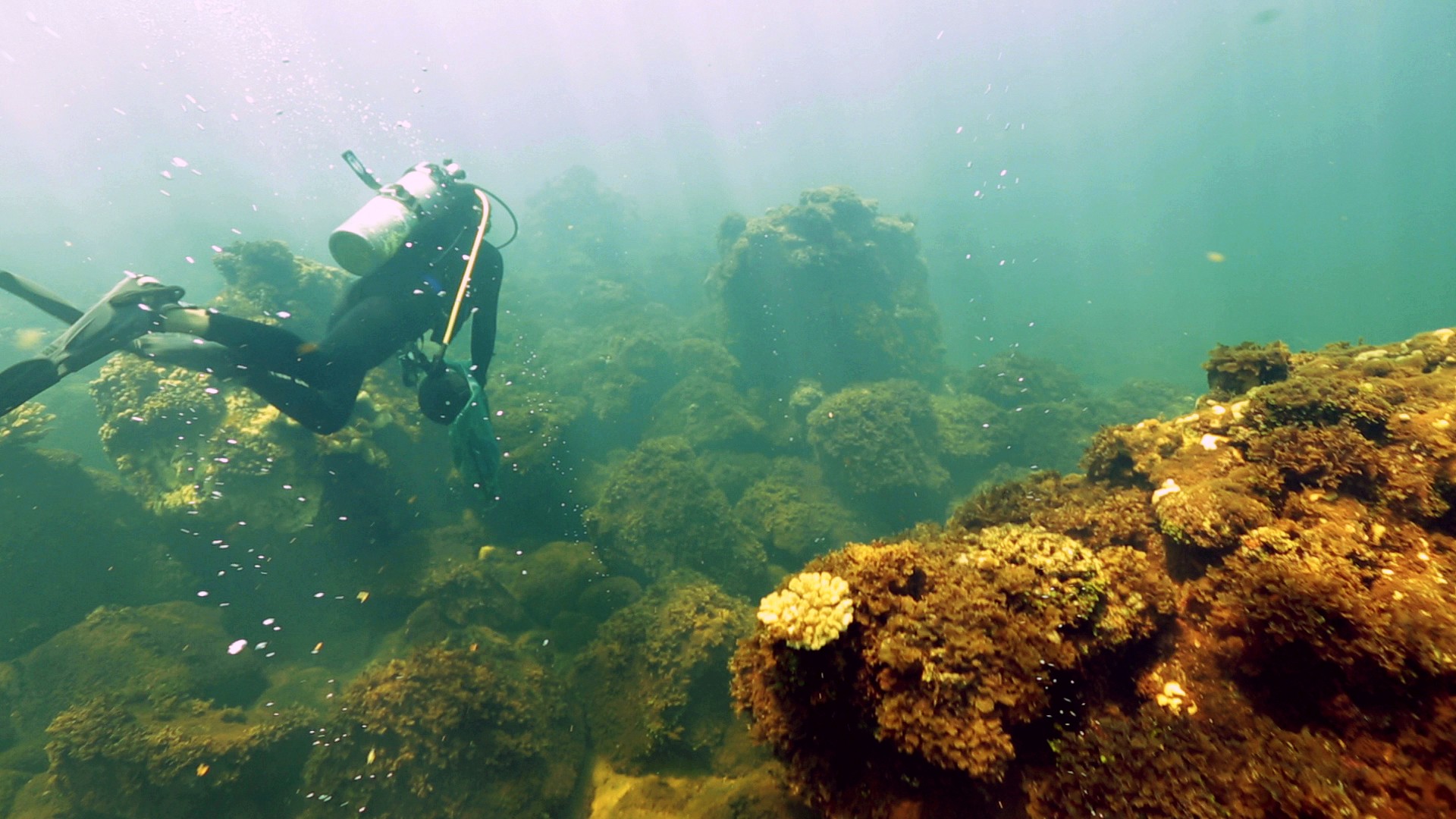
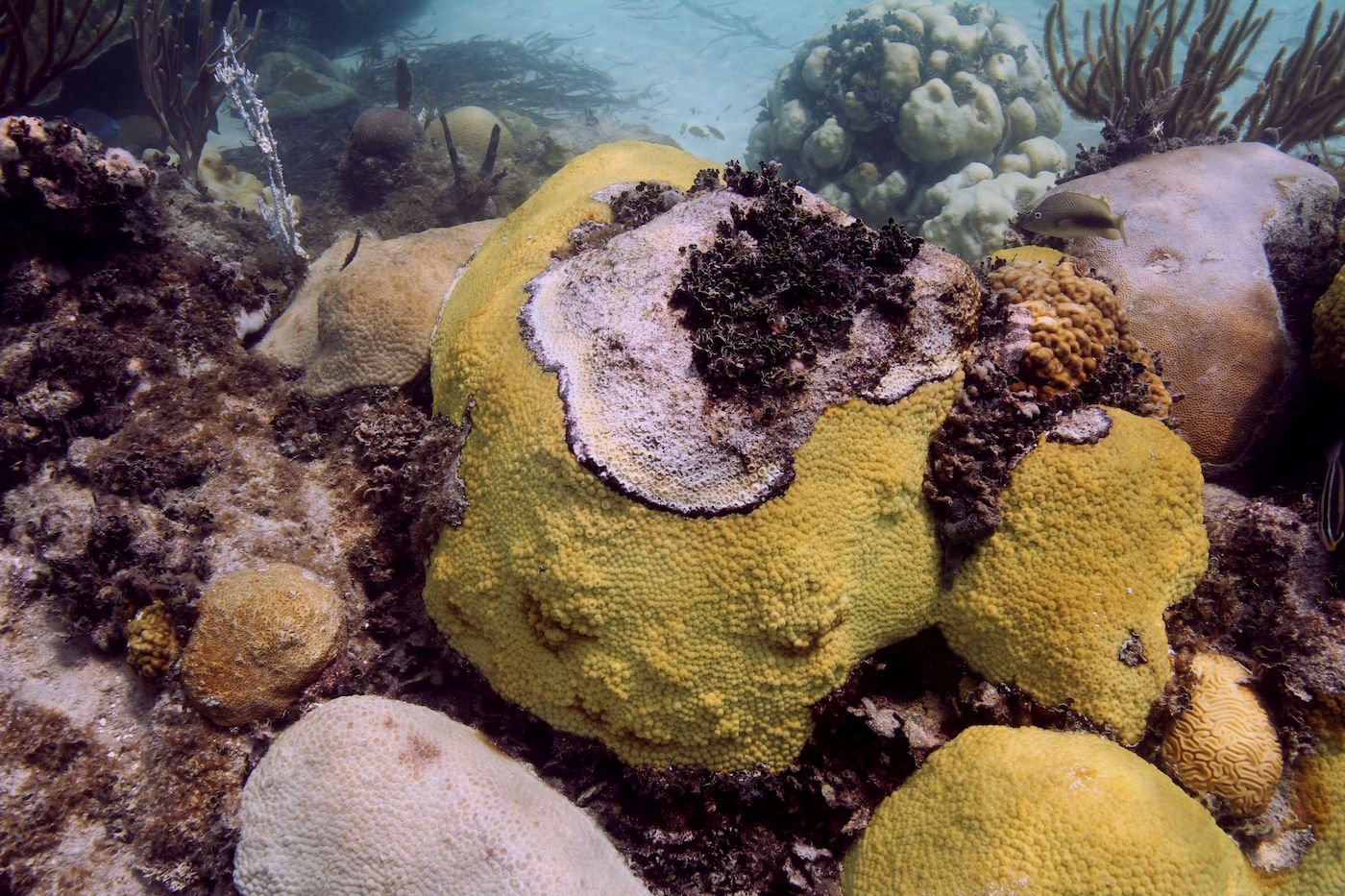
The 2016 Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratories’ (AOML) cadre of summer interns inspired us with a very promising group of motivated individuals. Fourteen students came from all over the country to complete a wide array of projects in different thematic areas of AOML’s workforce; Physical Oceanography, Ocean Chemistry and Ecosystems, Hurricane Research, Engineering, and Communications.AOML is home to some of the nation’s leading scientists, and internships offer a great opportunity for students to learn alongside these experts and develop skills that they will take with them in the future. The summer internships also expose students to careers at a federal research laboratory. NOAA offices are located all across the country, so students who enjoy their summer internship can consider NOAA or other federal science agencies for future employment when they enter the workforce.