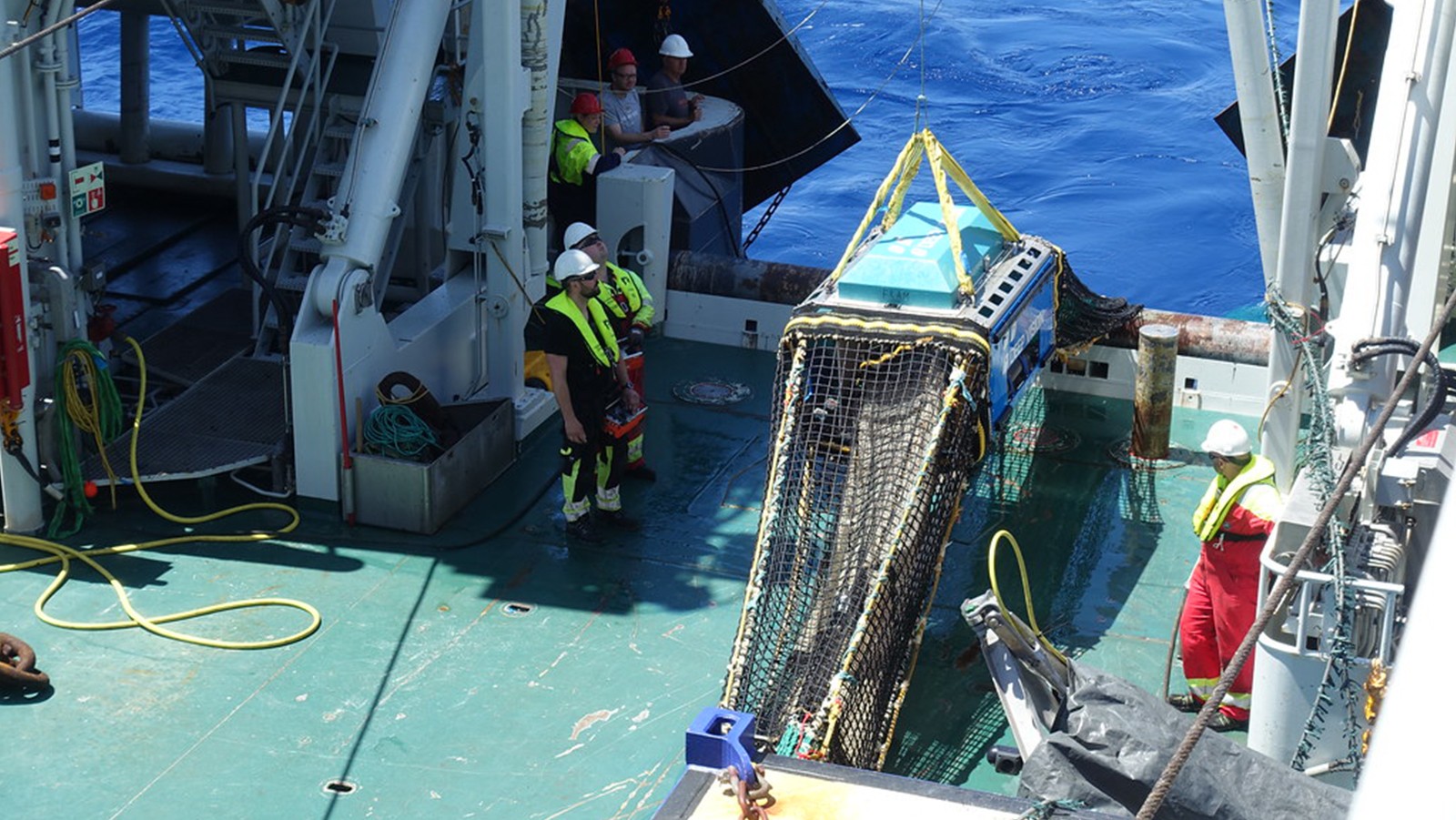
AOML is honored with NOPP Excellence in Partnering Award
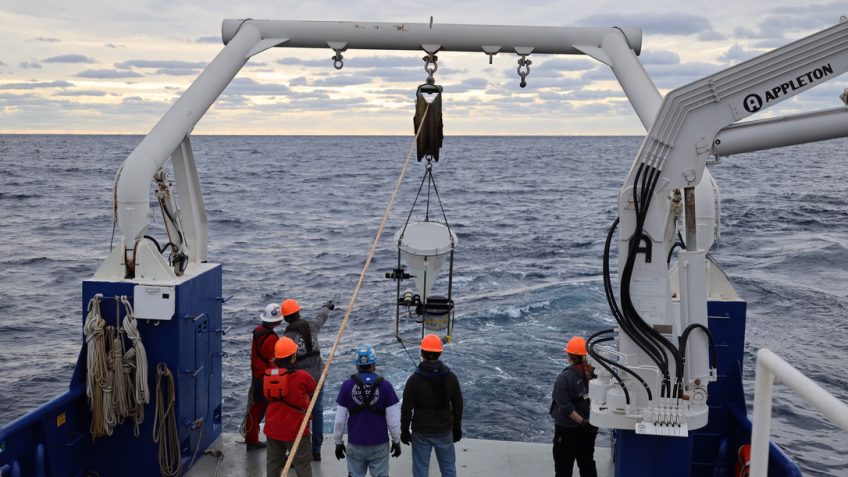
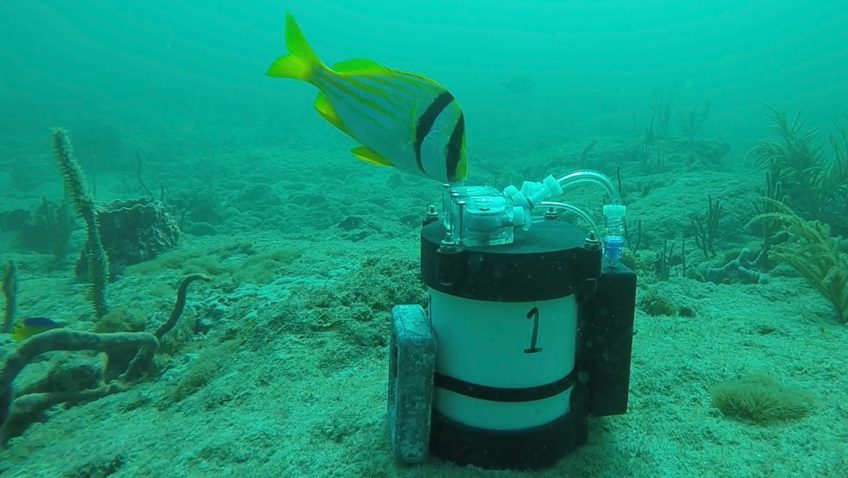
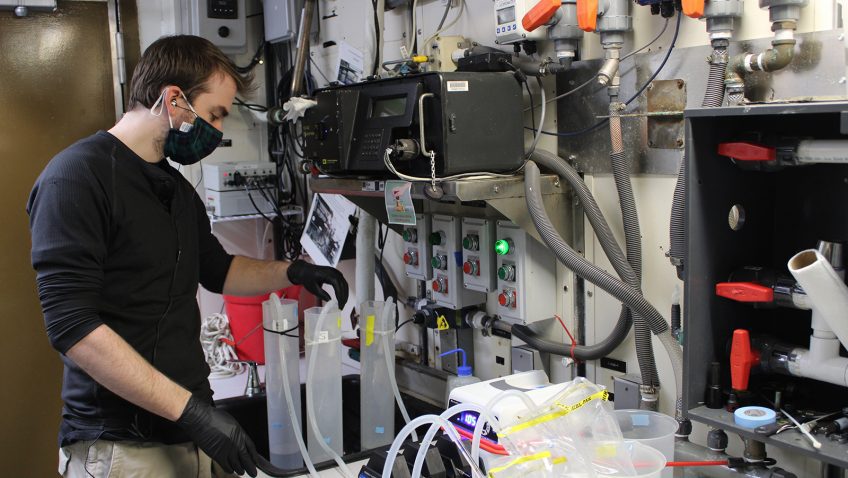
Phytoplankton covering the ocean’s surface are responsible for over 50% of the oxygen that has been produced on Earth. In a spoonful of oceanwater, there are thousands of these microscopic organisms of different species. And without them, most – if not all – marine food webs would collapse. Studying what species comprise planktonic communities in […]