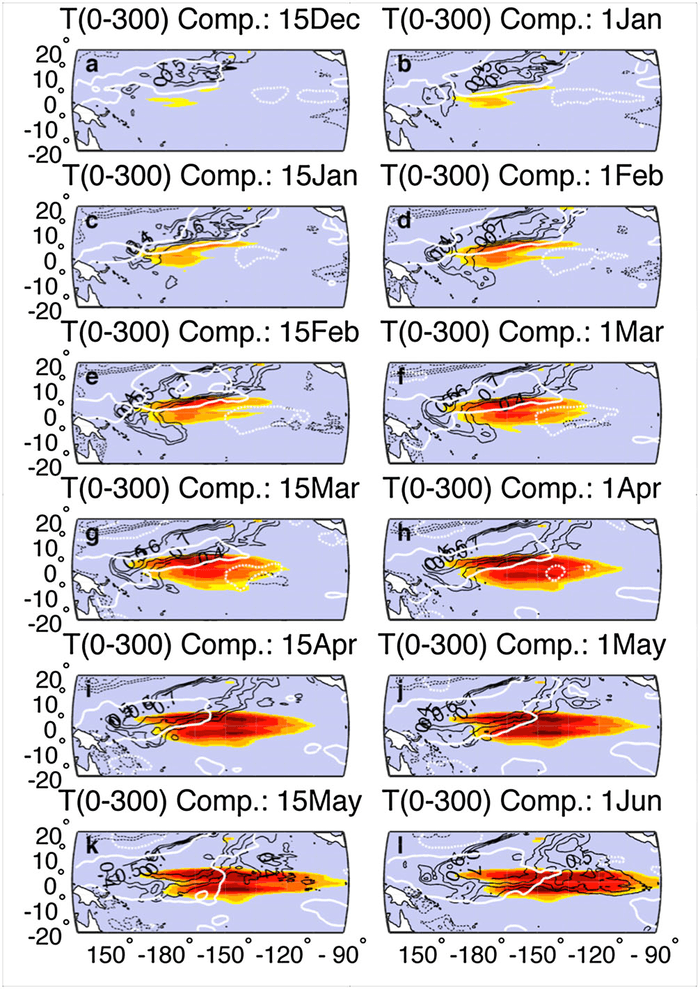
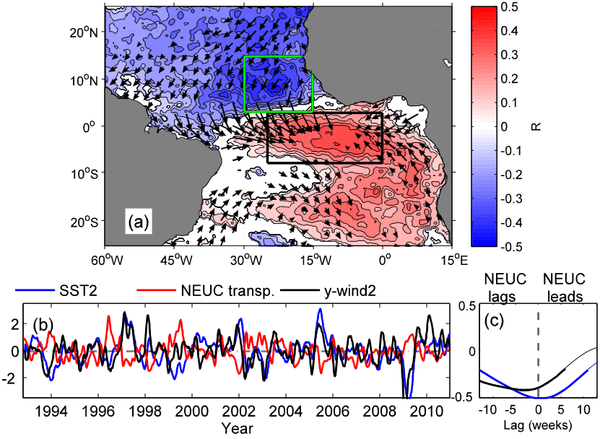
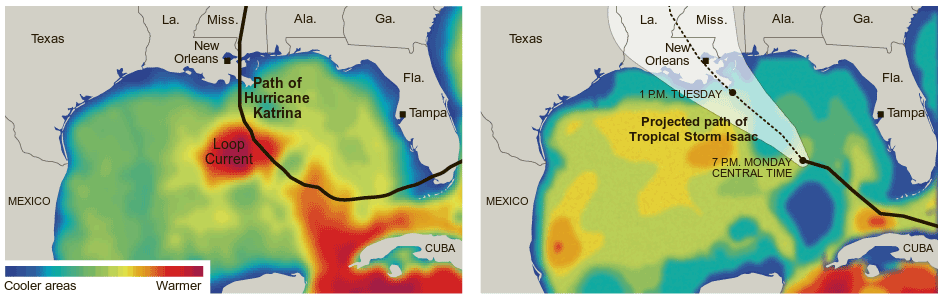
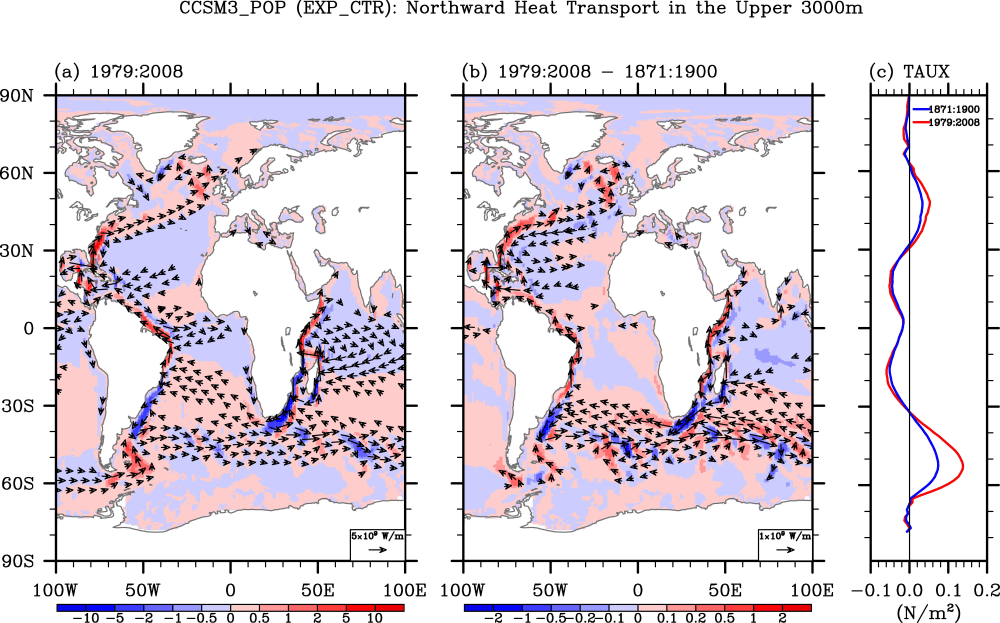
Triggering of El Nino through trade-wind induced charging of the equatorial Pacific
In a recent study by scientists at Boston University, PHOD, and NCAR, a new mechanism was uncovered for initiating ENSO events wherein SLP-generated North Pacific trade winds induce subsurface heat content changes that serve as precursors to El Ninos. This trade-wind charging mechanism of the equatorial Pacific is fundamentally different from any previously diagnosed, and studies examining the surface and subsurface ocean dynamics associated with this mechanism are underway.