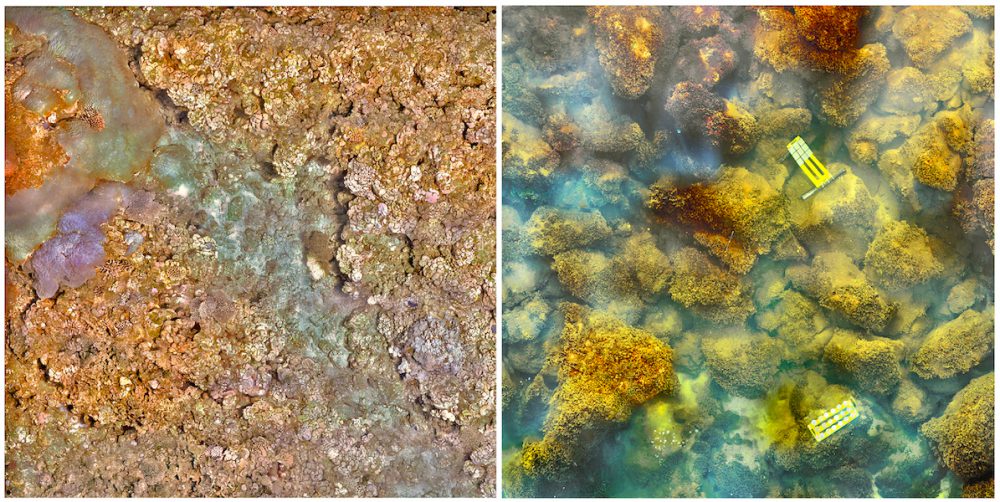
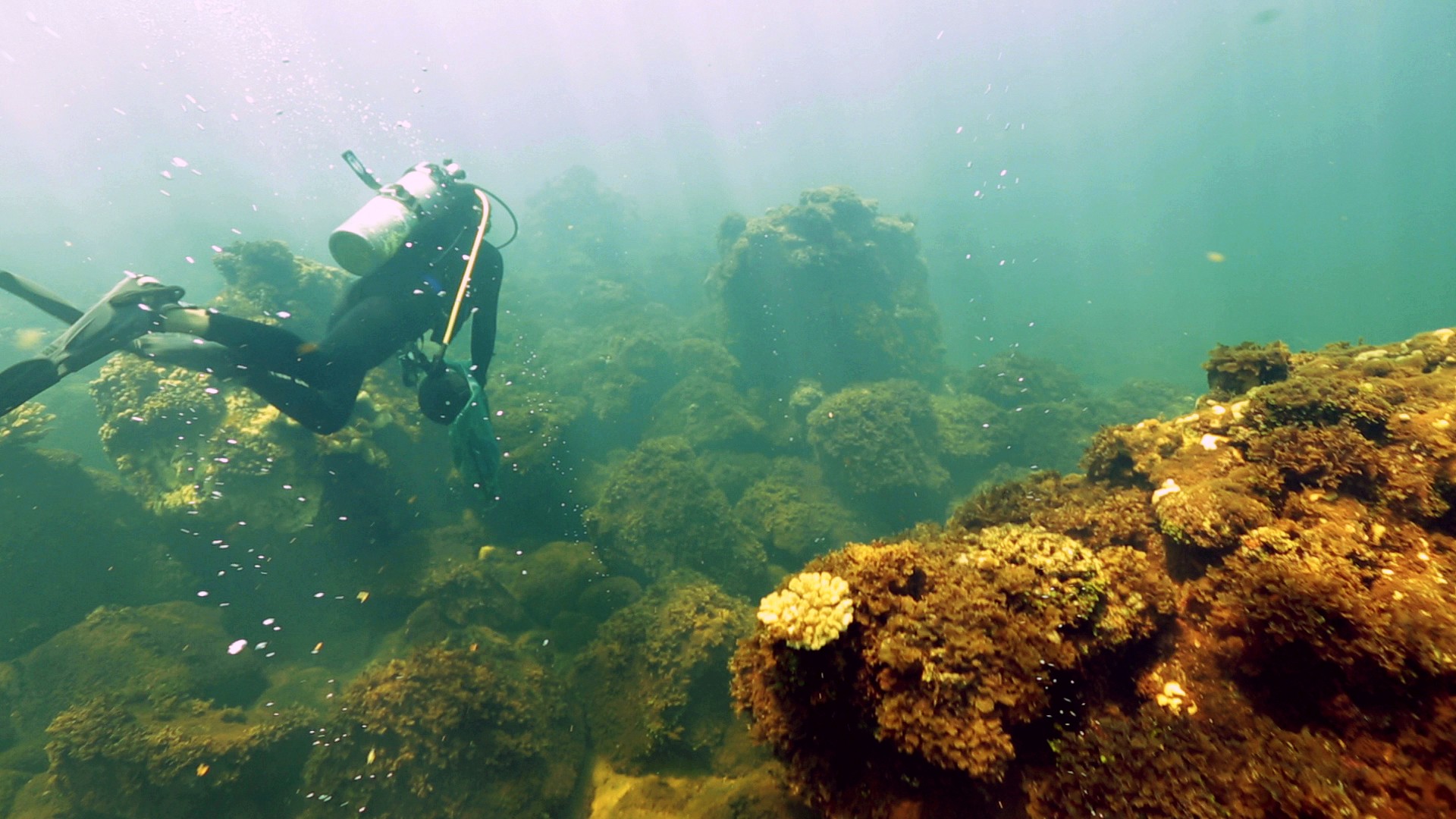
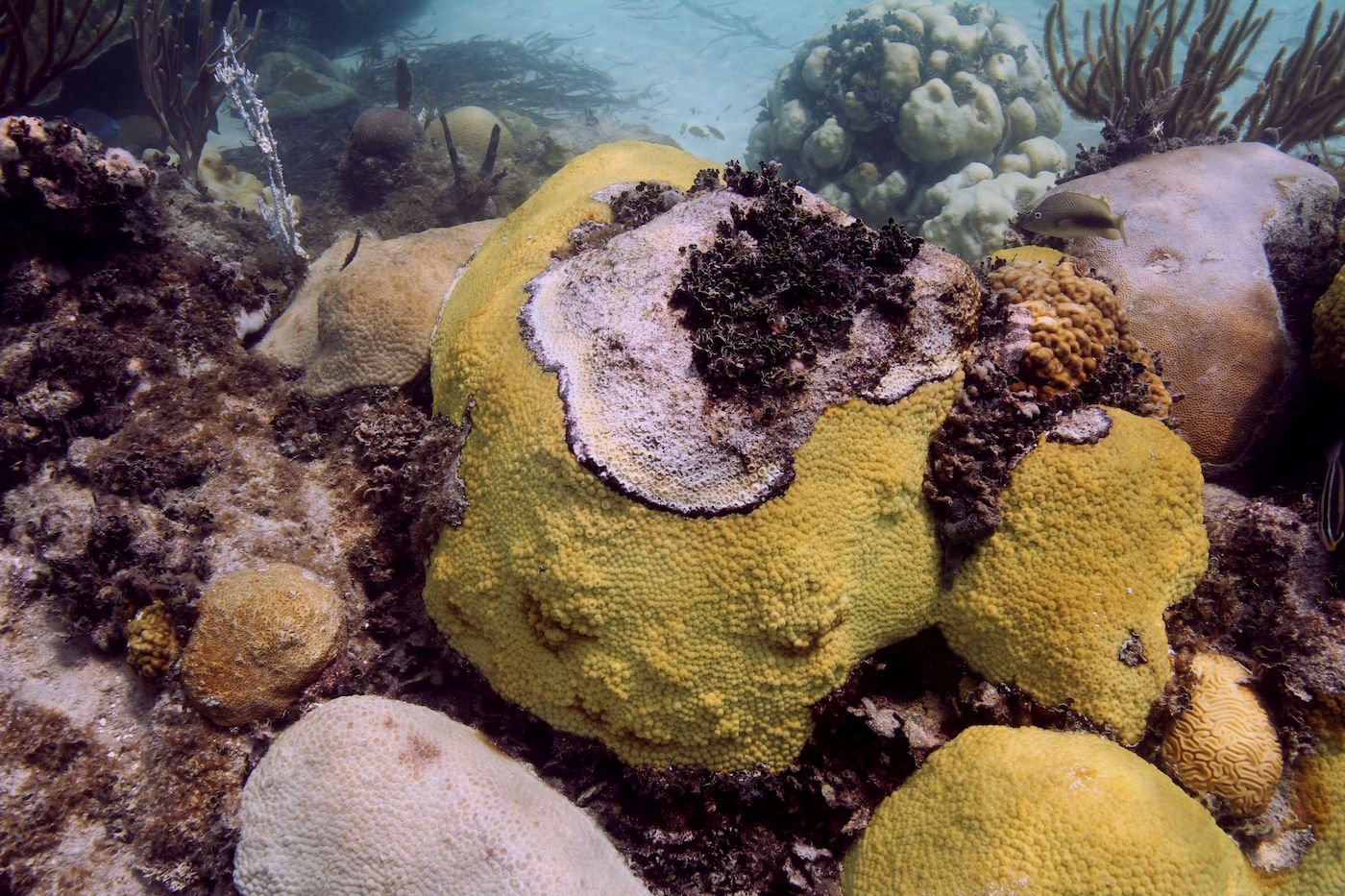
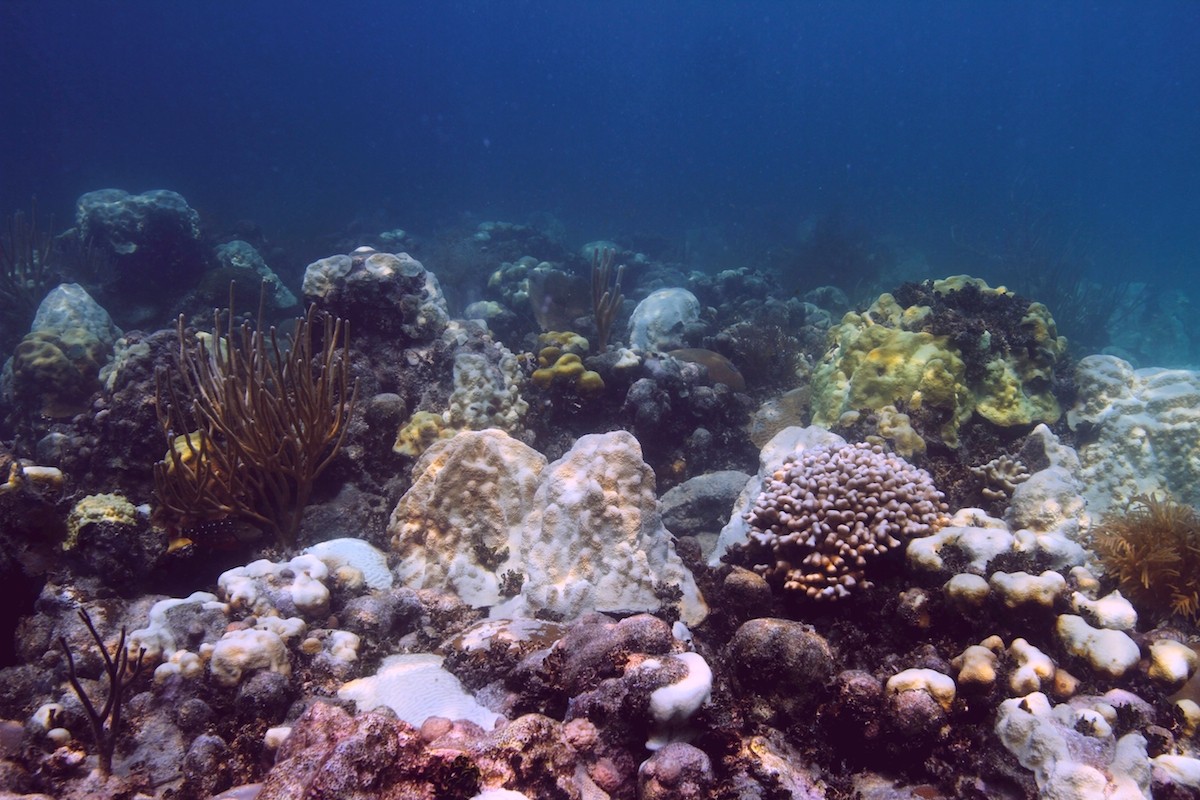
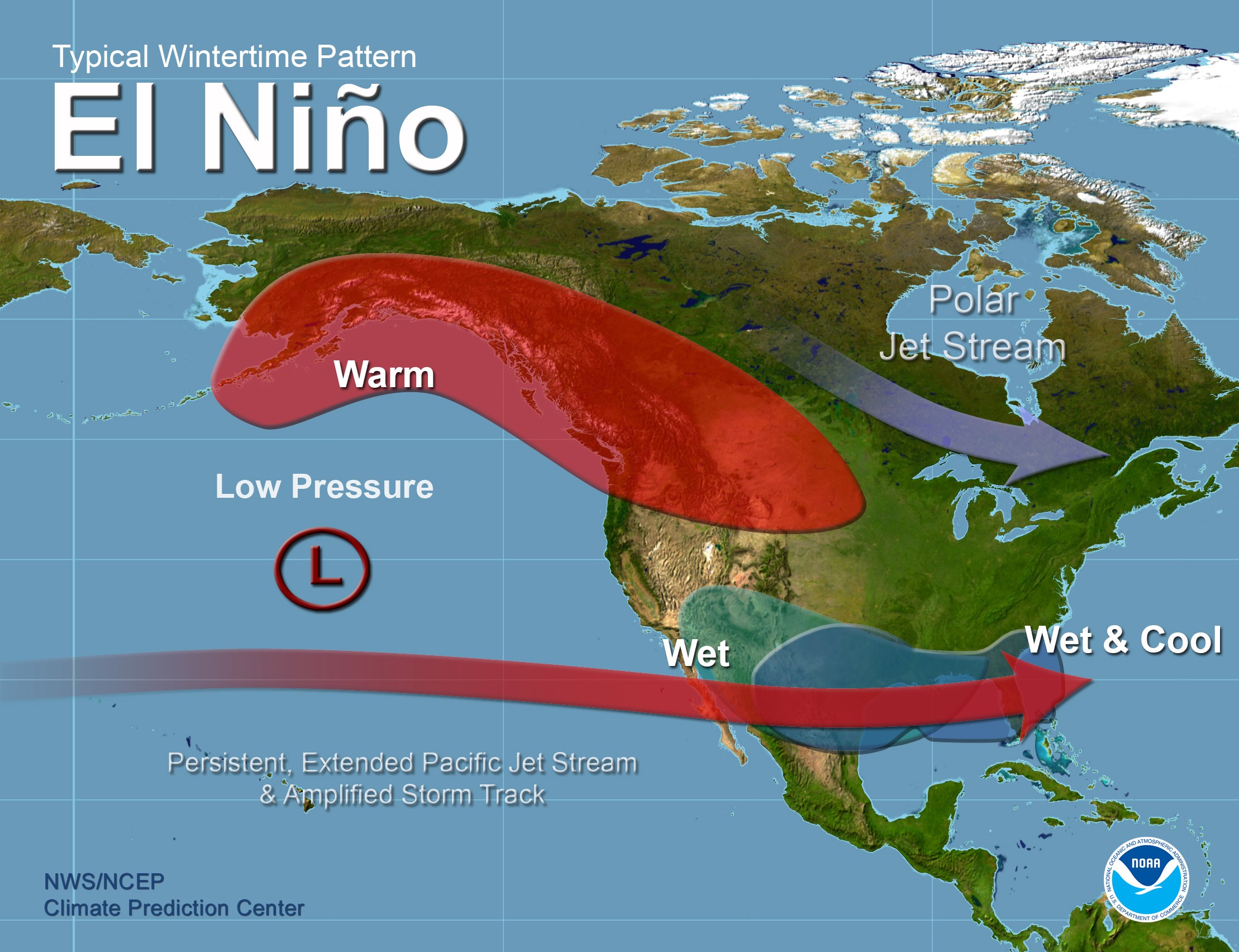
Volcano Spewing Carbon Dioxide Drives Coral to Give Way to Algae
The new research published online August 10 in Nature Climate Change provides a stark look into the future of ocean acidification – the absorption by the global oceans of increasing amounts of human-caused carbon dioxide emissions. Scientists predict that elevated carbon dioxide absorbed by the global oceans will drive similar ecosystem shifts, making it difficult for coral to build skeletons and easier for other plants and animals to erode them.