The Meridional Overturning Circulation
Monitoring Global Ocean Circulation
SCROLL TO LEARN MORE
Who We Are
The overturning circulation is one of the main mechanisms the ocean uses to move heat, salt, carbon, and nutrients throughout the global oceans. Achieving a more complete understanding of the behavior of the Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) requires an observational network spanning the globe.
AOML scientists and our national and international partners are leading several programs that make crucial observations of the MOC in both the North and South Atlantic. The AOML projects that monitor/measure the MOC include: Western Boundary Time Series, Southwest Atlantic MOC , GO-SHIP, Argo, and the eXpendable BathyThermograph (XBT) network.
Our Objectives
- Measure, describe, and understand the pathways and variability of the upper and lower limbs of the MOC in the North and South Atlantic Oceans.
- Assess the role of the MOC in redistributing heat and salt in the ocean, and how it affects regional and coastal sea level changes.
- Study the relationship between the MOC and extreme weather events, including global monsoons, heat waves, hurricanes, and droughts.
Read More News
Results & Research Impacts
The Importance of Long Term Time-Series Data on the Meridional Overturning Circulation.
Key Findings & Accomplishments
With our partners, our WBTS project helped generate a 16-year daily time series of the MOC and heat transport in the North Atlantic.
Daily Time Series
The SAM project, along with SAMOC partners, has collected 10 years of daily MOC transport data in the South Atlantic.
Year Time Series
Analysis of Argo and XBT data, along with altimetry data, allow us to generate 28-year long records of the MOC at multiple latitudes in both the North and South Atlantic.
Year Record
We have over 100 coast-to-coast XBT transects from 2000 to present and 7+ GO-SHIP transects that have been used to estimate the strength of the MOC at various latitudes.
Degrees North
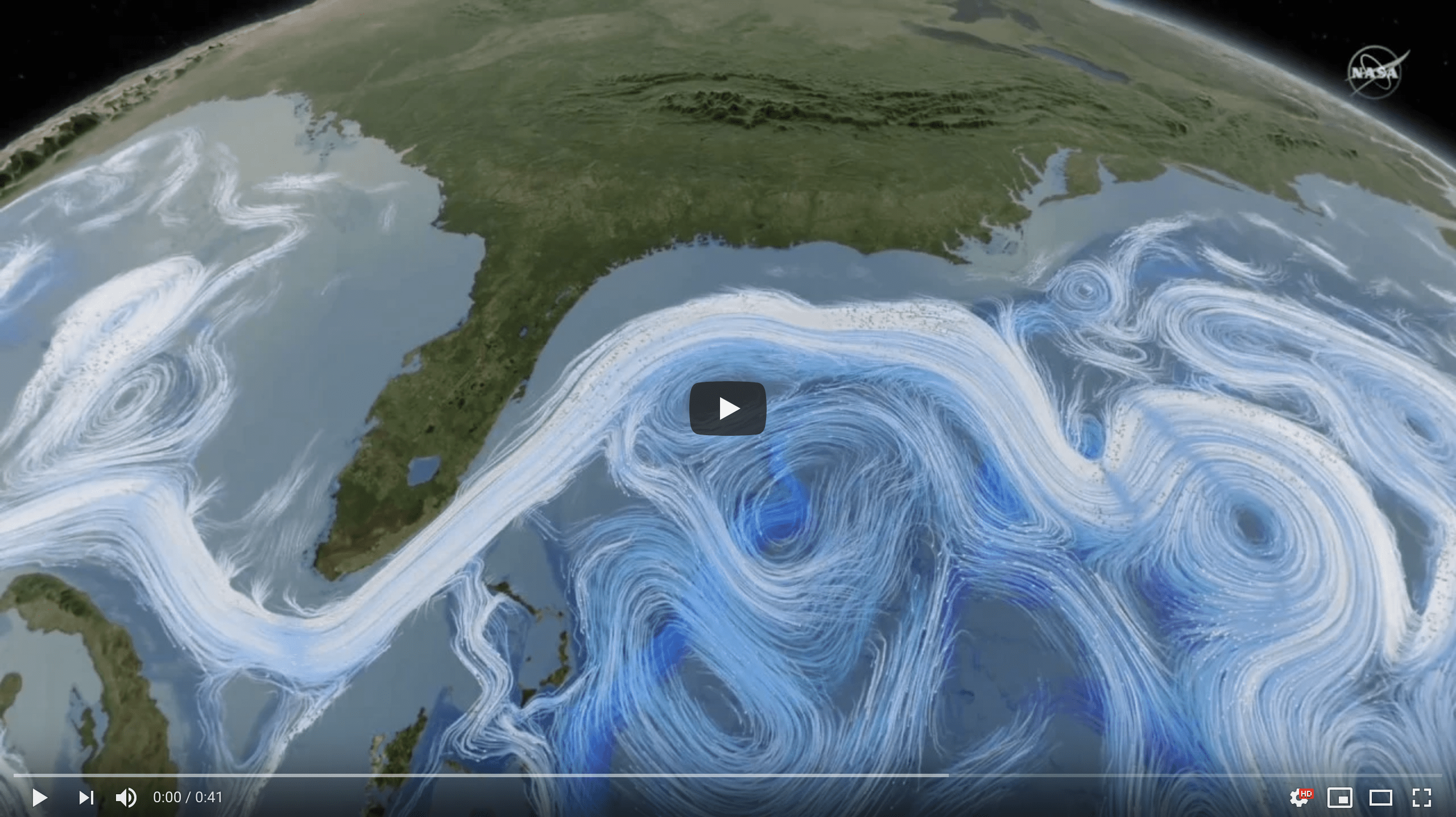
What is the Overturning Circulation
The Oceanic Conveyer Belt
A “meridian” is a north-south line on the globe along a constant longitude. The term “meridional,” is commonly used to refer to motion that is primarily in the north-south direction.
The Meridional Overturning Circulation is a component of ocean circulation, which constantly moves water, heat, salt, carbon, and nutrients north-south within the ocean basins, and ultimately between the ocean basins and around the globe. In the Atlantic Ocean, warm and salty water in the upper ocean is transported from the South Atlantic towards the Nordic Seas (Greenland, England, and Northern Canada), where, after losing its heat to the atmosphere and mixing with ambient water masses, it sinks and forms deep water that flows south all the way down toward Antarctica.
Read More
At the same time, near the coast of Antarctica, even heavier waters are formed. These waters flow north along the seafloor into the North Atlantic where they slowly rise and mix with other waters that flow back to the south. The MOC is responsible for about two-thirds of the oceanic northward heat transport and, thus, plays an important role in regulating the Earth’s climate system.
Changes in the Atlantic MOC determine how much heat is transported and influence regional heat content variations. This makes monitoring the Meridional Overturning Circulation critical for tracking changes in the global and regional climate and weather.
Observational MOC arrays are constructed so that they measure the strength of the circulation from coast to coast as the flow crosses a line of constant latitude either in the North Atlantic (e.g., from North America to North Africa) or South Atlantic (from South America to South Africa).
See the video below by NASA to learn more about why the MOC is important, or check out the tweet thread we did about the #thermohalinecirculation with Renellys Perez.
The #thermohalinecirculation is a global overturning circulation made of stratified water masses. The upper layer is warmer, lighter & sits on top of the colder and denser deep layer. These layers travel around the global oceans, exchanging waters and nutrients along the way. pic.twitter.com/yLvw33dcn5
— NOAA AOML (@NOAA_AOML) August 30, 2018
Effects on Global Climate
Regional Sea Level
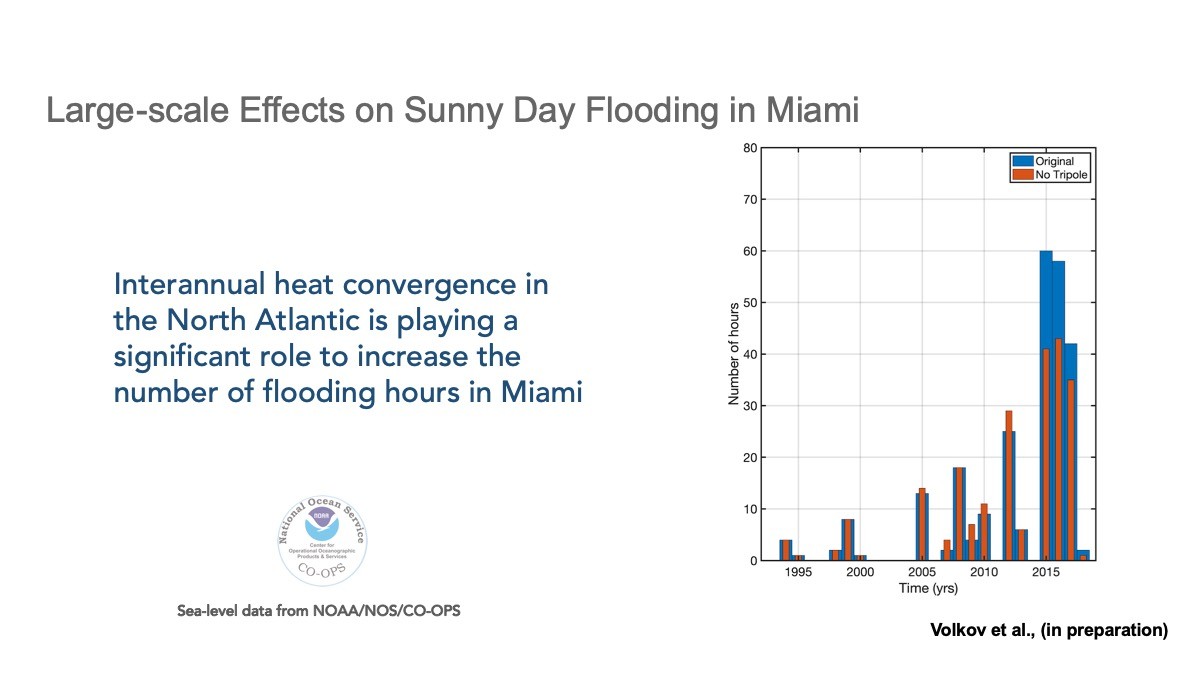
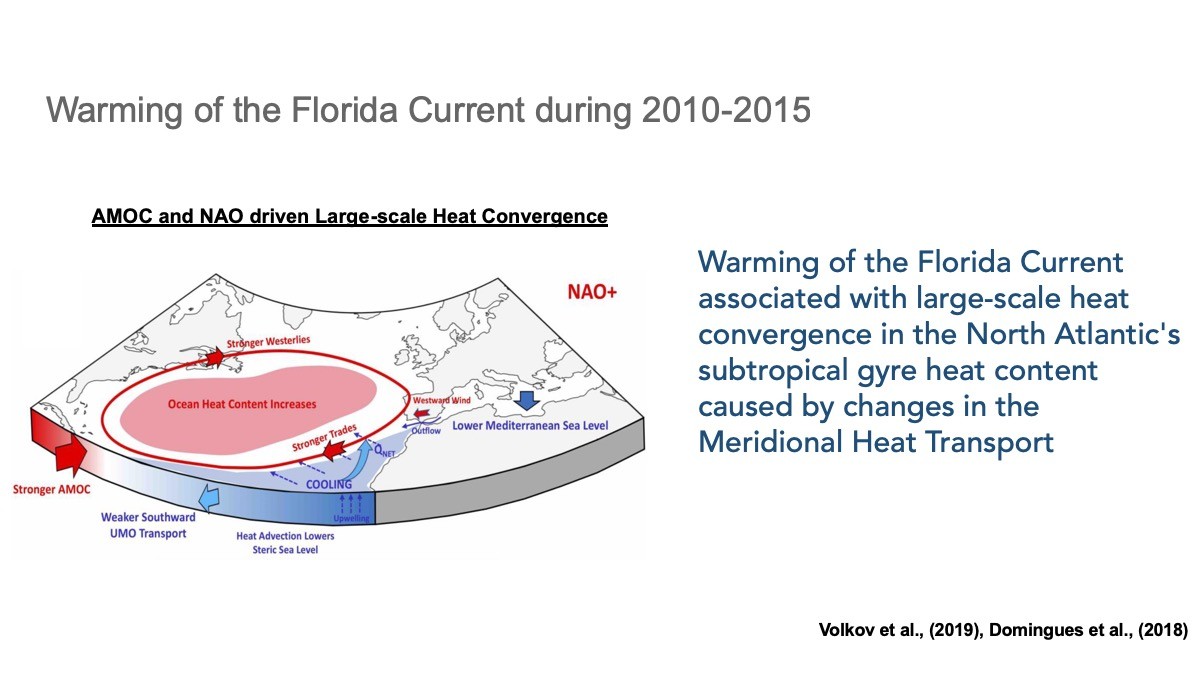
Heat moved around the oceans by the MOC largely controls the regional oceanic heat content. It has recently been shown that this movement of heat also impacts the year-to-year variability of sea level both along the U.S. southeastern coastline and along the coastlines around the Mediterranean Sea. Continuous observations of the MOC can potentially be used to develop or improve coastal sea level predictions.
Read More
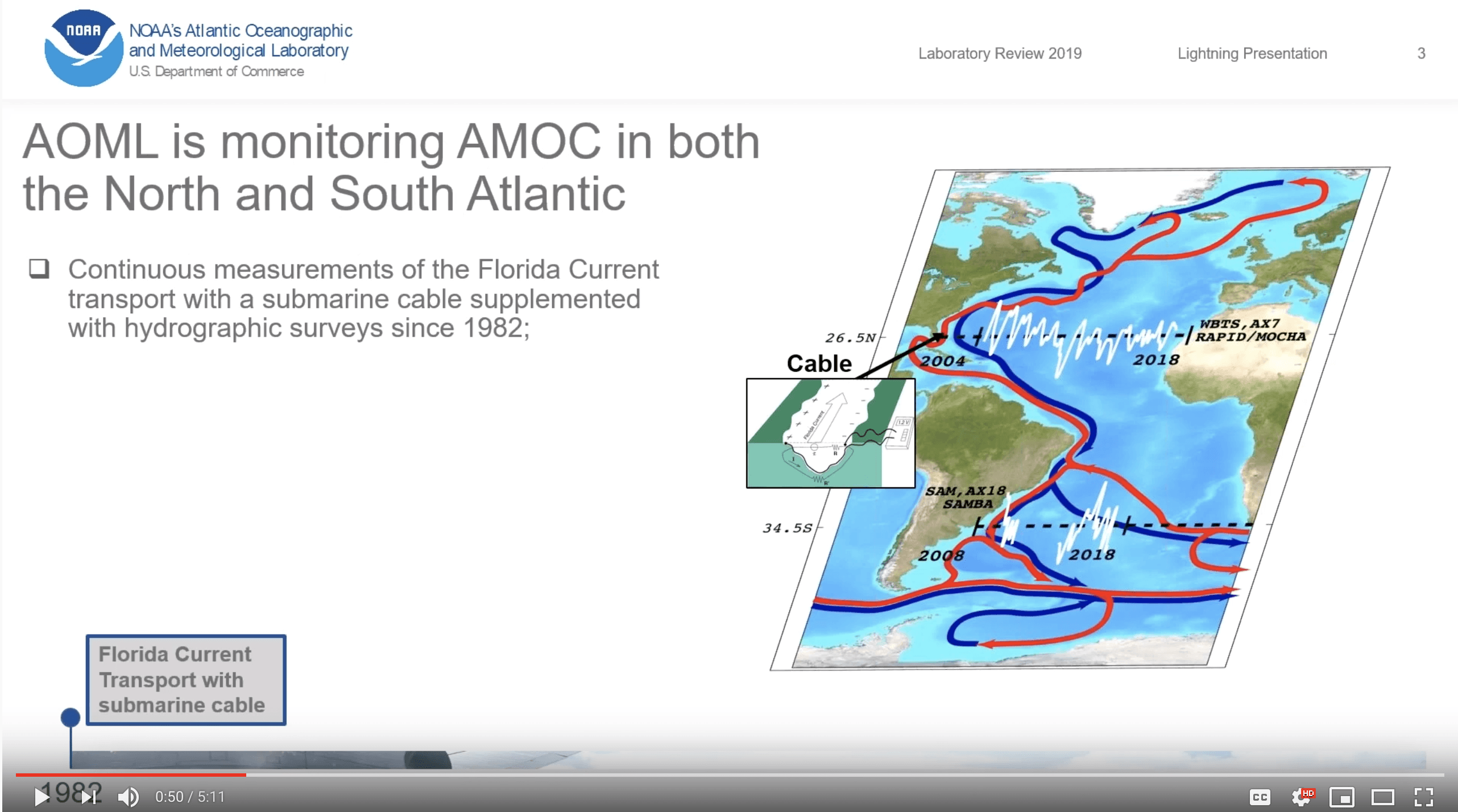
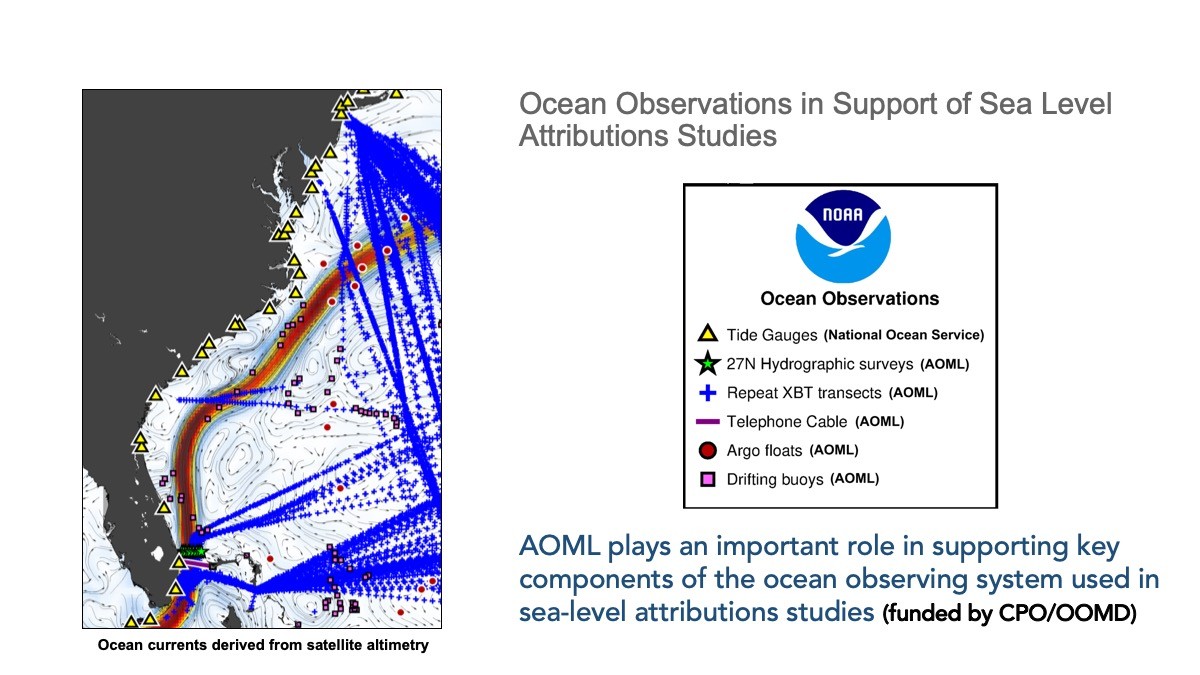
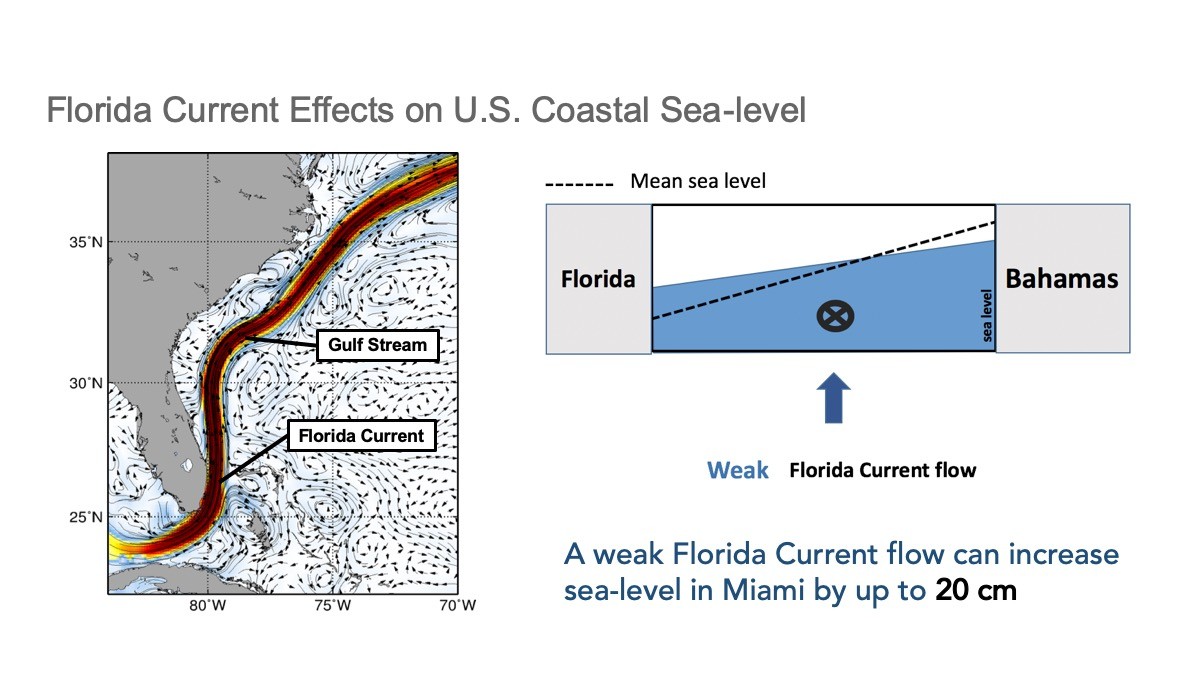
One of AOML’s contributions to MOC monitoring is a system that measures the transport of the Gulf Stream near the Florida coast using voltages on a submarine cable. These daily observations started back in 1982, and now provide the longest nearly-continuous record of a boundary current transport in the world. Changes in the Gulf Stream strength directly affects sea levels along the eastern coast of Florida. A stronger current is associated with lower sea levels along the east coast of Florida, and a weaker current is associated with higher sea levels.
Oceanic Heat Content Change
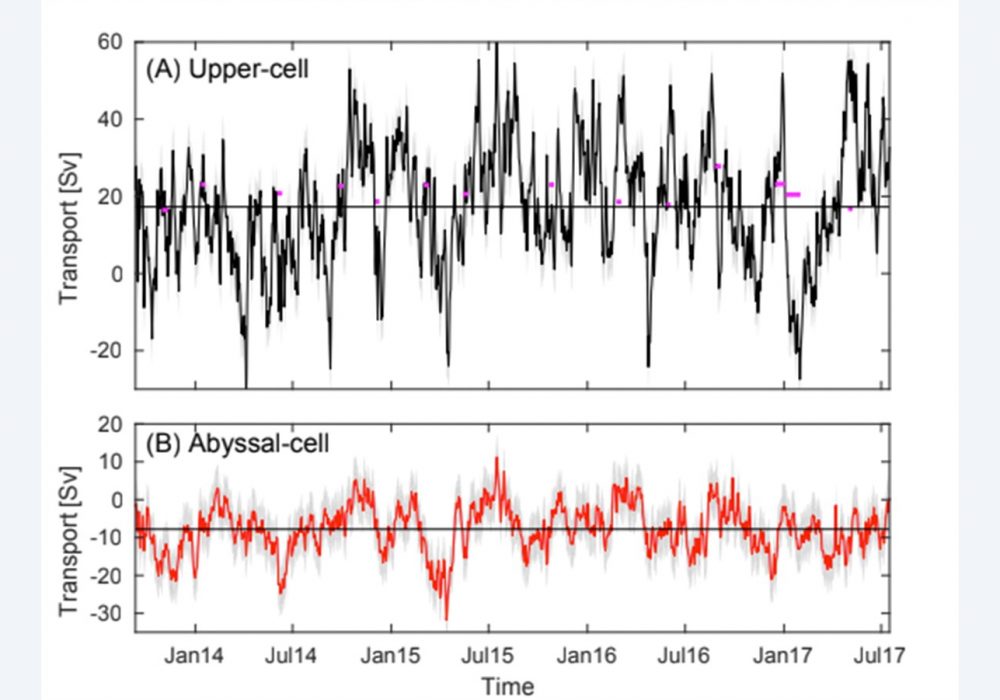
Several ongoing projects are investigating the variability of the Meridional Overturning Circulation in both the North and the South Atlantic Ocean using shipboard measurements, moored buoys, and satellite data. These studies involve measurements of the full-water-column, full-basin-width, meridional velocity, temperature, and salinity along a line of constant latitude: 26.5N in the North Atlantic and 34.5S in the South Atlantic. This is crucial, because the Atlantic Ocean is unique as the only basin where heat is transported northward in both hemispheres, strongly impacting the heat content.
Extreme Weather
The MOC is a driver of global climate and has a substantial impact on precipitation patterns. Studying these patterns helps our physical oceanographers provide data and insights that can improve weather forecasts beyond the current weather timescales of up to 10 days. We also conduct research to understand how the MOC is connected to monsoons and extreme weather events such as heat waves and tornadoes.
How do we monitor the MOC?
Observing Systems and the MOC
Read the plain-language article about several different types of observational systems that are used by scientists to measure the complex nature of the meridional overturning circulation.
Measuring Ocean Transport
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation plays a crucial role in redistributing heat and salt throughout the global oceans. Achieving a more complete understanding of the behavior of the MOC system requires a comprehensive observational network that spans the entire Atlantic basin.
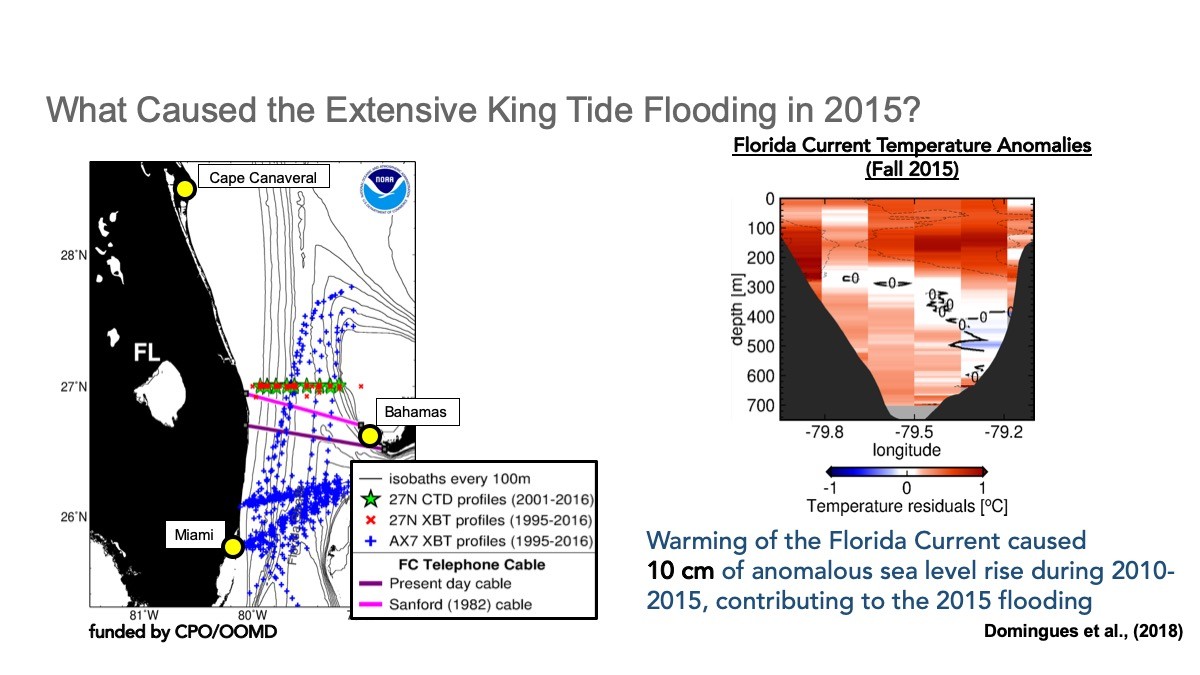
The Florida Current
AOML has continuously monitored the Florida current since 1982 to learn more about how local and global sea level rise are connected over time and space. These observations, taken at 26.5N latitude in the Atlantic, allow AOML scientists to draw important conclusions about the speed of the Meridional Overturning Circulation over long and short timescales. Results from long-term monitoring and subsequent research helps to improve coastal sea level predictions.
Click through the slides below to learn more about the Florida Current and its impacts on South Florida.
To watch the full presentation click here.


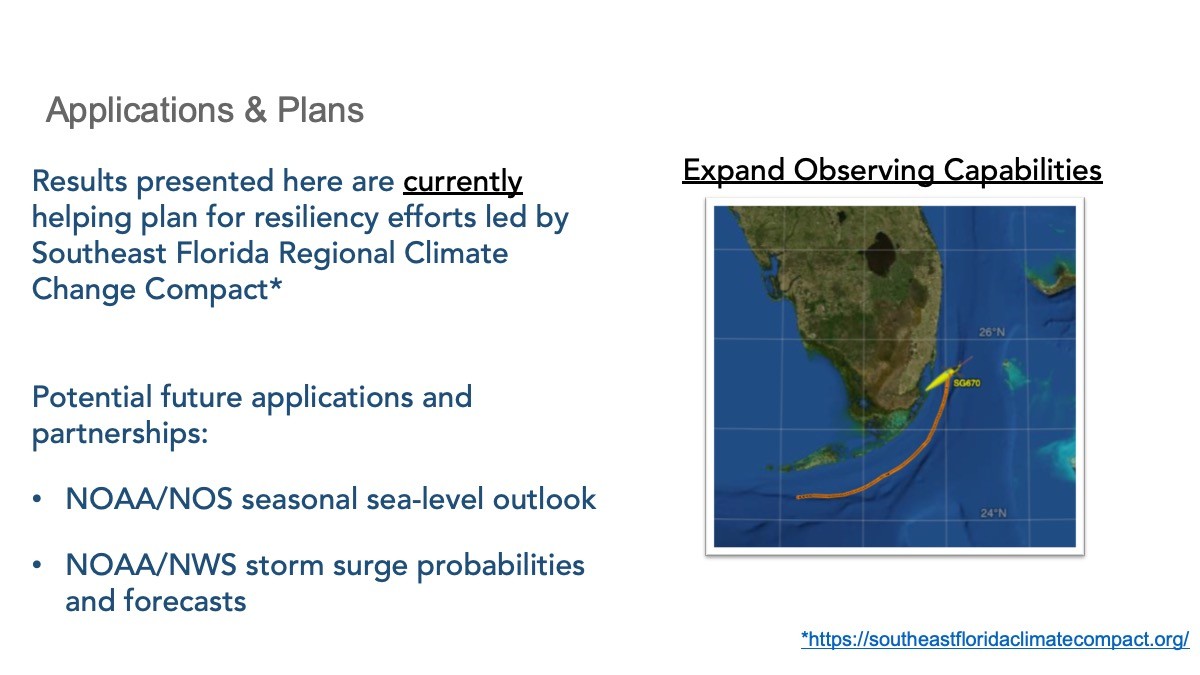
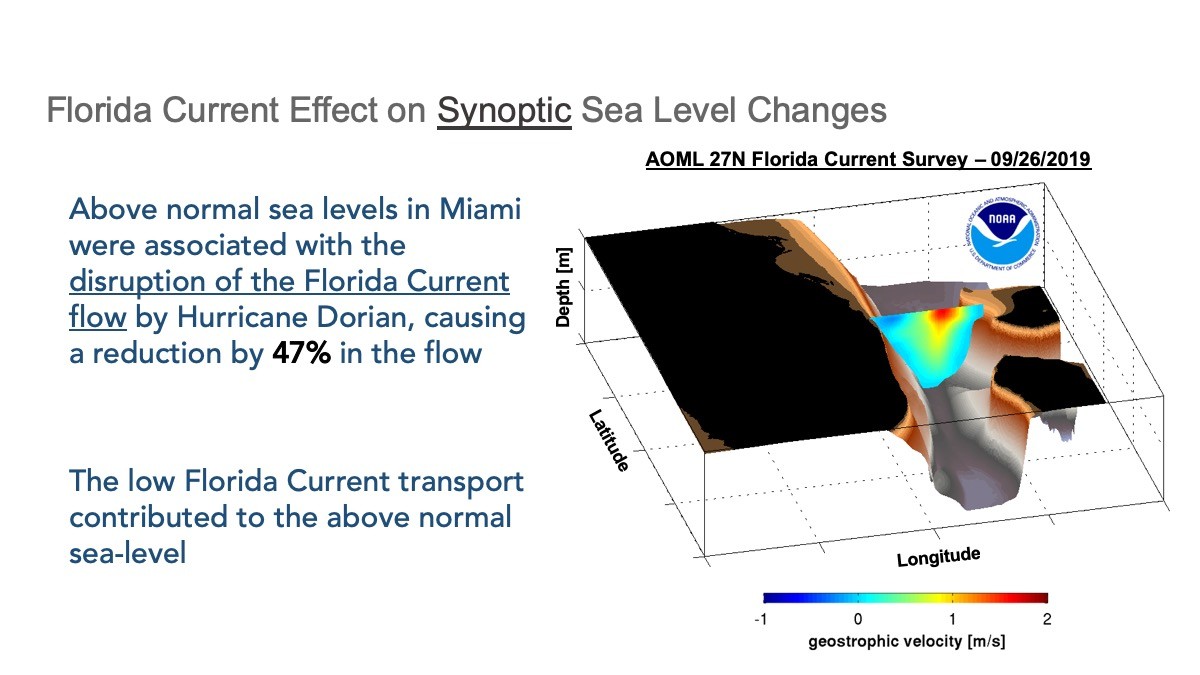
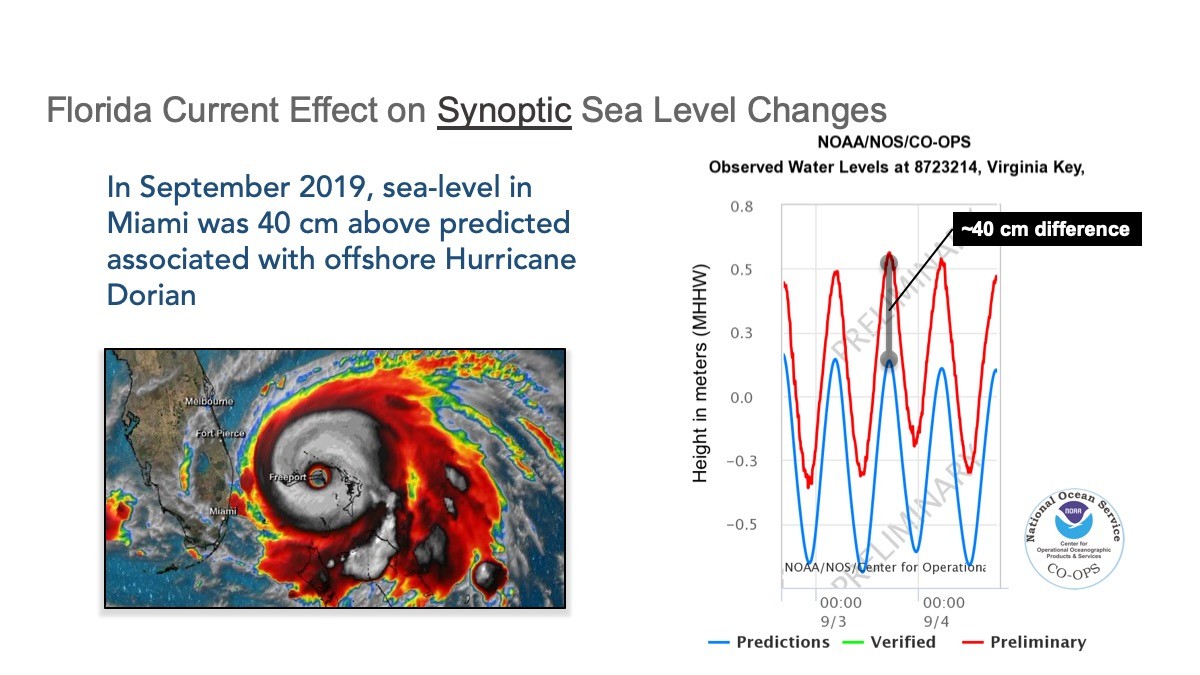
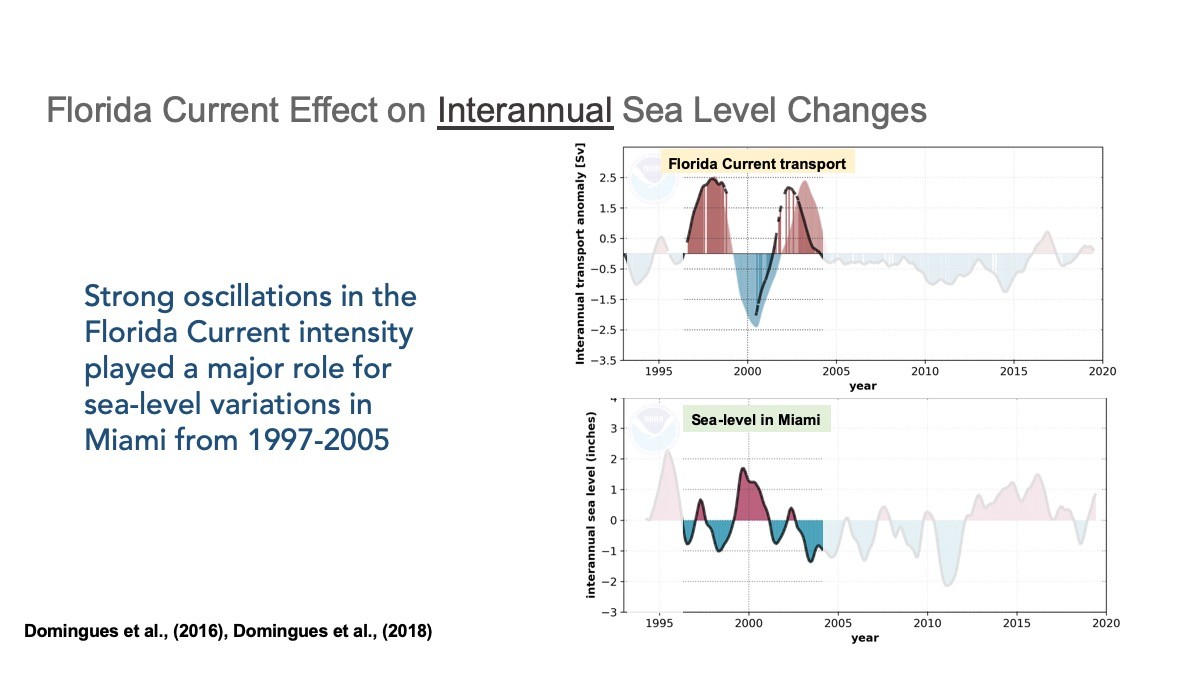
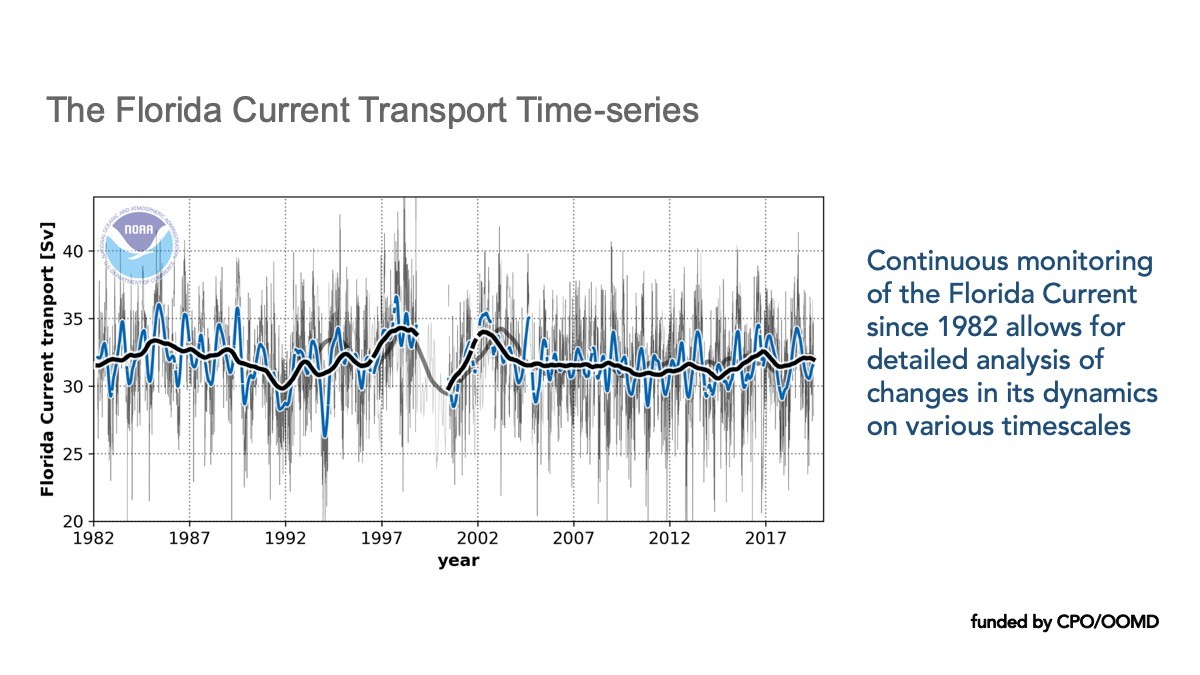





















Expanding our Reach Beyond South Florida.
Trends across the Atlantic.
Watch the Lightning Presentation: Monitoring the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation in both Hemispheres
Read More
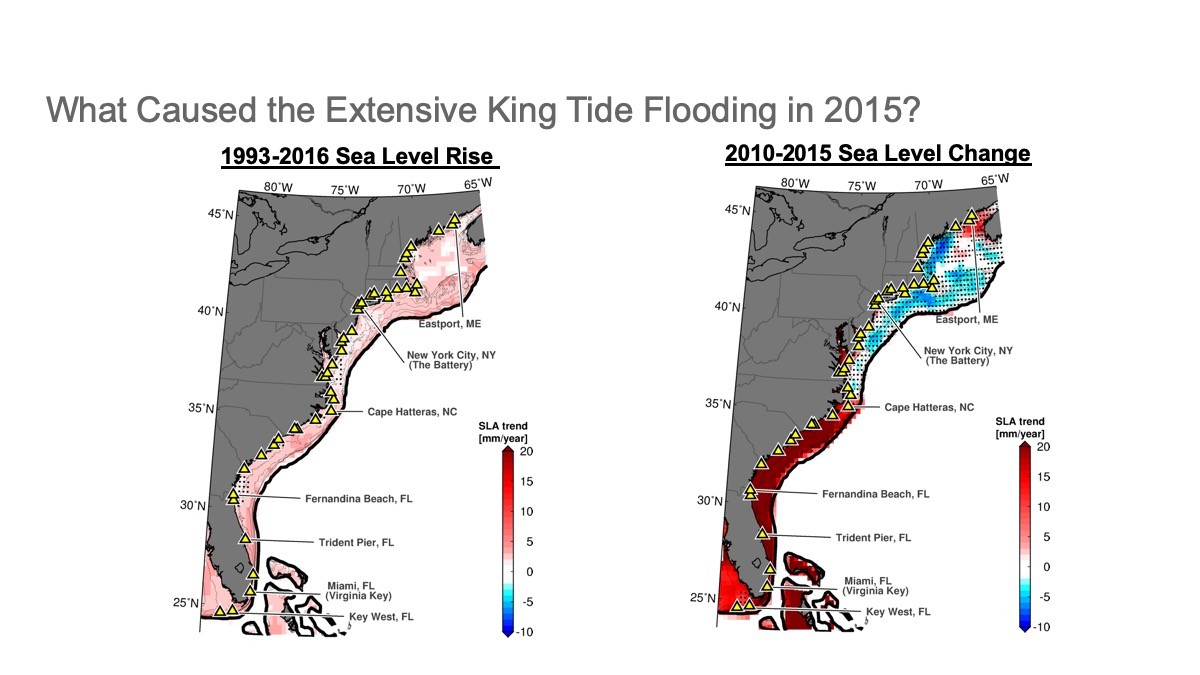
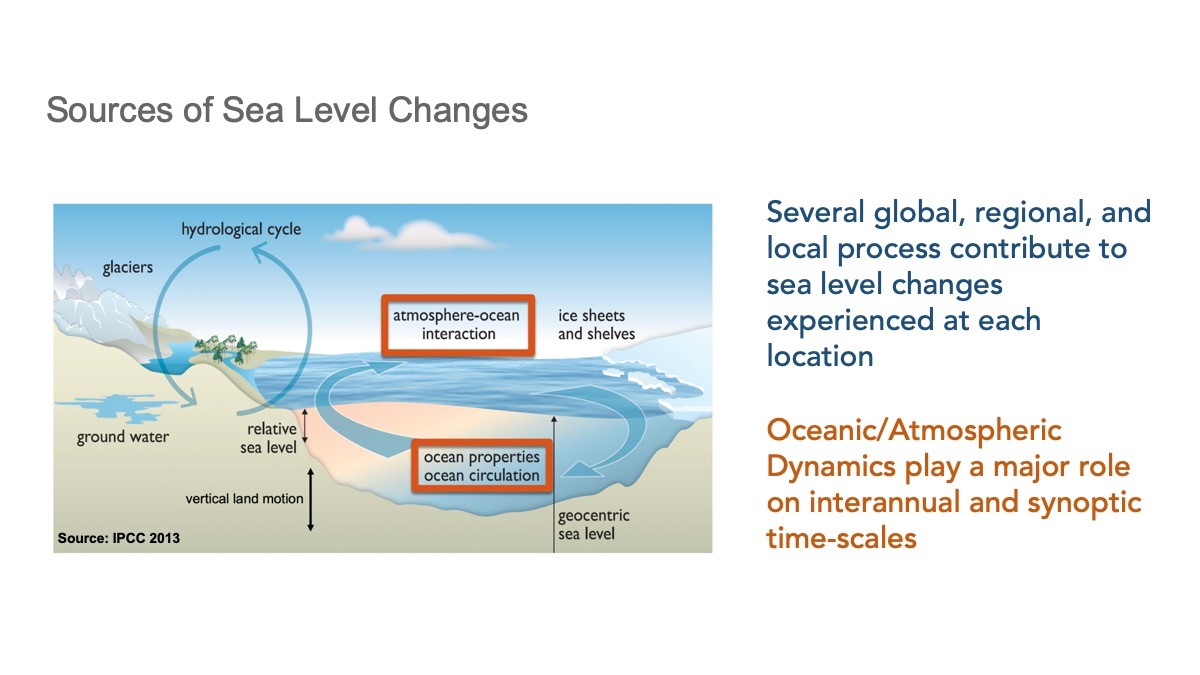
Global mean sea level rise caused by ocean warming and melting of ice sheets and glaciers is one of the most alarming aspects of climate change. However, while the global mean sea level is rising, regional sea level trends are quite different, with some regions rising faster than others or even experiencing decreasing sea levels. For example, a pronounced acceleration of sea level rise in 2010-2015 was observed south of Cape Hatteras along the U.S. eastern coastline, while a deceleration occurred further north. This regional sea level variability is largely due to the changing dynamics of the ocean and atmosphere. These dynamics also further influence regional sea level changes region by region and over time.
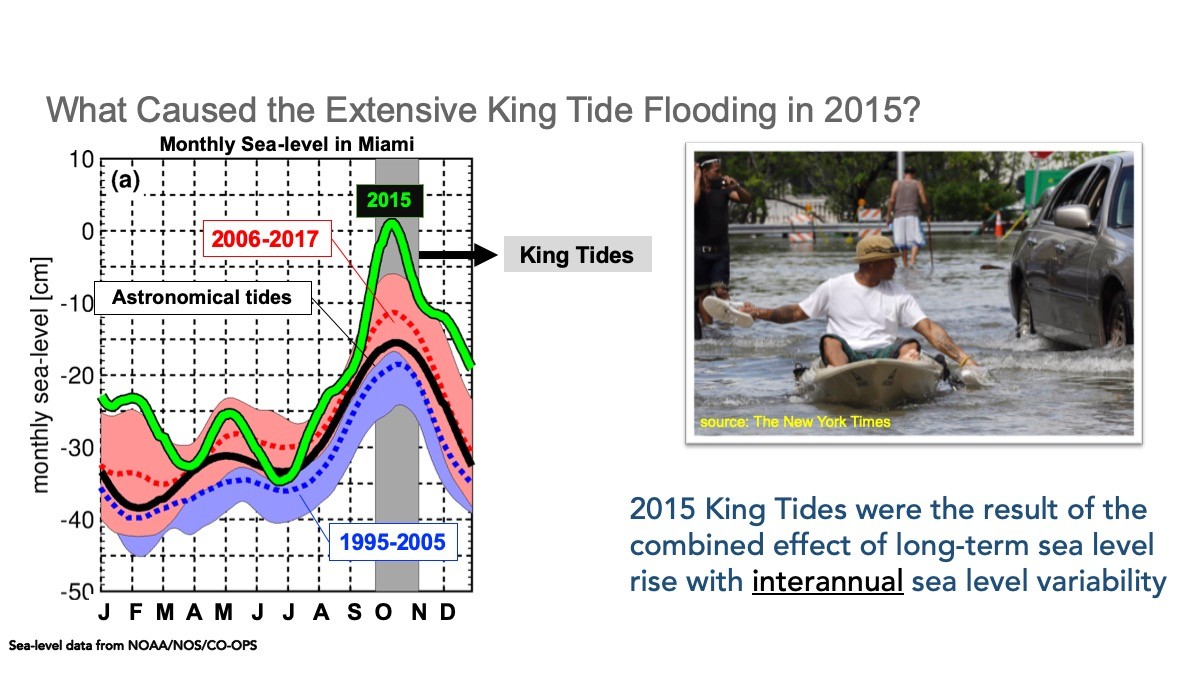
These large-scale, slow, sea level pattern changes are added on top of shorter-period (and often stronger) sea level changes that coastal communities directly experience every day. These can include tides, storm surge, and the strength of the Gulf Stream. To improve regional sea level predictions, it’s important to understand both the large scale and small scale patterns and to explore how they change over time. Read how AOML scientists are discovering how ocean dynamics affect regional sea level in the Mediterranean Sea and along the U.S. southeastern seaboard.
Extreme Weather Events
In order to expand weather forecasts beyond the typical timescales, we need information from the surface ocean and the ocean at depth, as well as the land.
-Hosmay Lopez, Ph.D
Extreme weather events are responsible for large mortality and vast economic impact in the U.S. on a yearly basis. However, the current operational forecasts for extreme weather are limited to only several days in advance. There is a pressing need for extending the time frame of severe weather forecast beyond the 7-10 days’ time scale. Research conducted at AOML shows a physical link between the state of the ocean and high impact extreme weather events, such as heat waves and tornadoes.
Changes in the Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) influences the occurrence of heat waves in the U.S., as well as global monsoon precipitation. AOML scientists have found evidence that weaker northward transports of heat within the ocean in the South Atlantic leads to stronger Northern Hemisphere monsoons about 20 years later. This research and related studies are allowing AOML scientists to link monsoon intensity and other severe weather events to changes in the MOC. Click on the link below to learn more about the extreme weather research happening at AOML.
Observations in the South Atlantic
Traditionally, most Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) observations have been focused on the North Atlantic and Southern Oceans where the largest volumes of new deep waters are formed. However, to understand the feedback and interaction between the waters formed in the North Atlantic and Southern Oceans it is imperative to improve our understanding of the pathways of the upper and lower limbs of the MOC in the South Atlantic Ocean. Numerical climate models indicate that important water mass transformations and exchanges occur in the South Atlantic. These exchanges are thought to control the stability of the entire MOC flow system. Recognition of the importance of the South Atlantic led to the formation of an international group dedicated to advancing our understanding of the role of the South Atlantic Ocean in the MOC system, as well as the establishment of an observing system to capture key components of the circulation: these endeavors are known as the South Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or SAMOC initiative. The SAMOC initiative is a collaboration involving partners in Argentina, Brazil, France, Germany, Spain, South Africa, and the United States (NOAA/AOML). The main objective of the SAMOC initiative is to measure the strength and variability of the MOC in the South Atlantic, and how it transports water mass properties like heat and salt, to link those variations with weather phenomena and climate system variability.
XBT
AOML collects expendable bathythermograph (XBT) data on two transects spanning the subtropical oceans on quarterly repeats: in the North Atlantic since 1995 along AX07 running between Spain and Miami, Florida, and in the South Atlantic since 2002 along AX18 between Cape Town, South Africa, and Buenos Aires, Argentina. These data capture the upper limb of the MOC transport, which provide a means to monitor the variability in MOC and its associated heat transport. AOML currently provides quarterly reports for the North and South Atlantic MHT using data from these two repeat XBT transects.
South Atlantic Meridional Heat Transport (SAMHT)
Observations in the South Atlantic have been historically sparse both in space and time compared to the North Atlantic. To enhance our understanding of the Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) and Meridional Heat Transport (MHT) variability in the South Atlantic, AOML developed a methodology to estimate the MOC and MHT by combining sea surface height measurements from satellite altimetry and in situ measurements (Dong et al., 2015). This new methodology allows us to estimate the MOC and MHT in real time.
Argo and Altimetry
There is increasing evidence that the South Atlantic may be playing a crucial role to the MOC variability. Therefore, in an attempt to understand the variability of the upper branch of the Meridional Overturning Circulation in the South Atlantic, a three dimensional absolute velocity product is constructed using sea surface height measurements from satellite altimetry, observations from Argo floats, and wind fields. These velocity fields along with the hydrographic profiles are then used to estimate meridional volume and heat transport at several latitudes in the South Atlantic. The analysis has been expanded into the North Atlantic where the integrated meridional volume and heat transports are derived at two latitudes.
Sharing Resources Delivers Results.
Expanding Our Reach Through Partnerships.
5+
Countries
Countries involved in joint trans-basin mooring arrays with AOML in the North and South Atlantic Filler text FLLER TEXT FILLER TEXT
8000+
Daily Estimates
Daily estimates of the MOC collected in the North and South Atlantic through the collaborative mooring arrays.
250+
Ship Days
Ship days on research vessels provided by international partner organizations, saving NOAA more than US$10M in ship time costs.
20+
Deep Ocean Moorings
Deep ocean moorings supported by partners in the trans-basin MOC arrays in the North and South Atlantic.