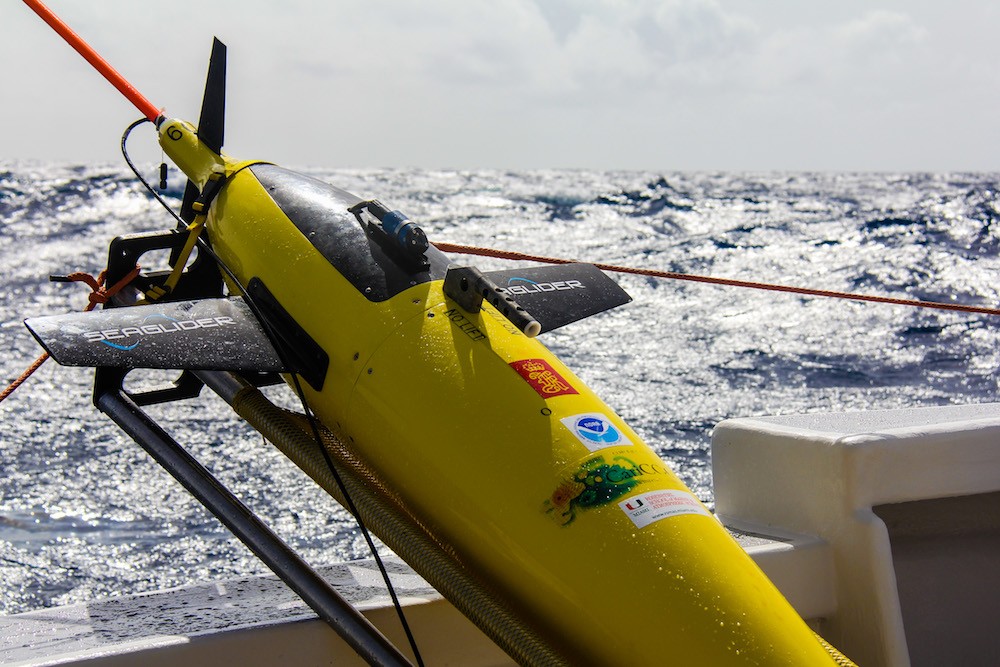
Scientists strategically deployed the gliders during the peak of hurricane season, from July through November 2017, collecting data in regions where hurricanes commonly travel and intensify. The gliders continually gathered temperature and salinity profile data, generating more than 4,000 profiles to enhance scientific understanding of the air-sea interaction processes that drive hurricane intensification.
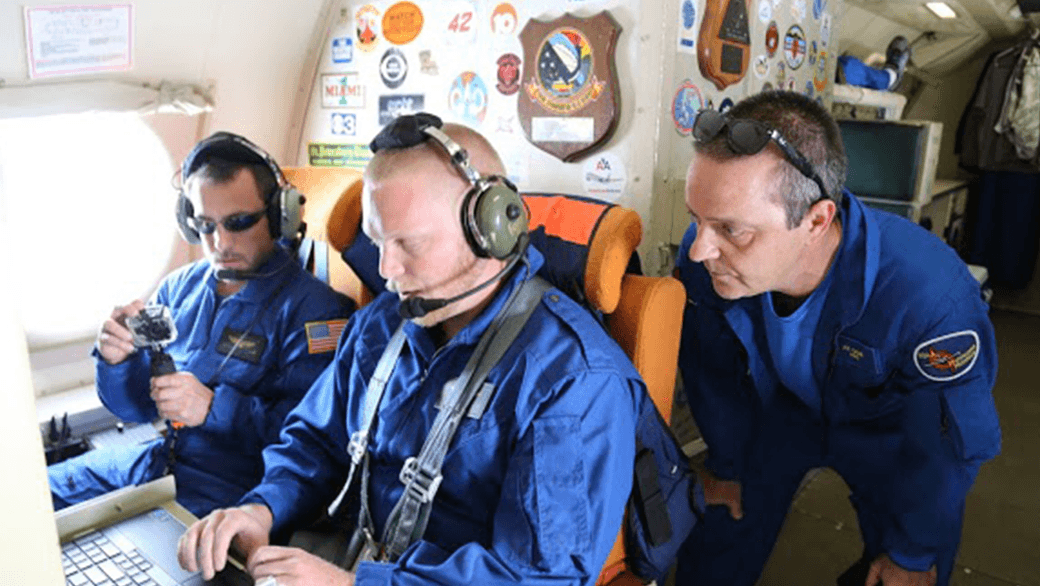
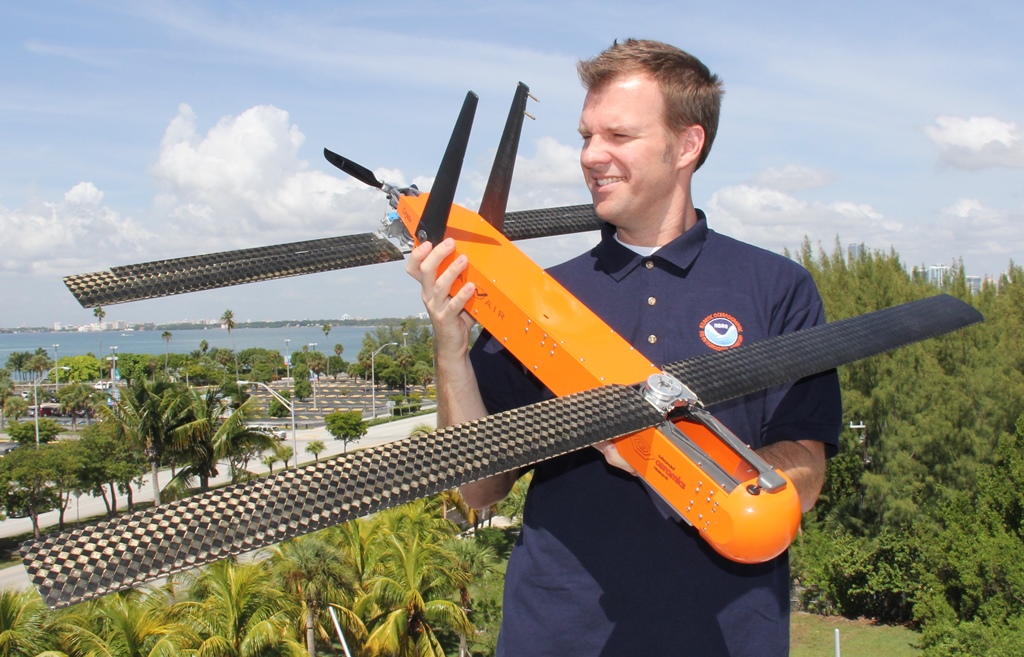
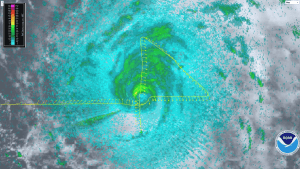
NOAA successfully deployed unmanned aircraft from a NOAA P-3 Hurricane Hunter directly into a hurricane for the first time. NOAA deployed four Coyote Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) in Hurricane Edouard during flights conducted September 15-17, 2014 out of Bermuda. Scientists on board the P-3 aircraft received meteorological data from the Coyote UAS in both the eye and surrounding eyewall of Hurricane Edouard.
“Data from these new and promising technologies have yet to be analyzed but are expected to provide unique and potentially groundbreaking insights into a critical region of the storm environment that is typically difficult to observe in sufficient detail,” said Joe Cione, a NOAA Hurricane Researcher and Principal Investigator for the Coyote project.
Post-Hurricane Sandy federal funding, the Disaster Relief Appropriations Act of 2013, provided NOAA with the opportunity to test this new technology in hopes of better understanding and evaluating how storms evolve and intensify. The goal of the Coyote is to collect temperature, pressure and wind observations below 3,000 feet, where manned aircraft cannot fly safely.
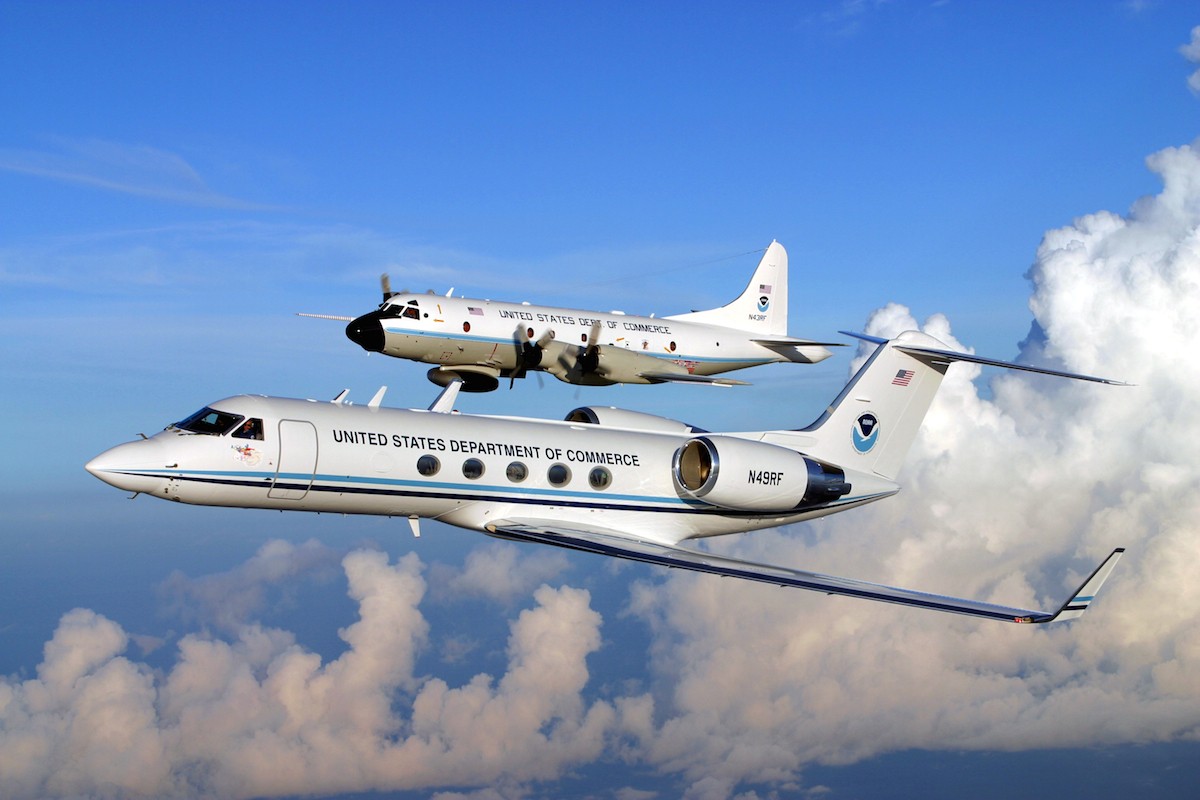
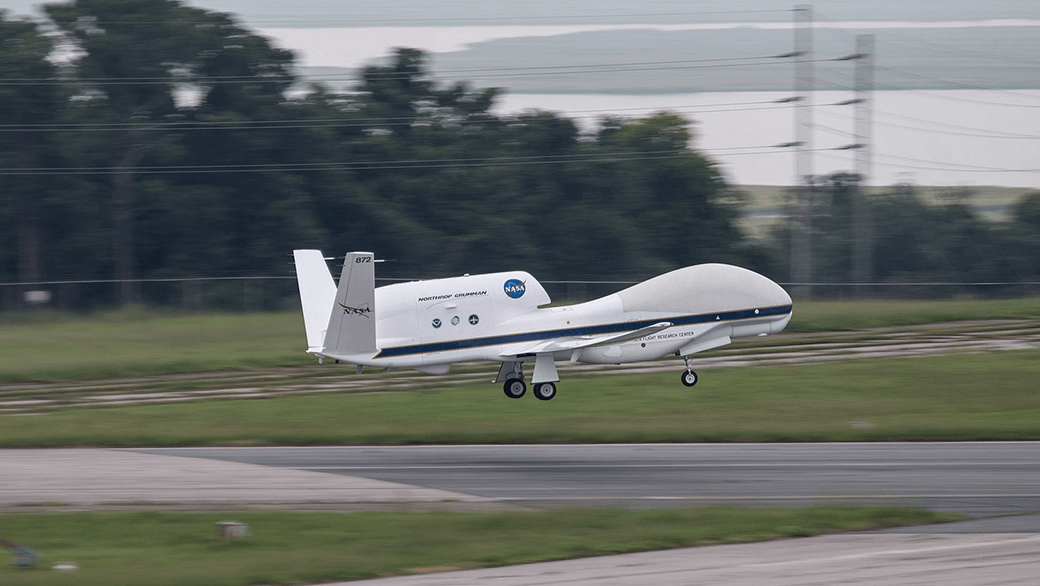
NOAA’s Aircraft Operations Center (AOC) maintains two P-3 Orion turboprop aircraft and Gulfstream-IV jet for hurricane observations. These aircraft also flew in Hurricane Edouard as a part of a larger experiment to collect data for hurricane model evaluation. These hurricane research efforts are designed to provide insight and understanding that translates into improved hurricane model forecasts. The improvement of this Environmental Intelligence gives forecasters tools to help prepare communities for possible hurricane impacts.
The Government of Bermuda hosted these missions and effectively served as international partners in NOAA’s effort to improve hurricane forecasts for all countries affected by these storms. NOAA looks forward to continued research into the application of air-deployed unmanned aircraft to support and improve hurricane research and forecasts.