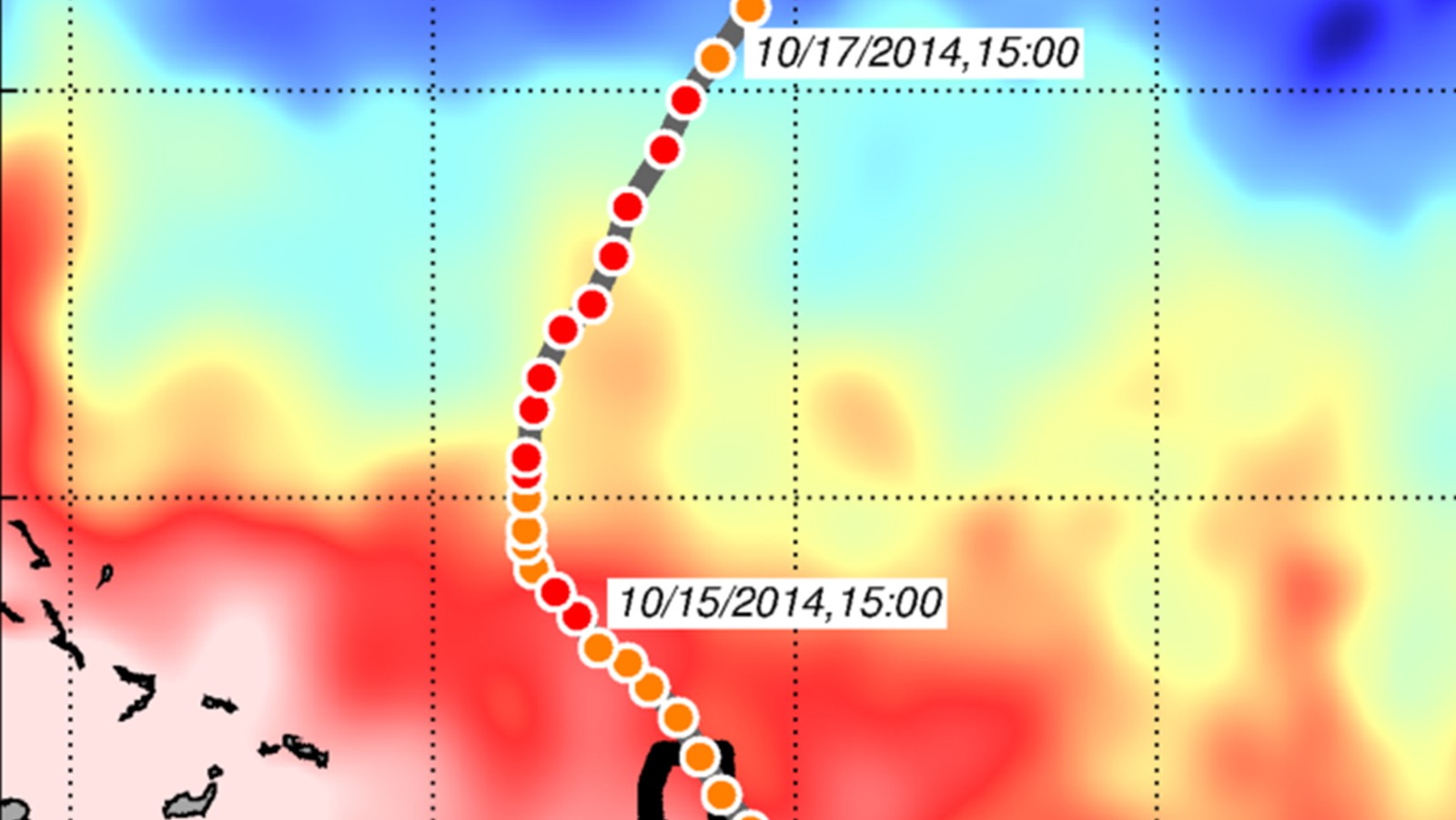
In a recent study published in Weather and Forecasting,* AOML researchers and their colleagues used NOAA’s HWRFHYCOM operational hurricane forecast model to quantify the impact of assimilating underwater glider data and other ocean observations into the intensity forecasts of Hurricane Gonzalo (2014). Gonzalo formed in the tropical North Atlantic east of the Lesser Antilles on October […]