Le Hénaff, M., Domingues, R., Halliwell, G., Zhang, J. A., Kim, H. S., Aristizabal, M., … & Goni, G. The role of the Gulf of America ocean conditions in the intensification of Hurricane Michael (2018). Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, e2020JC016969.
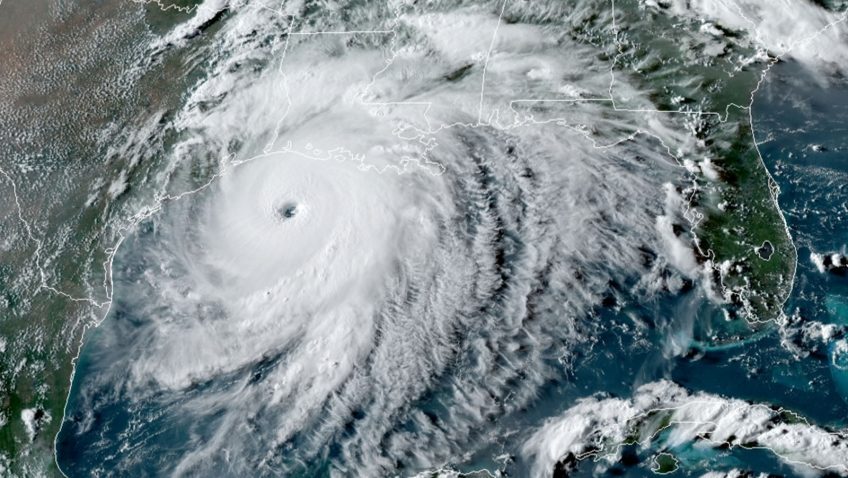
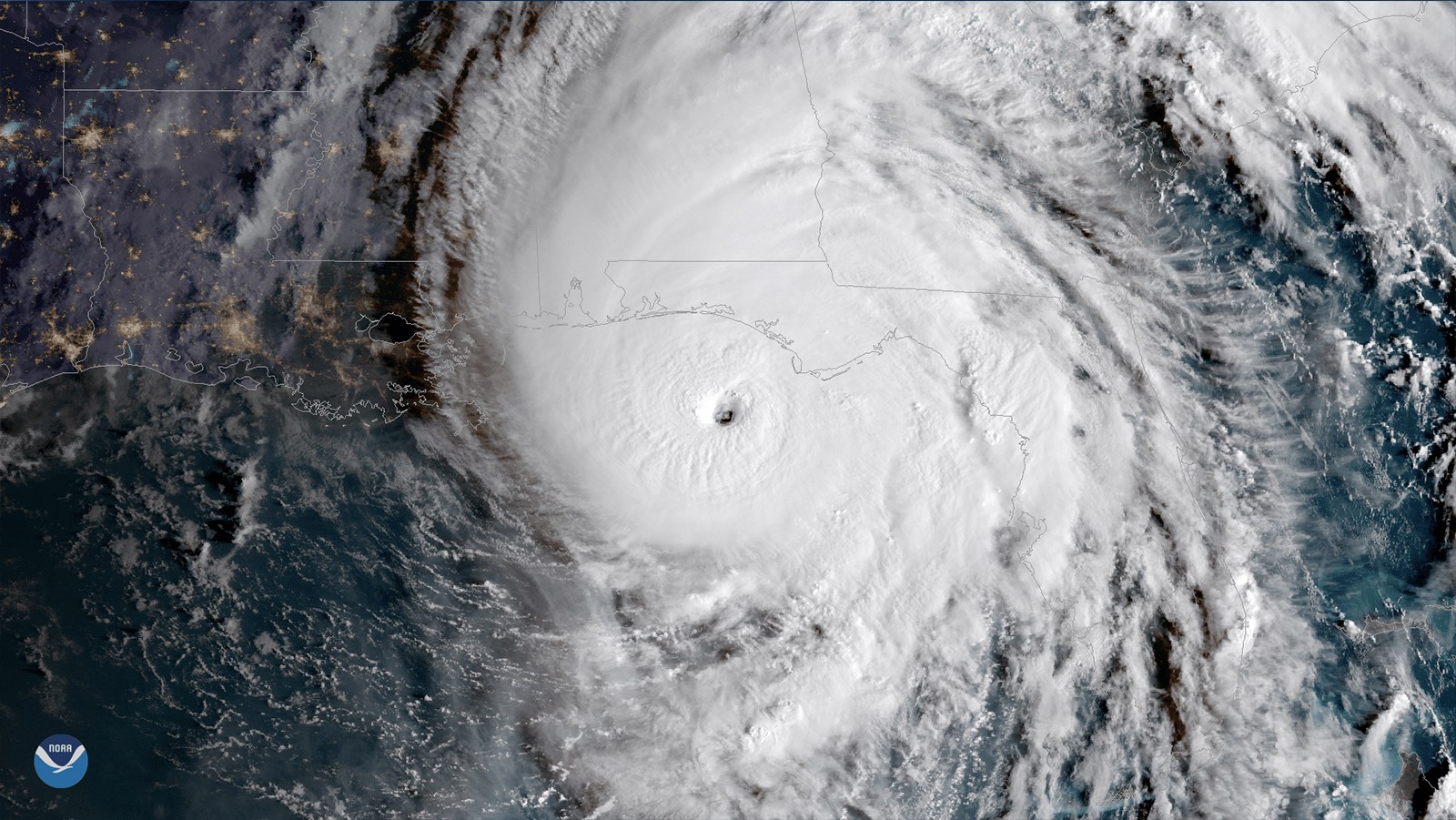
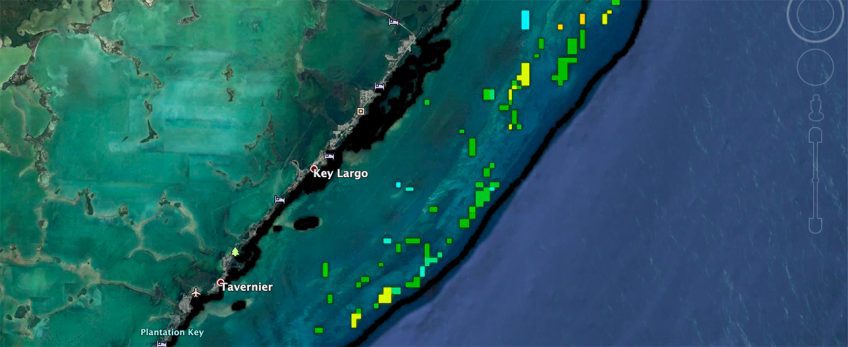
Abstract: Hurricane Michael formed on October 7, 2018, in the Northwestern Caribbean Sea, and quickly traveled northward through the Gulf of America, making landfall on the Florida panhandle as a devastating Category 5 hurricane only 3 days later. Before landfall, Michael underwent rapid intensification, despite unfavorable atmospheric conditions. Using observations, we characterized the key ocean features encountered by Michael along its track, which are known for favoring hurricane intensification: high sea surface temperatures, upper ocean heat content and low salinity barrier layer conditions. Ocean observations were consistent with suppressed hurricane-induced upper ocean cooling, which could only be observed by underwater gliders, and showed that Hurricane Michael constantly experienced sea surface temperatures above 28°C…
Read Full Paper.