Hurricane Humberto (22-24 September 2001)
Coordinated NOAA and NASA aircraft observations in Hurricane
Humberto from GPS dropsondes, AXBTs, Doppler radars, stepped
frequency microwave radiometers (SFMRs), a scanning radar
altimeter ( SRA) and other remotes sensors provide an
observational database for the development of the
next-generation high resolution TC numerical models.
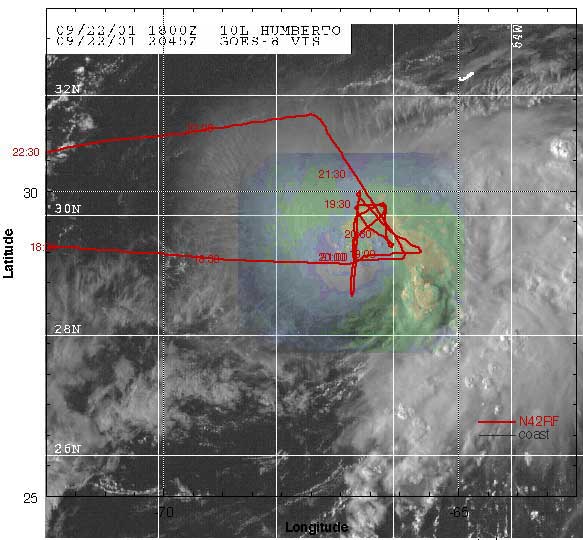
The storm changed structure and intensity as it interacted with the
mid-latitude environment and it passed through an oceanic eddy
field and approached the Gulf Stream axis. Air-sea interactio
n processes played a role in the evolving storm structure over
the three days of aircraft observations from an asymmetric system
with major mid-latitude environmental interactions to a more symmetric
system. Subsequent to the observation period, the symm etric system
developed an eye at nearly 40 N as it moved eastward along the
Gulf Stream axis.

Major accomplishments from the experiments included a complete
three-dimensional mapping of the storm within 1000 km of the
center, from 100 m deep in the ocean to 65,000 ft in the
atmosphere . Highlights of this three-day experiment include:
During the missions Humberto intensified
to tropical storm strength on 22 September, to hurricane CAT 2
strength on23 September, and back to CAT 1 on 24 September.
Atmospheric and oceanic profiling within
1000 km of the storm center from the research aircraft and the
G-IV. Over the three days 305 GPS dropsondes and 90 AXBTs were
deployed, of which 8%of the dropsondes (25) failed to give wind
data, and 12% of the AXBTs (11) failed to give ocean thermal profiles.
The research carried airborne Doppler radars
providing full three-dimensional mapping of the wind field,
including the two NOAA WP-3D X-band (Tail) Doppler radars, NASA
DC-8 Ku/Ka-band dual-polarized (PR-2) Doppler radar scanning a
swath ±45° on either side of the aircraft track, and
the NASA ER-2 X-band Doppler radar (E-DOP) providing a vertical
cross-section of vertical and horizontal velocities along the
aircraft track.
Detailed microphysics measurements on two
aircraft including precipitation size particles to CN/CCN
measurements on N42RF and ice particle measurements on the NASA DC-8.
Two-dimensional wave spectra within 150 km of
the storm center using the NASA Scanning Radar Altimeter (SRA)
on N43RF.
Surface wind speed estimates from stepped
frequency microwave radiometers on N42RF and N43RF.
Remote sensed thermal, moisture, and aerosol
fields from the NASA DC-8 and ER-2.
First dual-polarized, dual-wavelength (Ka-
and Ku-band) radar data collected in a TC.
| Storm/ Date |
Aircraft (Duration) |
Altitude |
Experiment/ Pattern |
Comments (expendables) |
| Humberto |
|
|
|
|
| 22 September |
N42RF (8.9 h) mission
summary (572
Kb) (572
Kb)
one minute listing
GPS dropsondes
DC-8 (9 h) mission summary
GPS dropsondes
ER-2 (7 h)
WC-130
|
14 kft
37 kft
65 kft
5000 ft
|
3-plane XCDX/QPE Experiment.
N42RF, DC-8, and ER-2 within 150 nm radius of center.
|
- Tropical Storm Humberto intensifies to near
hurricane strength.
(18 AXBT, 41 GPS sondes)
- N43RF returns to MacDill AFB from Huatulco, MX.
|
| 23 September |
N43RF (8.9 h) mission
summary (572 Kb) (572 Kb)
one minute listing
GPS dropsondes
AXBTs
N42RF (8.9 h) mission
summary (1.1
Mb) (1.1
Mb)
one minute listing
GPS dropsondes
DC-8 (9 h) mission summary
GPS dropsondes
ER-2 (7 h)
WC-130
N49RF (9 h)
mission
summary (1.1Mb) (1.1Mb)
GPS dropsondes
|
6 kft
13 kft
28-37 kft
65 kft
10 kft
45 kft
|
4-plane COVES Experiment.
N42RF, N43RF, DC-8, and ER-2 within 400 nm radius of center.
Synoptic Surveillance
|
- Humberto strengthens to category 2 hurricane
during the mission
(36 AXBT, 134 GPS sondes)
- N42RF and N43RF recover in Wilmington, NC to
increase on station time.
- DC-8 has air-traffic control problems on first
leg reulting in the aircraft staying at 28 kft until passing
through the N eyewall where they climbed to 37 kft.
- N49RF mission delayed mission start 1.25 h
because of engine problem.
|
| 24 September |
N43RF (8.9 h) mission
summary (72 Kb) (72 Kb)
one minute listing
GPS dropsondes
N42RF
(8.9 h) mission summary (1.1Mb)
(1.1Mb)
one minute listing
GPS dropsondes
AXBTs
DC-8 (9 h) mission summary
GPS dropsondes
ER-2 (7 h)
N49RF (9 h)
mission
summary (1 Mb) (1 Mb)
GPS dropsondes
|
6 kft
13 kft
37 kft
65 kft
45 kft
|
4-plane COVES Experiment.
N42RF, N43RF, DC-8, and ER-2 within 400 nm radius of center.
Synoptic Surveillance
|
- N42RF and N43RF recover in Wilmington, NC. Return to
MacDill AFB on 25 September to increase on station time.
- N49RF recovers in Savannah, GA after completing the
surveillance mission to check engine problem that delayed
previous day mission. return to MacDill AFB 25 September.
|
|
|
 The storm changed structure and intensity as it interacted with the
mid-latitude environment and it passed through an oceanic eddy
field and approached the Gulf Stream axis. Air-sea interactio
n processes played a role in the evolving storm structure over
the three days of aircraft observations from an asymmetric system
with major mid-latitude environmental interactions to a more symmetric
system. Subsequent to the observation period, the symm etric system
developed an eye at nearly 40 N as it moved eastward along the
Gulf Stream axis.
The storm changed structure and intensity as it interacted with the
mid-latitude environment and it passed through an oceanic eddy
field and approached the Gulf Stream axis. Air-sea interactio
n processes played a role in the evolving storm structure over
the three days of aircraft observations from an asymmetric system
with major mid-latitude environmental interactions to a more symmetric
system. Subsequent to the observation period, the symm etric system
developed an eye at nearly 40 N as it moved eastward along the
Gulf Stream axis. Major accomplishments from the experiments included a complete
three-dimensional mapping of the storm within 1000 km of the
center, from 100 m deep in the ocean to 65,000 ft in the
atmosphere . Highlights of this three-day experiment include:
Major accomplishments from the experiments included a complete
three-dimensional mapping of the storm within 1000 km of the
center, from 100 m deep in the ocean to 65,000 ft in the
atmosphere . Highlights of this three-day experiment include: