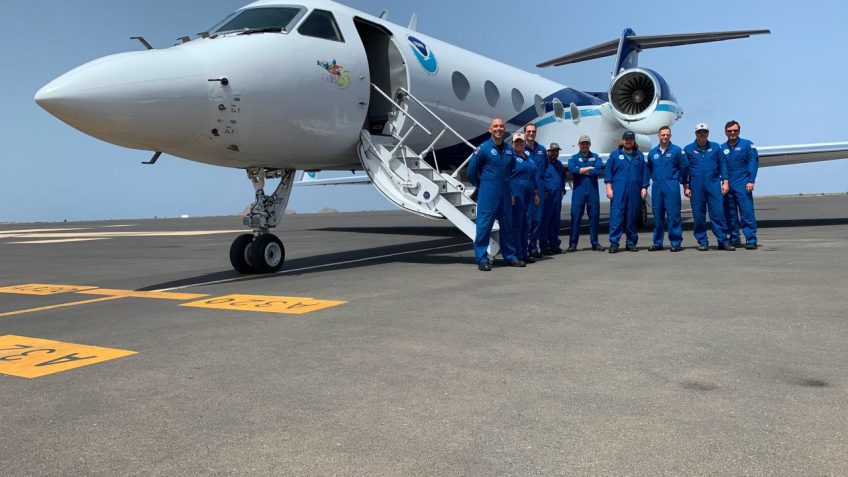
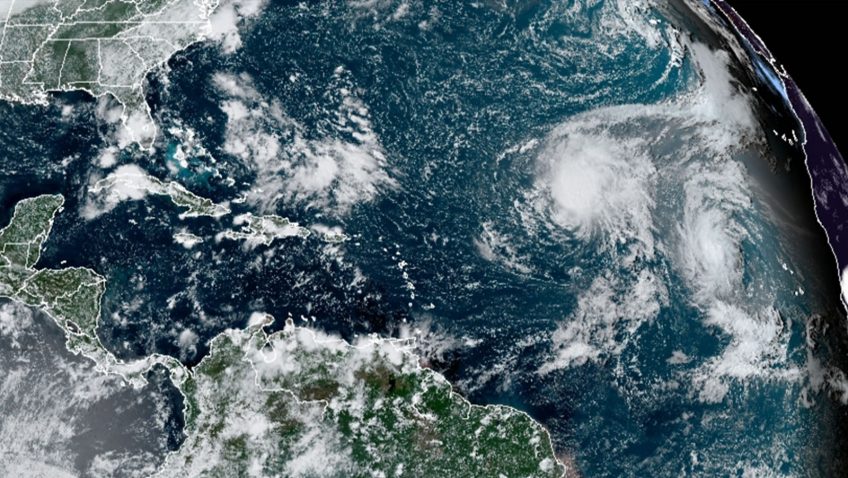
Scientists at AOML deployed to the Cabo Verde islands in August to explore how tropical waves that move off the coast of West African develop into tropical storms and hurricanes. These first-ever missions thousands of miles across the Atlantic mark the farthest distance traveled by NOAA’s Hurricane Hunters to help forecast models better predict the future track and intensity of developing storms.
Read Full Article
A recent study authored by five NOAA Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML) scientists (Lew Gramer, Jun Zhang, Ghassan Alaka, Andrew Hazelton, and Sundararamen Gopalakrishnan) was recently selected out of a variety of publications as a featured paper for EOS Science News by the American Geophysical Union.
Read Full Article
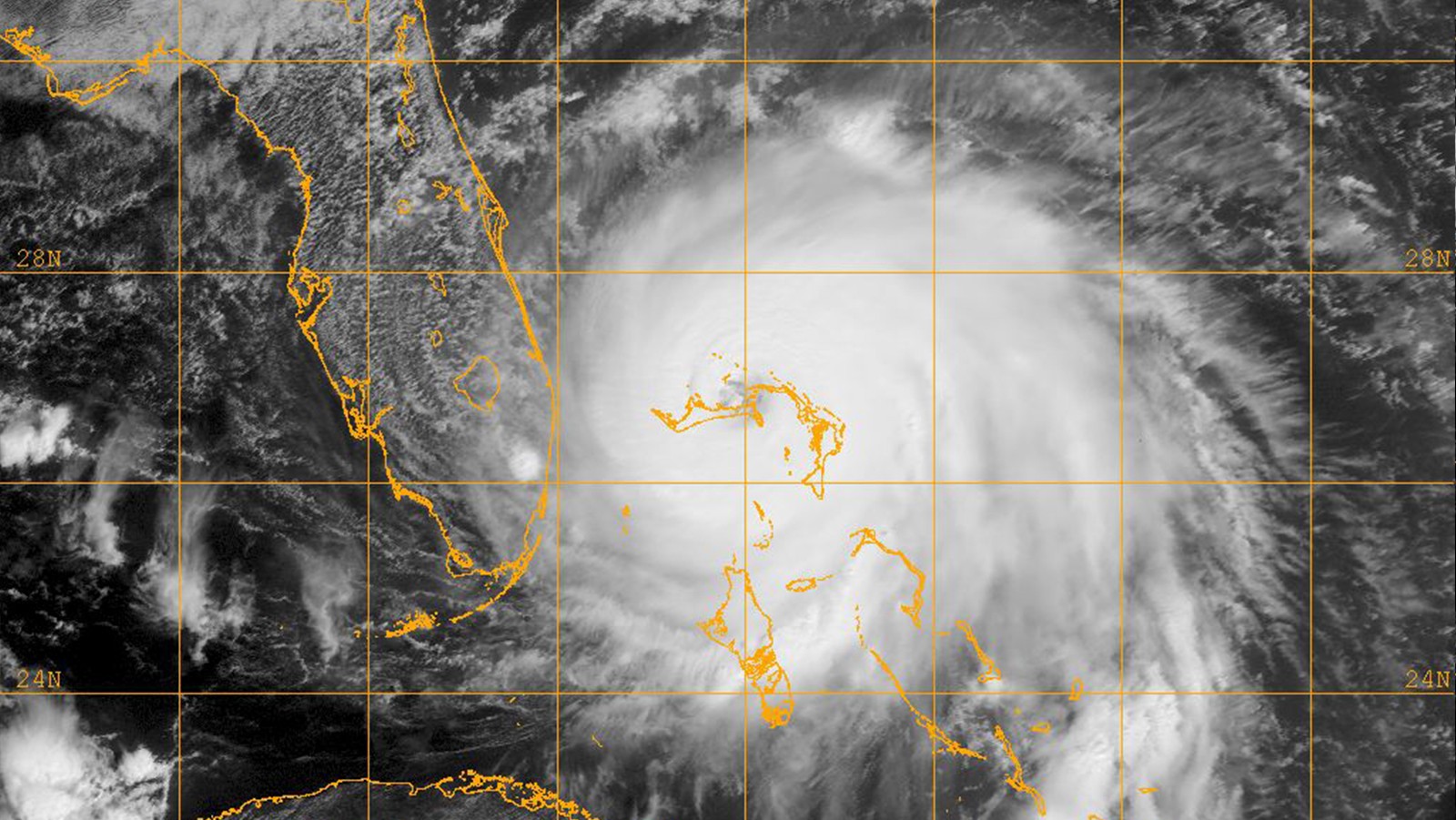
Hurricane Andrew made landfall on August 24, 1992, near Homestead, Florida, becoming one of the most catastrophic hurricanes in U.S. history. It had an extremely low central pressure of 922 millibars and maximum sustained wind speeds estimated at 165 miles per hour. The storm rapidly intensified less than 36 hours before landfall, leaving most residents less than a day to secure their homes and heed evacuation orders.
Read Full Article
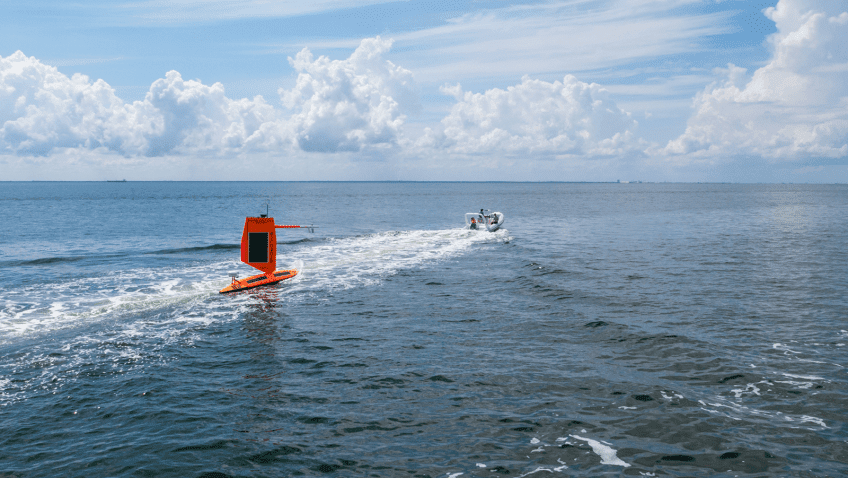
In partnership with NOAA, Saildrone Inc. is deploying seven ocean drones to collect data from hurricanes during the 2022 hurricane season with the goal of improving hurricane forecasting. For the first year, two saildrones will track hurricanes in the Gulf of America.
Read Full Article
Hurricane Field Program Data 2022 Storms Jump to data collected during each storm. Atlantic Basin Alex (AL01) Bonnie (AL02) PTC#04 ITOFS-East Earl (AL06) Fiona (AL07) Ian (AL09) Julia (AL13) Karl (AL14) Lisa (AL15) Nicole (AL17) Miscellaneous East Pacific Basin Agatha (EP02) Kay (EP12) Orlene (EP16) Roslyn (EP19) Please review HRD's Data Policy prior to downloading [...]
Read Full Article
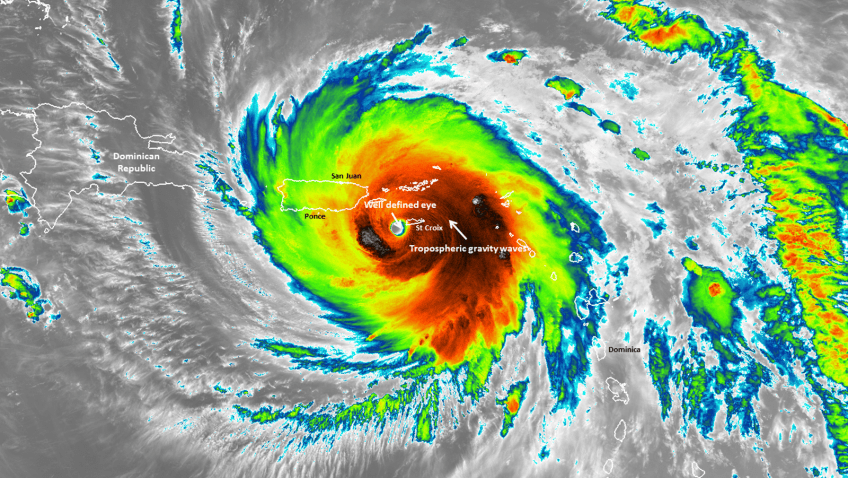
This summer during the 2022 Atlantic hurricane season, scientists at NOAA’s Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML) will once again be on the frontlines helping NOAA prepare the public for severe weather. They will also conduct new research on the complex processes of how tropical cyclones form, develop, and dissipate.
Read Full Article
Tropical cyclones intensify by extracting heat energy from the ocean surface, making the sea surface temperature under storms crucial for storm development. A recent study by researchers at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and NOAA’s Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory found that large amounts of rain under tropical cyclones can reduce the sea surface cooling induced by them.
Read Full Article
Observations obtained by the Coyote small Uncrewed Aircraft System led to a significant improvement in the analyses of Hurricane Maria’s (2017) position, intensity, and structure, according to new research published in the journal Monthly Weather Review. The study by scientists with the University of Miami’s Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies and Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML) highlights how the Coyote’s novel near-surface measurements helped to more accurately depict Hurricane Maria’s inner core, demonstrating their ability to improve forecasts.
Read Full Article
Warning the public of the damaging winds in tropical cyclones is critical for safeguarding communities in harm’s way. A new study by hurricane scientists at AOML is the first to quantify the value added to tropical cyclone intensity forecasts by storm-following nests. The research, published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, demonstrates that storm-following nests applied to multiple hurricanes in the same forecast cycle can improve intensity predictions by as much as 30%.
Read Full Article
After a year and a half of concerted effort between NOAA’s National Hurricane Center (NHC), Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML), and other NOAA offices, including the Weather Program Office, the Hurricane and Ocean Testbed (HOT) has been successfully launched in the newly designed William M. Lapenta Laboratory, named in memory of the late director of the National Centers for Environmental Protection. This testbed establishes a physical and virtual collaboration space for researchers and forecasters.
Read Full Article