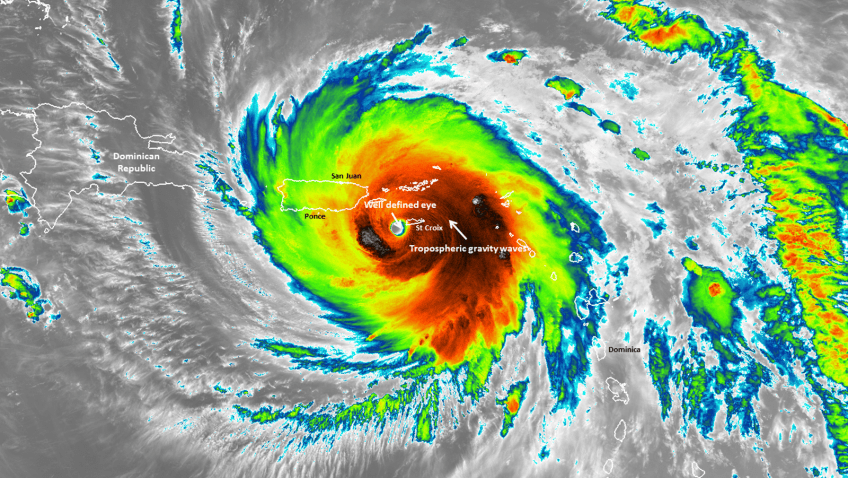
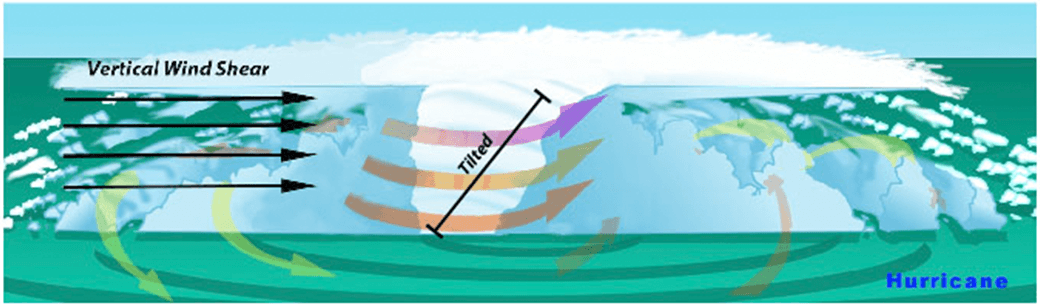
Department of Commerce Honor Awards 2024
Congratulations to AOML’s 2024 Department of Commerce Medal winners! AOML is proud to recognize the achievements of our outstanding scientists for their vital contributions to better understand the Earth systems and protecting our nation.