NOAA’s Global Drifter Program: Ocean Dynamics Data Improves Forecasting and Coastal Safety
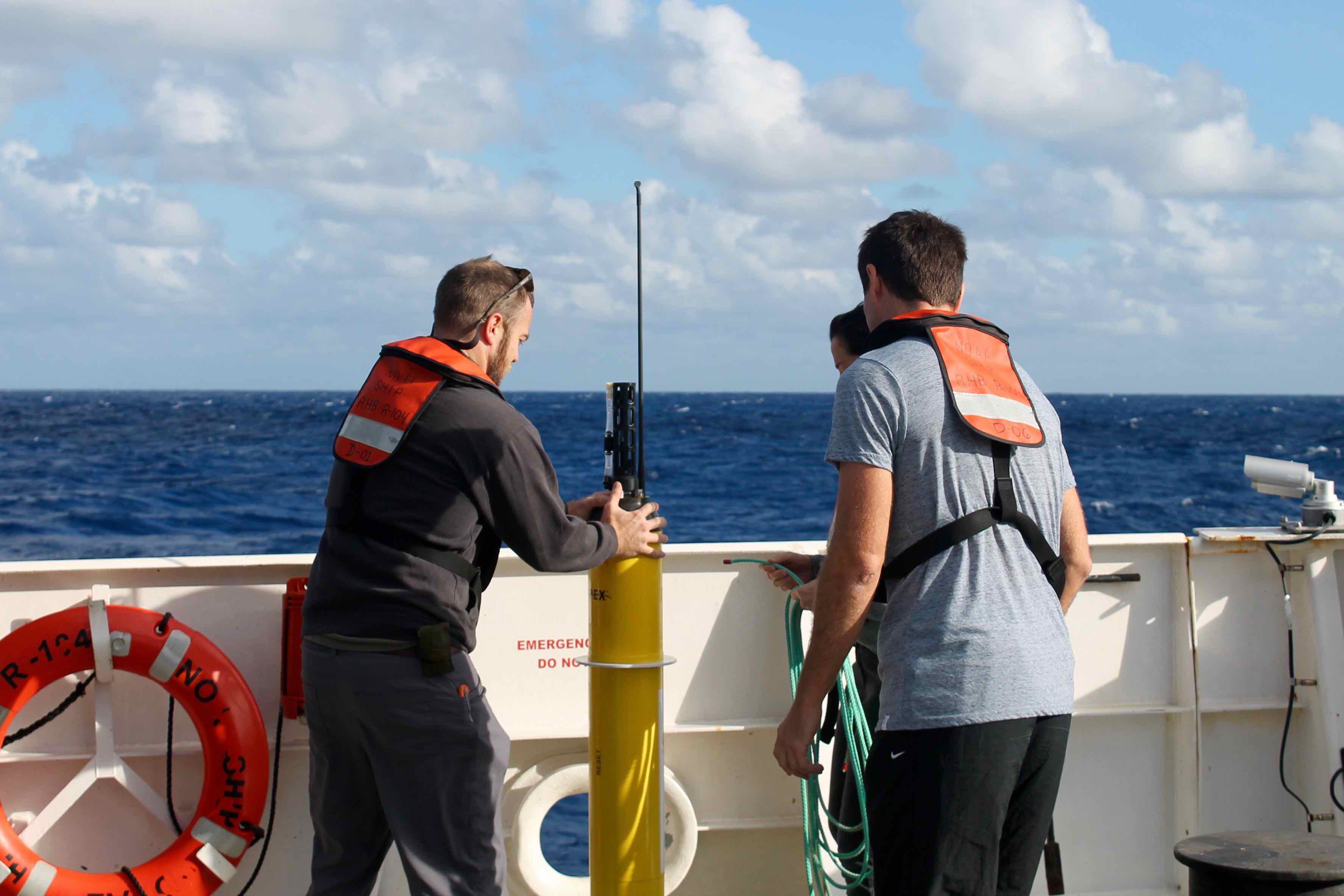
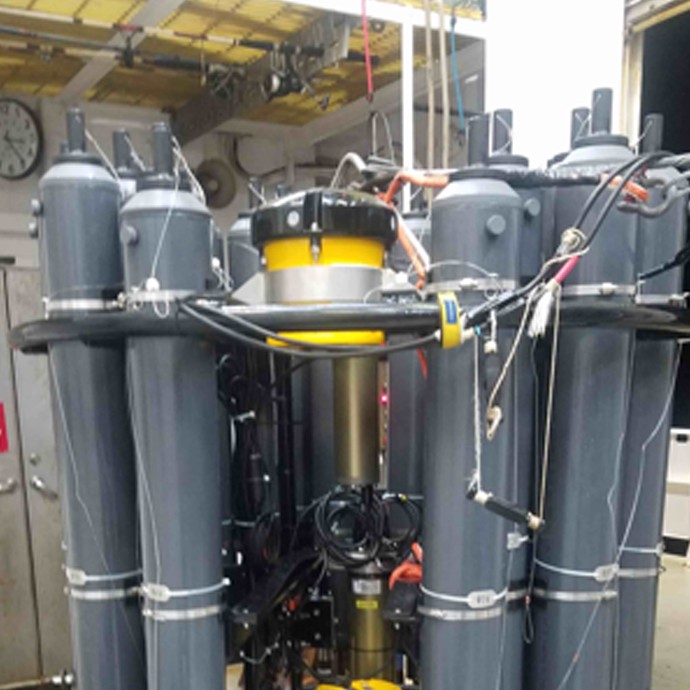
NOAA’s Global Drifter Program is a globally collaborative research project that provides near real-time marine data for the world. It allows us to record data for weather forecasts, track decadal patterns, and pinpoint inter-annual climate variations like El Nino Southern Oscillation. Global drifters provide observational verification for weather models, calibrate satellite observations, and collect and transfer new data about the ocean temperature, currents and barometric pressure.