State of the Climate in 2021 Report Released
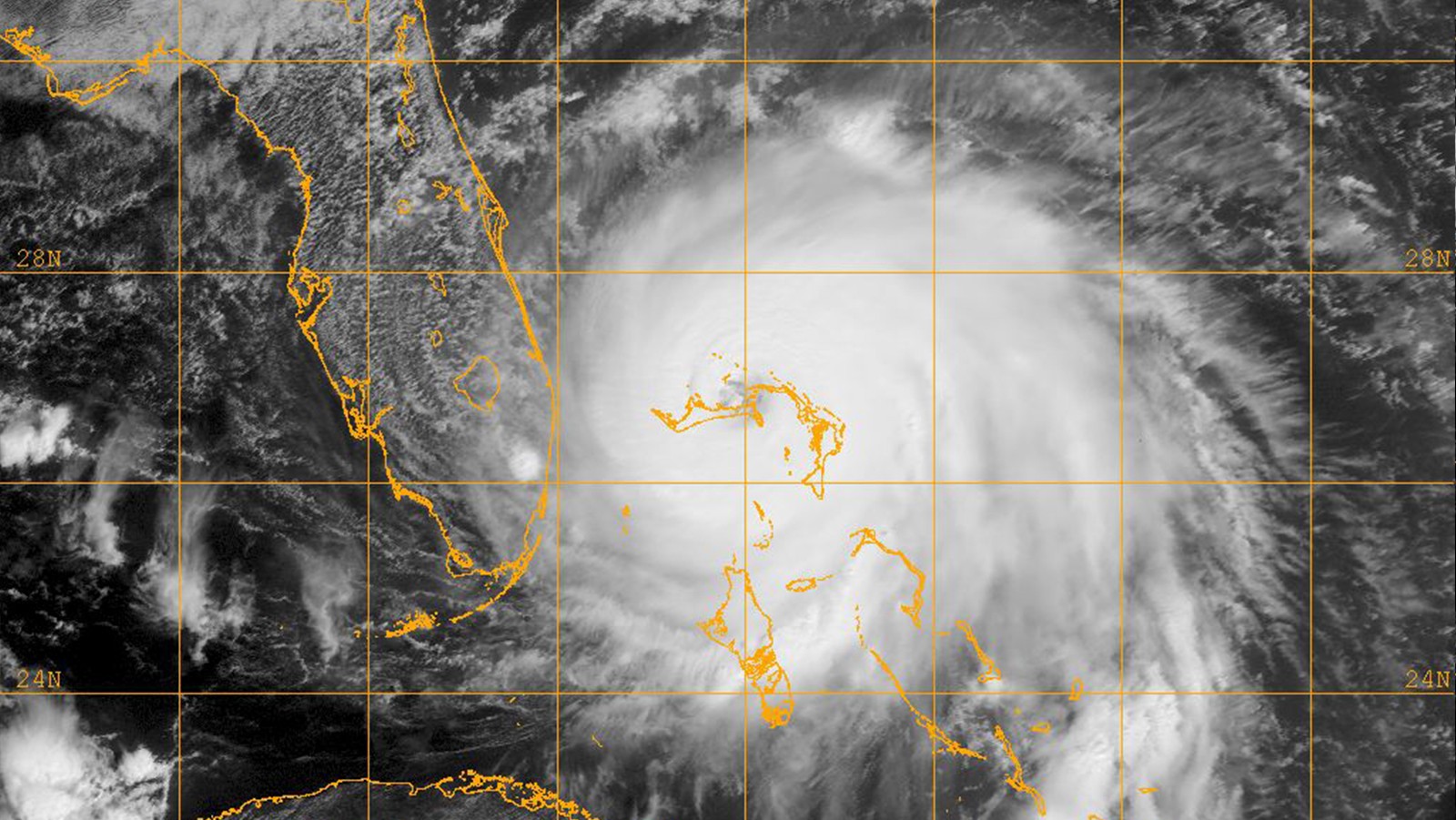
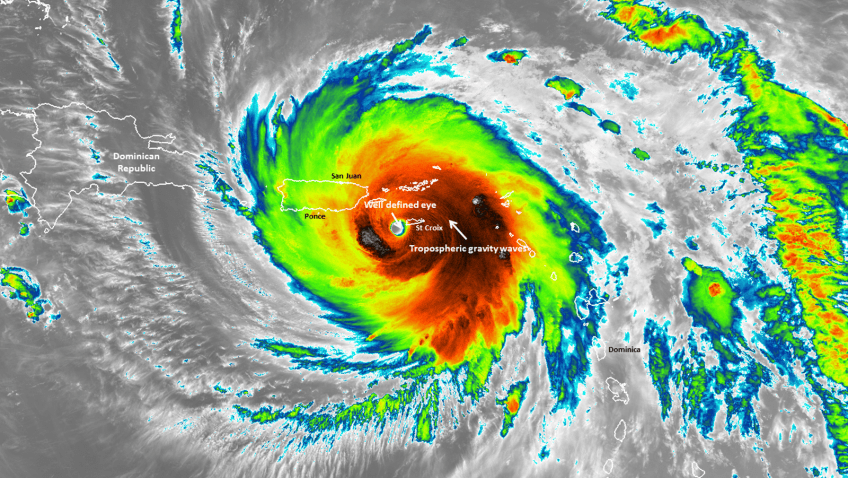
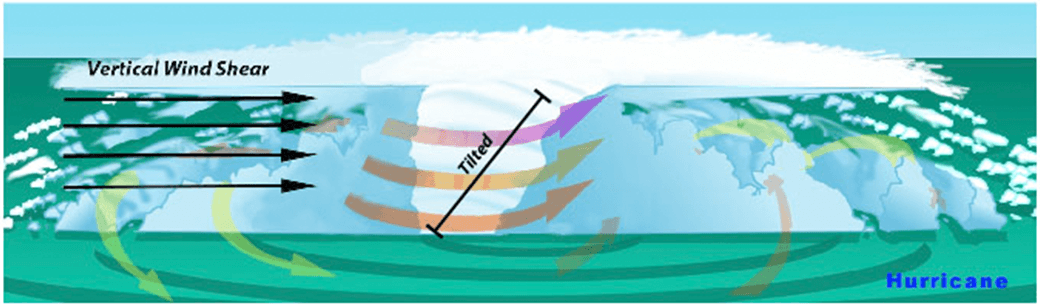
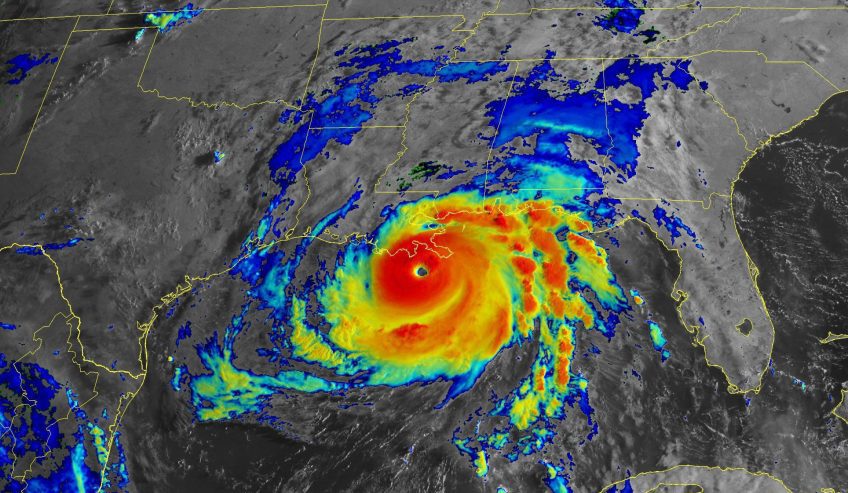
te of the Climate in 2021 report was released today by the American Meteorological Society, showing greenhouse gas concentrations, global sea levels, and ocean heat content reached record highs in 2021 despite a La Niña event taking place in the Pacific Ocean.