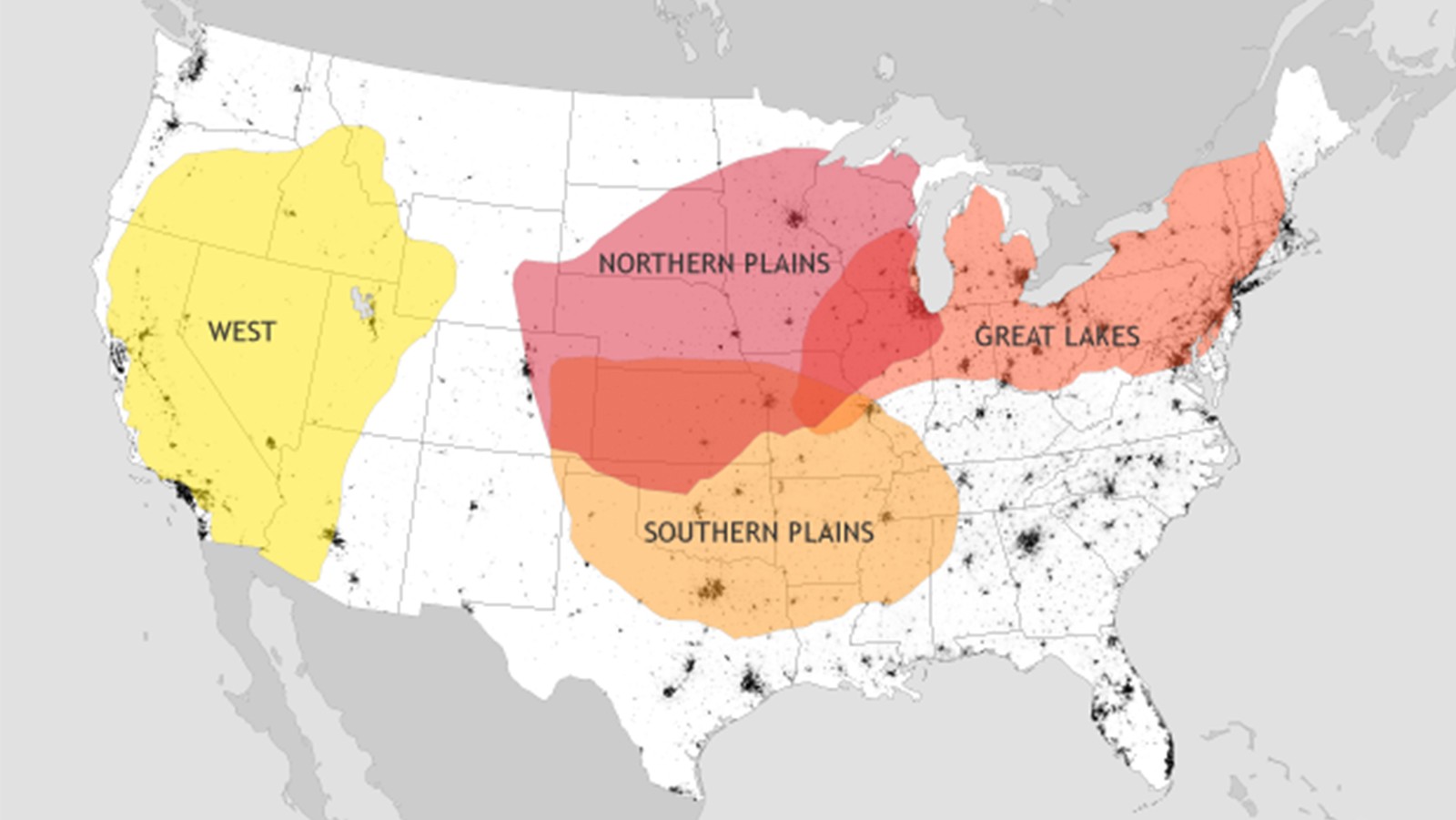
Early Emergence of Anthropogenically Forced Heat Waves in the Western United States and Great Lakes
Climate projections for the twenty-first century suggest an increase in the occurrence of heat waves. However, the time at which externally forced signals of anthropogenic climate change (ACC) emerge against background natural variability (time of emergence (ToE)) has been challenging to quantify, which makes future heat-wave projections uncertain. In a new article published in Nature Climate Change (Lopez et al., 2018), Hosmay Lopez and his team combine observations and model simulations under present and future forcing to assess how internal variability and ACC modulate US heat waves.