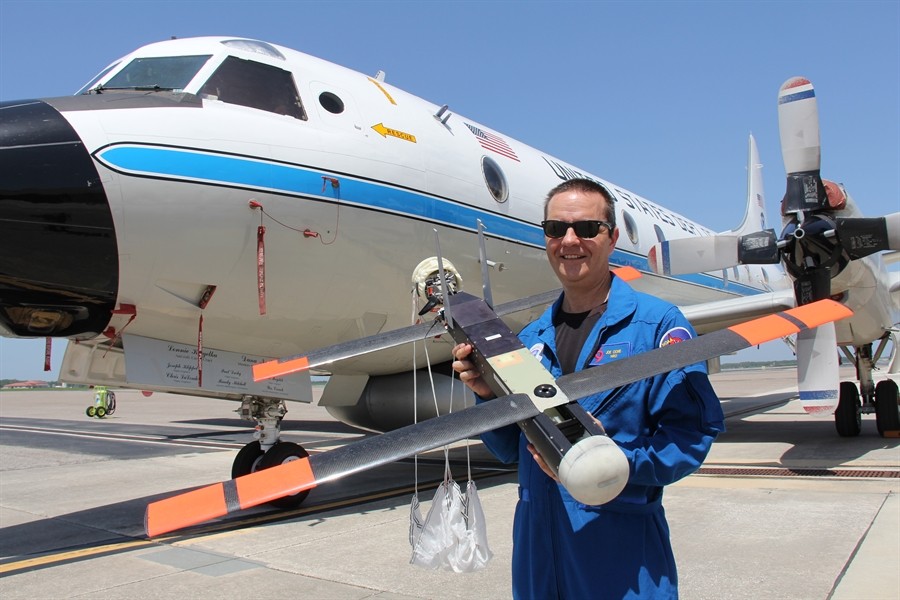
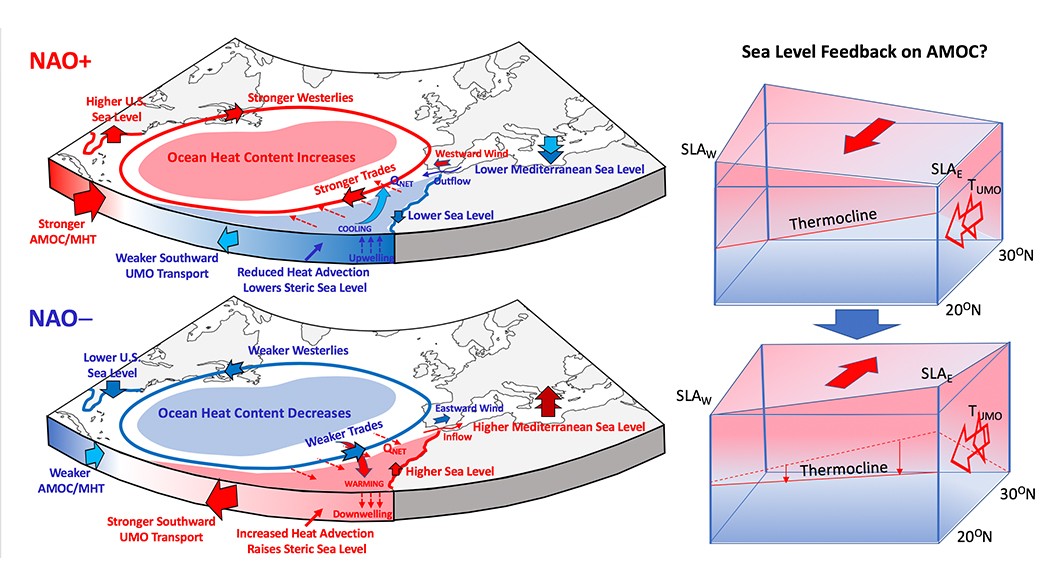
Braving the Eye of the Storm
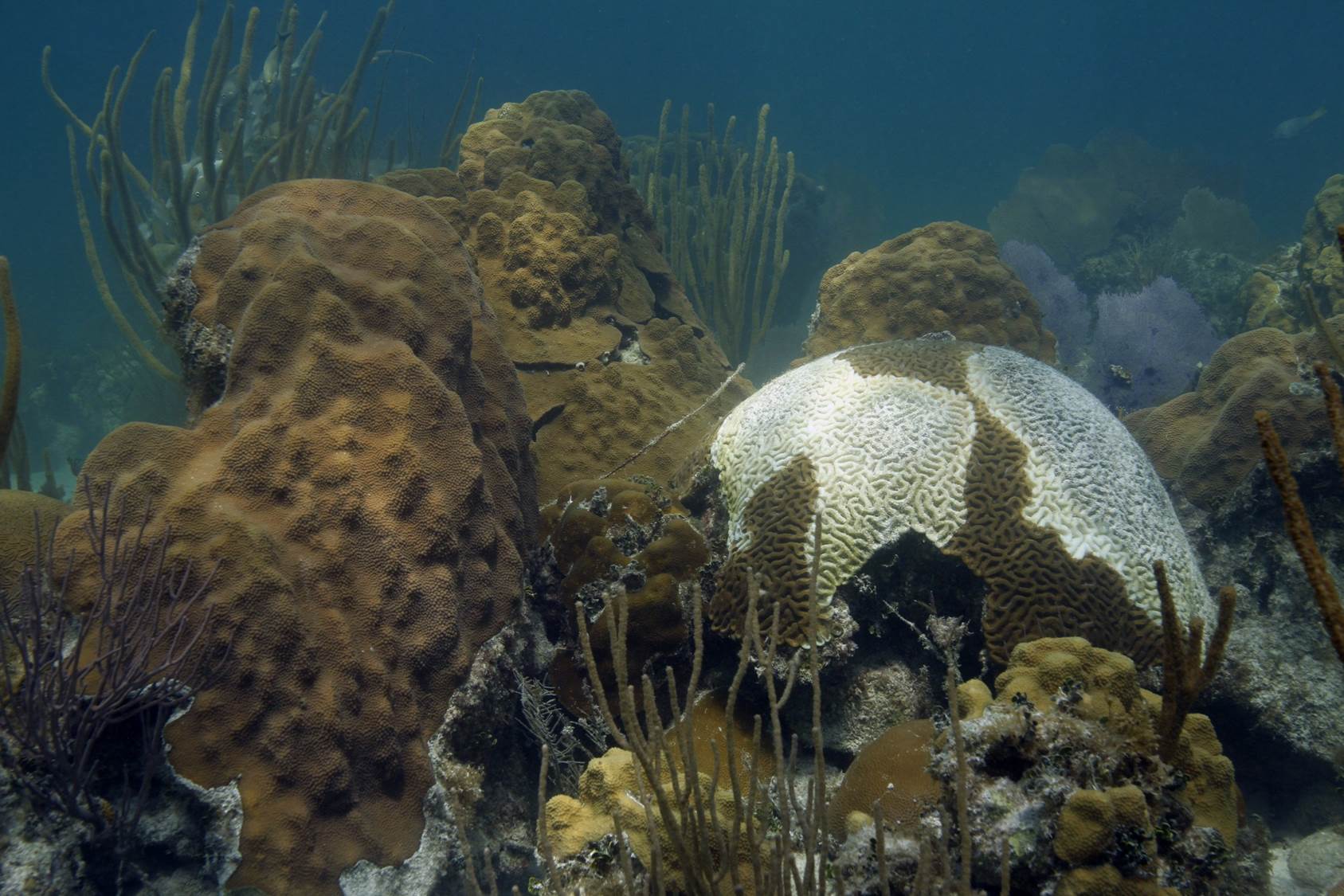
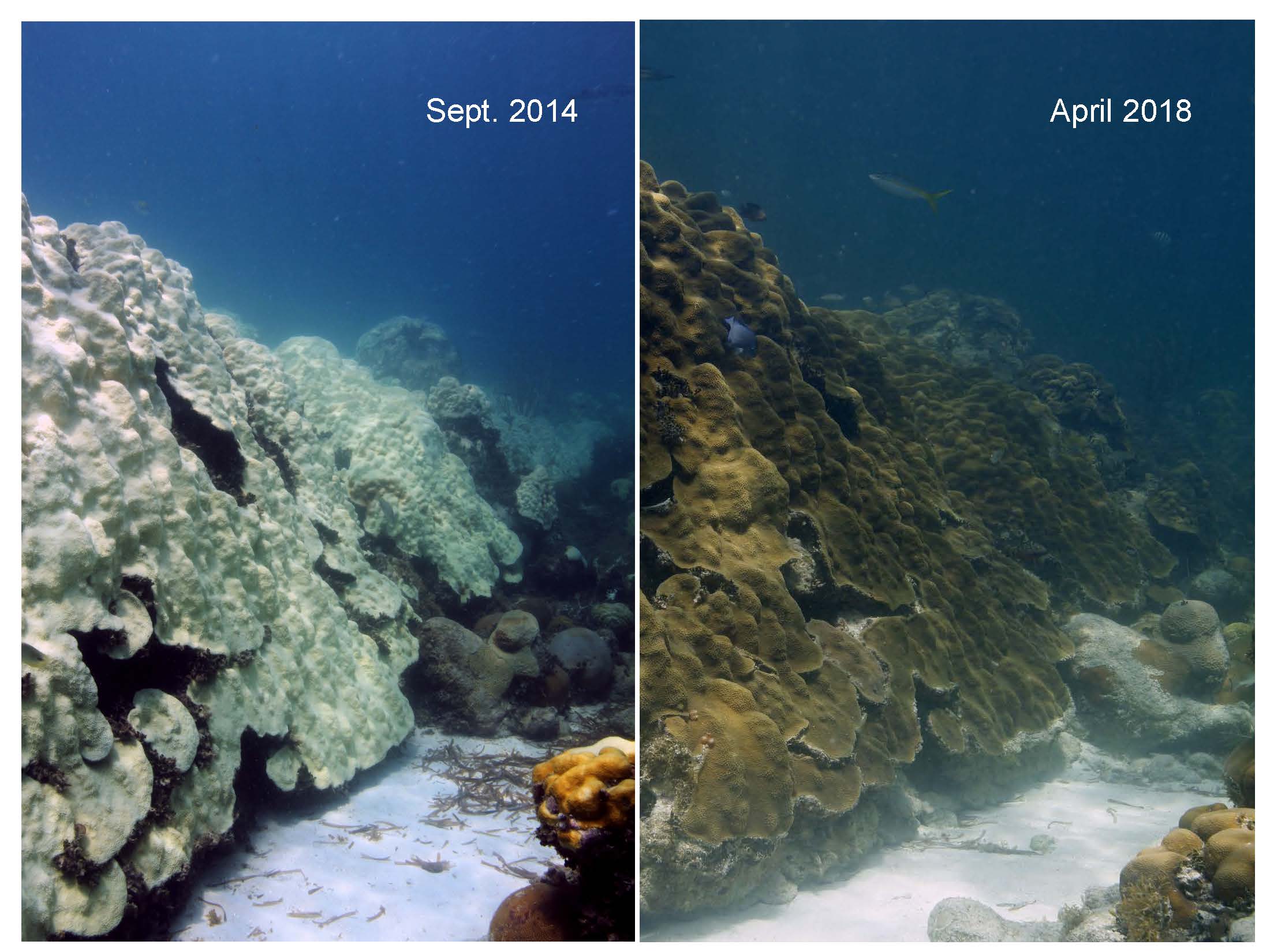
The most dangerous part of the hurricane is the eyewall close to the ocean. It’s where the storm draws energy from heat in the water, which influences how strong – and how quickly – the storm will develop. It’s also where the strongest winds lurk.Direct and continuous observations of the lower eye-wall would help forecasters understand critical information about the storm’s development. NOAA P-3 “Hurricane Hunters” routinely fly through hurricane eyewalls to gather storm data, but avoid flying close to the ocean because conditions are too hazardous.