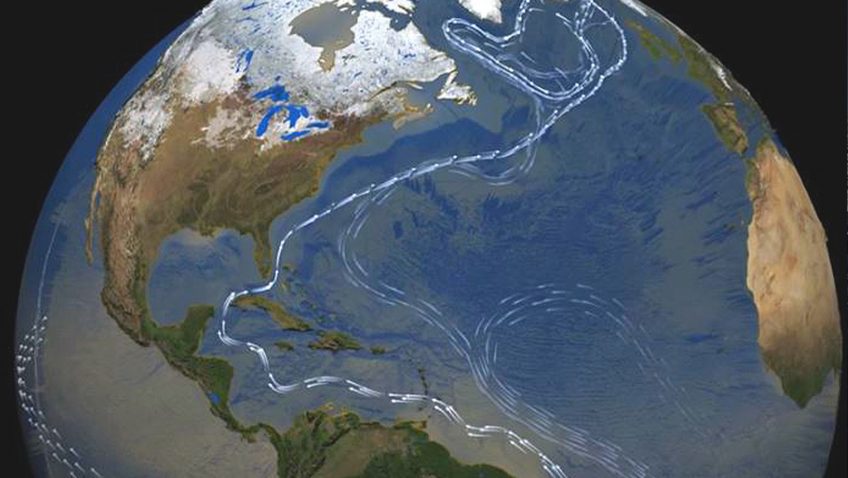
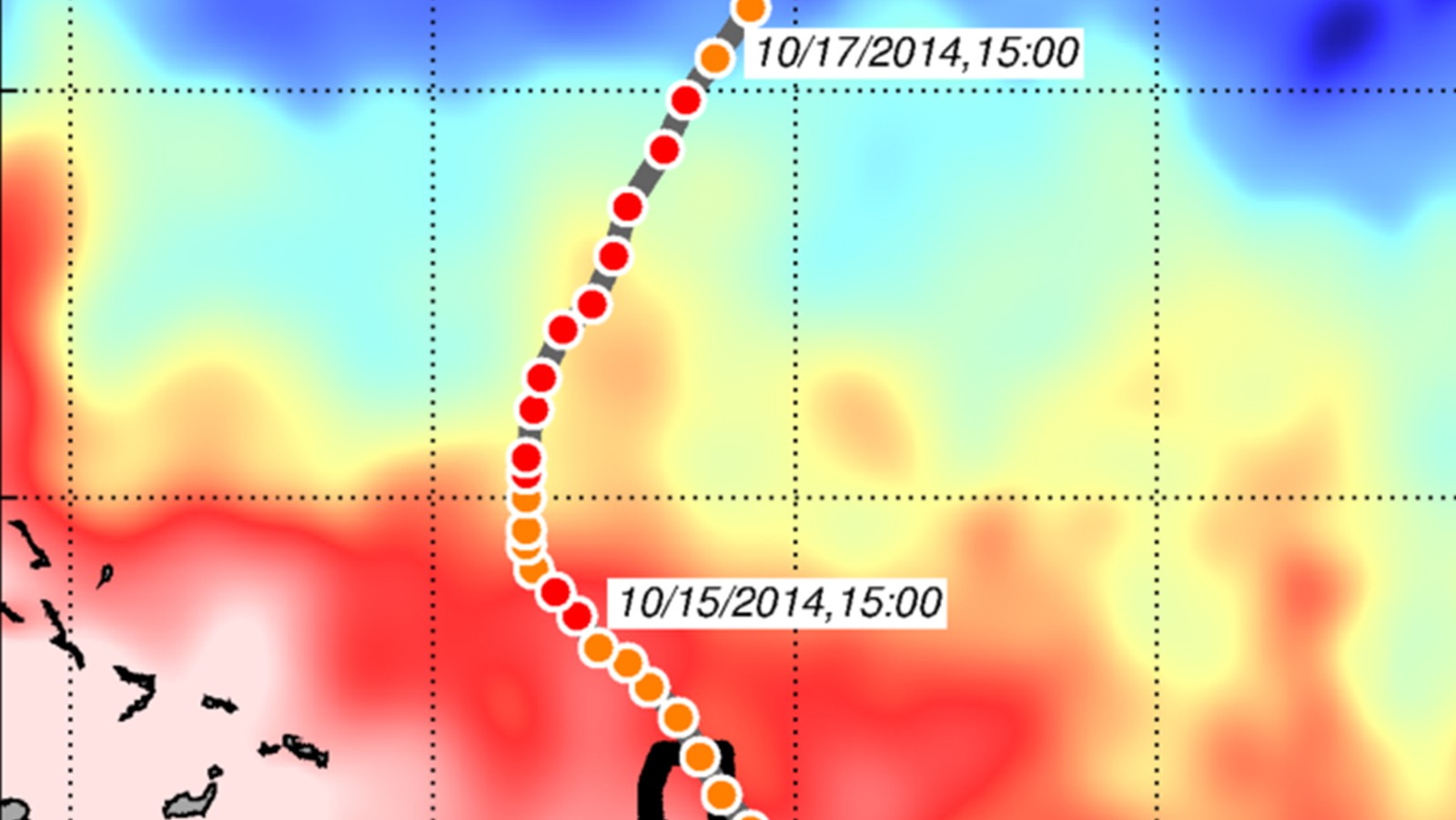
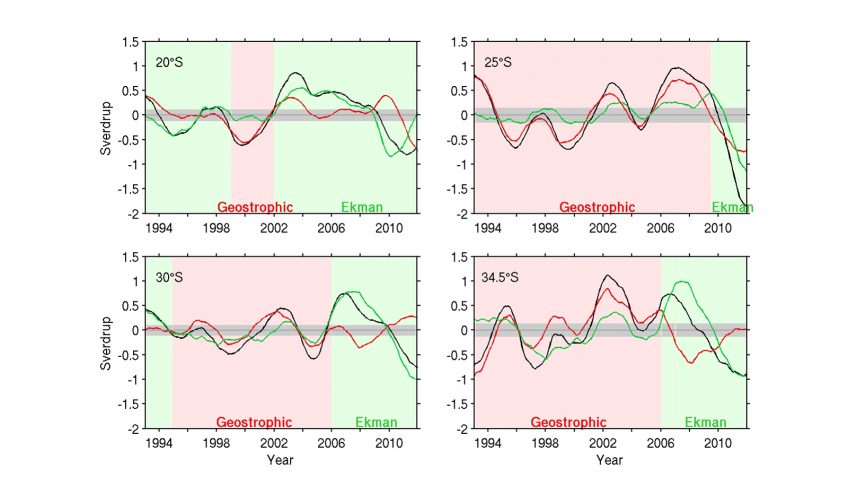
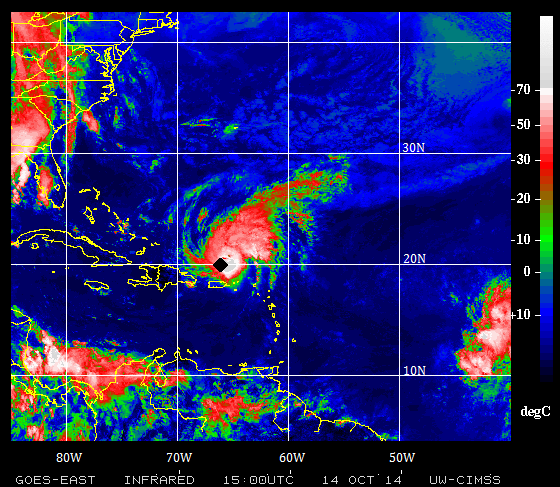
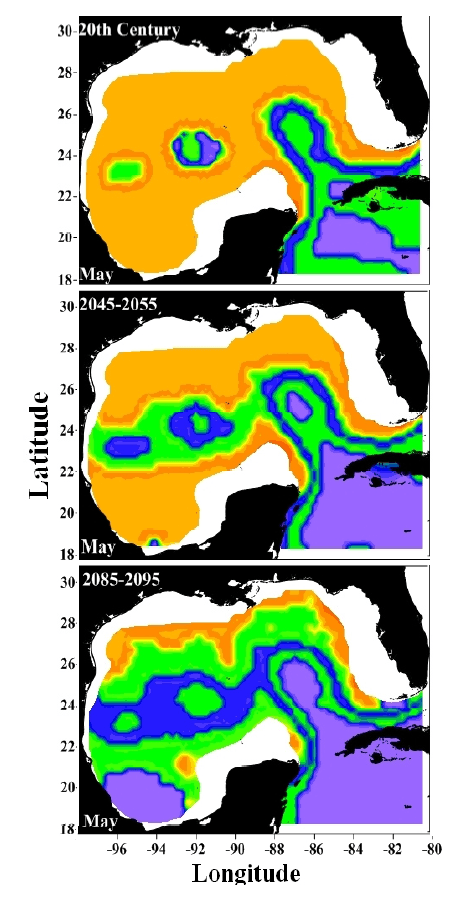
AOML physical oceanographers Molly Baringer, Ulises Rivero, Pedro Pena, Andrew Stefanick, Grant Rawson, Jay Hooper and Francis Bringas conducted a Western Boundary Times Series cruise aboard the UNOLS R/V Endeavor on February 15, 2015. Molly Baringer, AOML Deputy Director, served as chief scientist and was supported by additional crew from the University of Puerto Rico. Scientists measured full water column values of salinity, temperature, and oxygen. Scientists also telemetered data from a series of moorings along the 26th north parallel for a joint NOAA and National Science Foundation program designed to monitor the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation current. Francis Bringas also conducted a fall rate experiment that consisted of deploying 200 XBTs from different launch heights.