IFEX daily log
Friday, July 15, 2005
At the morning HRD conference call it was noticed that the area that had been the
target of the previous daysŐ missions remained in an unfavorable environment, with
moderate to strong 20-kt vertical shear in the vicinity. To the southeast, infrared imagery
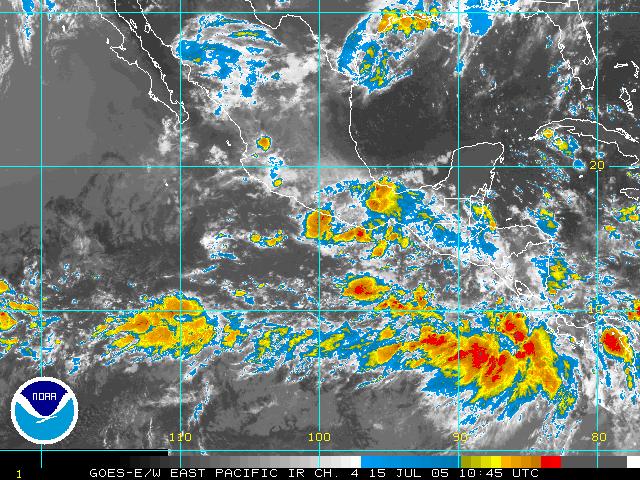
(Fig. 5) showed a widespread area of deep convection just offshore Costa Rica. This
general area had persisted since the previous day and was noticed in the discussions of
the previous day. It had been discounted as being ITCZ-related convection, but
severalfactors led to the conclusion that this may be the preferred location for genesis
rather than the one being targeted the previous day. First, the convection was quite
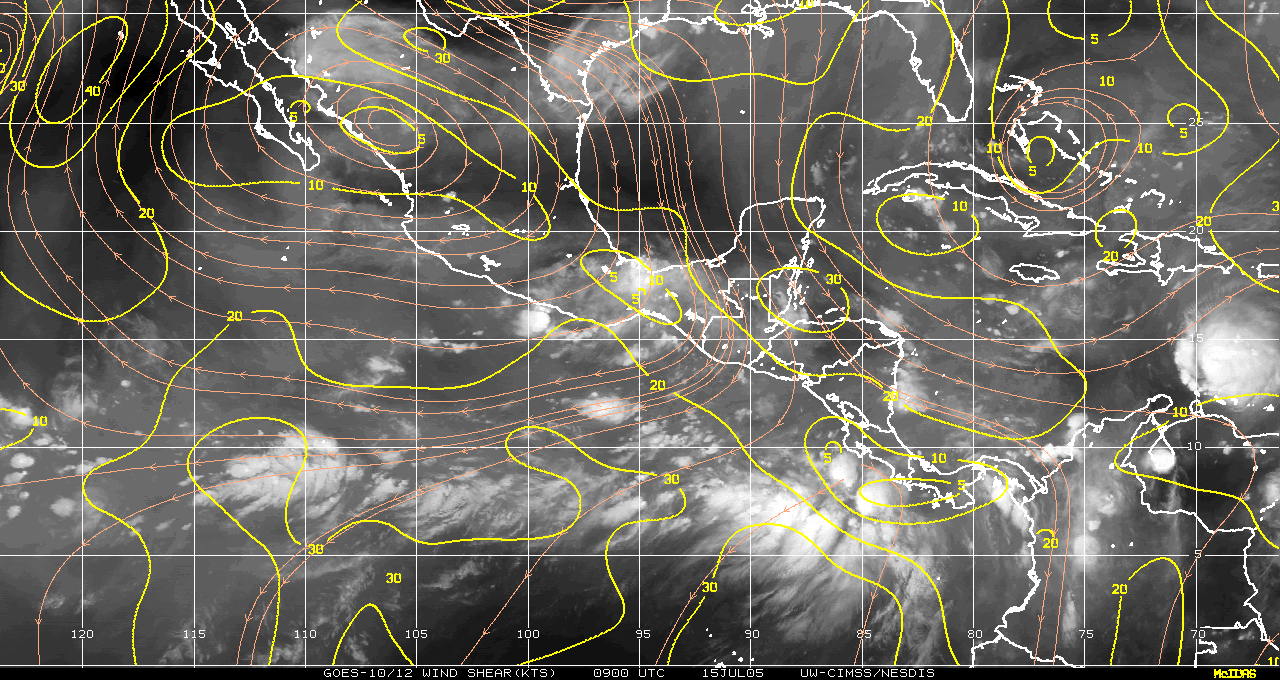 persistent. Second, the shear in this environment was more favorable for development
than over the area targeted yesterday (Fig. 6). Shear in the zone that was targeted
yesterday is still about 20 kts today, whereas the area with the persistent convection has a
region of 5-10 kt shear on the northeast edge of the convection. Third, observations
from the N43RF night flight indicated that there was fairly strong low-level
northeasterlies off the west coast of Costa Rica and Nicaragua and southwesterly flow
persistent. Second, the shear in this environment was more favorable for development
than over the area targeted yesterday (Fig. 6). Shear in the zone that was targeted
yesterday is still about 20 kts today, whereas the area with the persistent convection has a
region of 5-10 kt shear on the northeast edge of the convection. Third, observations
from the N43RF night flight indicated that there was fairly strong low-level
northeasterlies off the west coast of Costa Rica and Nicaragua and southwesterly flow
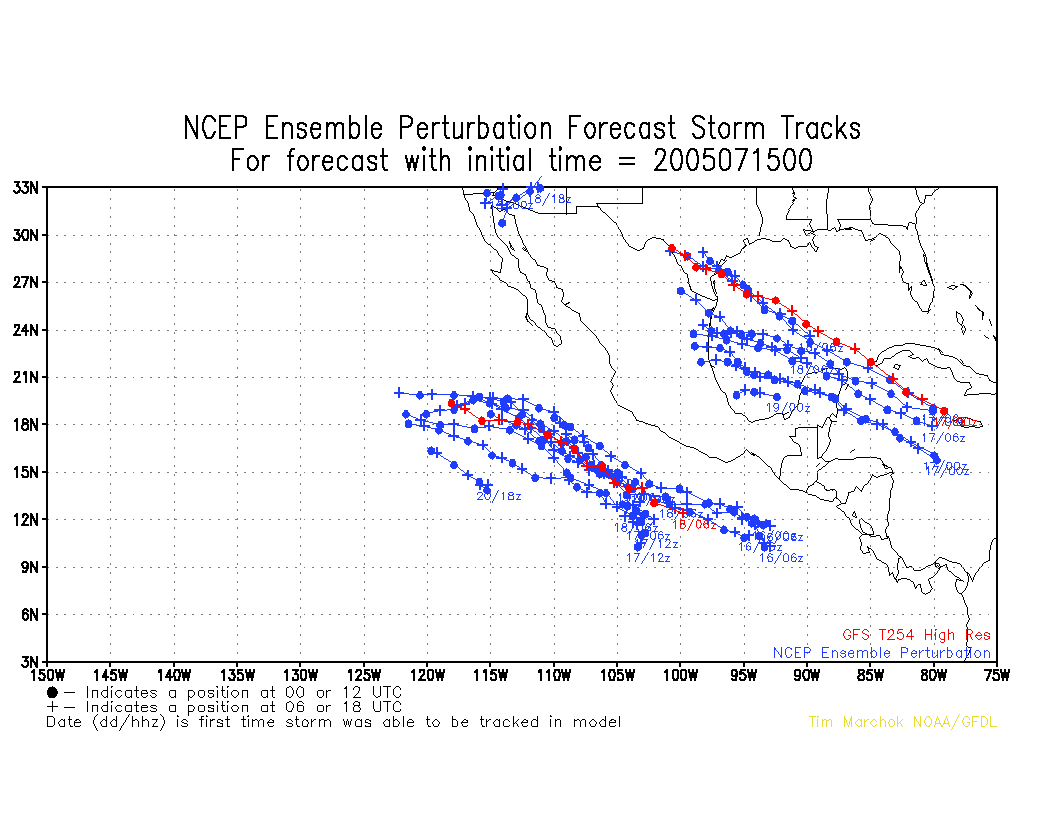 further out into the water, indicating a possible shear axis or convergence zone. Fourth,
global model forecast ensembles (Fig. 7) have begun to predict genesis in the region just
west of the deep convection in the next 1-3 days. For these reasons, we decided to shift
our target to the area of deep convection between about 5 and 10 N and 84 and 90 W.
The pattern planned for N42RF (Fig. 8) was a modified diamond pattern intended to
cover the maximum amount of territory as possible. The axis of the diamond would be
further out into the water, indicating a possible shear axis or convergence zone. Fourth,
global model forecast ensembles (Fig. 7) have begun to predict genesis in the region just
west of the deep convection in the next 1-3 days. For these reasons, we decided to shift
our target to the area of deep convection between about 5 and 10 N and 84 and 90 W.
The pattern planned for N42RF (Fig. 8) was a modified diamond pattern intended to
cover the maximum amount of territory as possible. The axis of the diamond would be
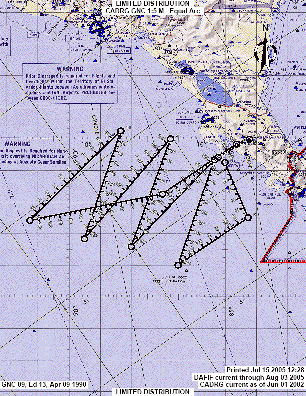 oriented along a WNW-ENE axis, roughly aligned parallel and just to the north of a
convergence line suggested by QuikScat imagery confirmed by a subsequent overpass
(Fig. 9). At flight level, there is a clear cyclonic shear axis or gyre centered roughly at7.5
N 85.5 W. There is some evidence of whitecaps at the surface south of this feature. It is
possible that the feature was developed by the deep convection that had formed during
oriented along a WNW-ENE axis, roughly aligned parallel and just to the north of a
convergence line suggested by QuikScat imagery confirmed by a subsequent overpass
(Fig. 9). At flight level, there is a clear cyclonic shear axis or gyre centered roughly at7.5
N 85.5 W. There is some evidence of whitecaps at the surface south of this feature. It is
possible that the feature was developed by the deep convection that had formed during
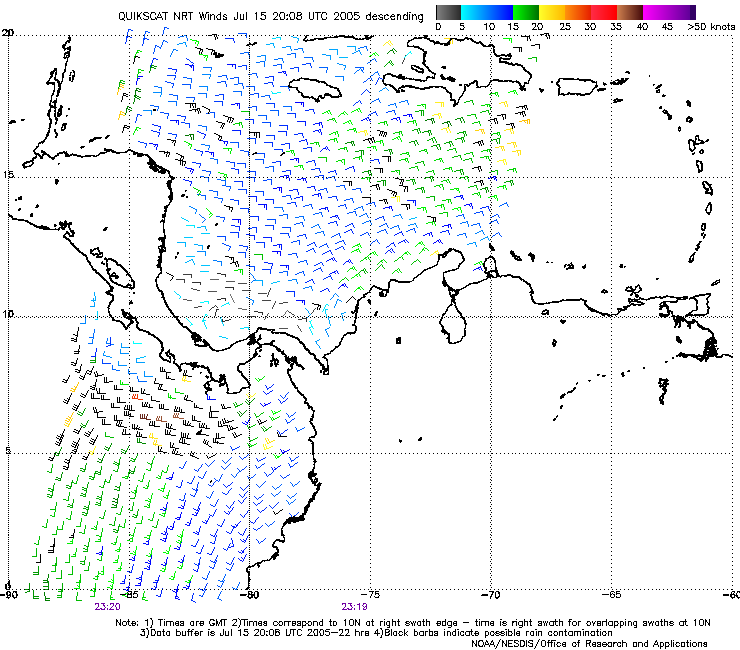 the previous night, but that is impossible to say definitively since no aircraft was in this
system the previous night, except for a passby with F/AST imagery by N43RF. There are
large areas of anvil debris throughout much of the flight, and some areas of stratiform
rain with convective elements embedded within them. There are several areas of near
white-out conditions in terms of visibility due to the presence of stratiform cloud.
the previous night, but that is impossible to say definitively since no aircraft was in this
system the previous night, except for a passby with F/AST imagery by N43RF. There are
large areas of anvil debris throughout much of the flight, and some areas of stratiform
rain with convective elements embedded within them. There are several areas of near
white-out conditions in terms of visibility due to the presence of stratiform cloud.
During the flight the pattern was modified slightly. The pattern was changed to
cut off the northern tip of the top triangle, and to extend the southwest end of the pattern
to the south and the east. The purpose of this change was to try to straddle the flight-
level cyclonic wind shift (i.e., to provide more observations in the flight-level
southwesterly flow.
Observations from the flight by N42RF during the day have helped to guide the
pattern planning for N43RF. N43RF is planning to fly the square-spiral pattern, and have
asked N42RF for a centroid for the pattern. Based on flight-level observations of the
cyclonic wind shift/gyre, N42RF identified the center as being at 7.5 N 86 W. Assuming
a movement of 6 degrees/day, that makes for a motion of 3 degrees over a 12-h period.
This seems awfully fast, so an assumed motion of 1.5 degrees was made for the system.
That puts the centroid at 7.5 N 87.5 W at the time N43RF will be in the pattern. The
square-spiral pattern covers about 3 degrees of area, and takes about 3.5 to 4 h to execute.
Since the ferry for this mission will be so short, the size of the pattern can be expanded if
necessary. Upon further inspection of the flight-level winds, it appears that a fairly
clearly-defined wave is evident, with an axis at about 87 or 88 W. That bodes well for
possible future development, since there is a forcing mechanism (i.e., the wave) and the
environment is favorable (i.e., relatively low shear and low-level convergence associated
with strong southwesterly flow at the surface). It will be very interesting to see how the
system evolves tonight and into tomorrow. Surface winds are strong southwesterlies
throughout the region, with magnitudes as high as 25 kt.
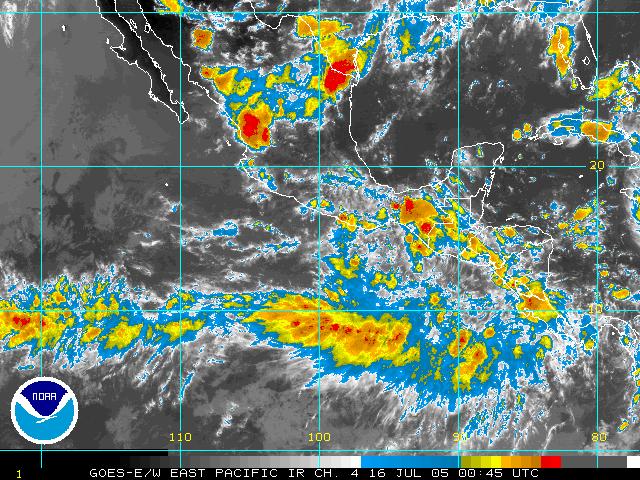 By the end of the flight, infrared imagery (Fig. 10) showed widespread ITCZ
convection at about 8 N 100 W and areas of convection in the target region around 8 N
88 W. The cloud patterns further west continue to show striations oriented NE-SW,
suggesting a fair amount of northeasterly shear over that area, while the cloud patterns in
the target area show much less evidence of experiencing shear, even though the amount
of cold cloud tops is less than that further west. That may be normal, though, since the
typical diurnal cycle is governed by little convection during the day and a blossoming of
convection during the overnight hours. This is why it will be so important for N43RF to
fly into the region tonight, and then for N42RF to fly into the same target the following
day, to document the changes to the atmosphere that arose as a result of the convective
heating.
By the end of the flight, infrared imagery (Fig. 10) showed widespread ITCZ
convection at about 8 N 100 W and areas of convection in the target region around 8 N
88 W. The cloud patterns further west continue to show striations oriented NE-SW,
suggesting a fair amount of northeasterly shear over that area, while the cloud patterns in
the target area show much less evidence of experiencing shear, even though the amount
of cold cloud tops is less than that further west. That may be normal, though, since the
typical diurnal cycle is governed by little convection during the day and a blossoming of
convection during the overnight hours. This is why it will be so important for N43RF to
fly into the region tonight, and then for N42RF to fly into the same target the following
day, to document the changes to the atmosphere that arose as a result of the convective
heating.
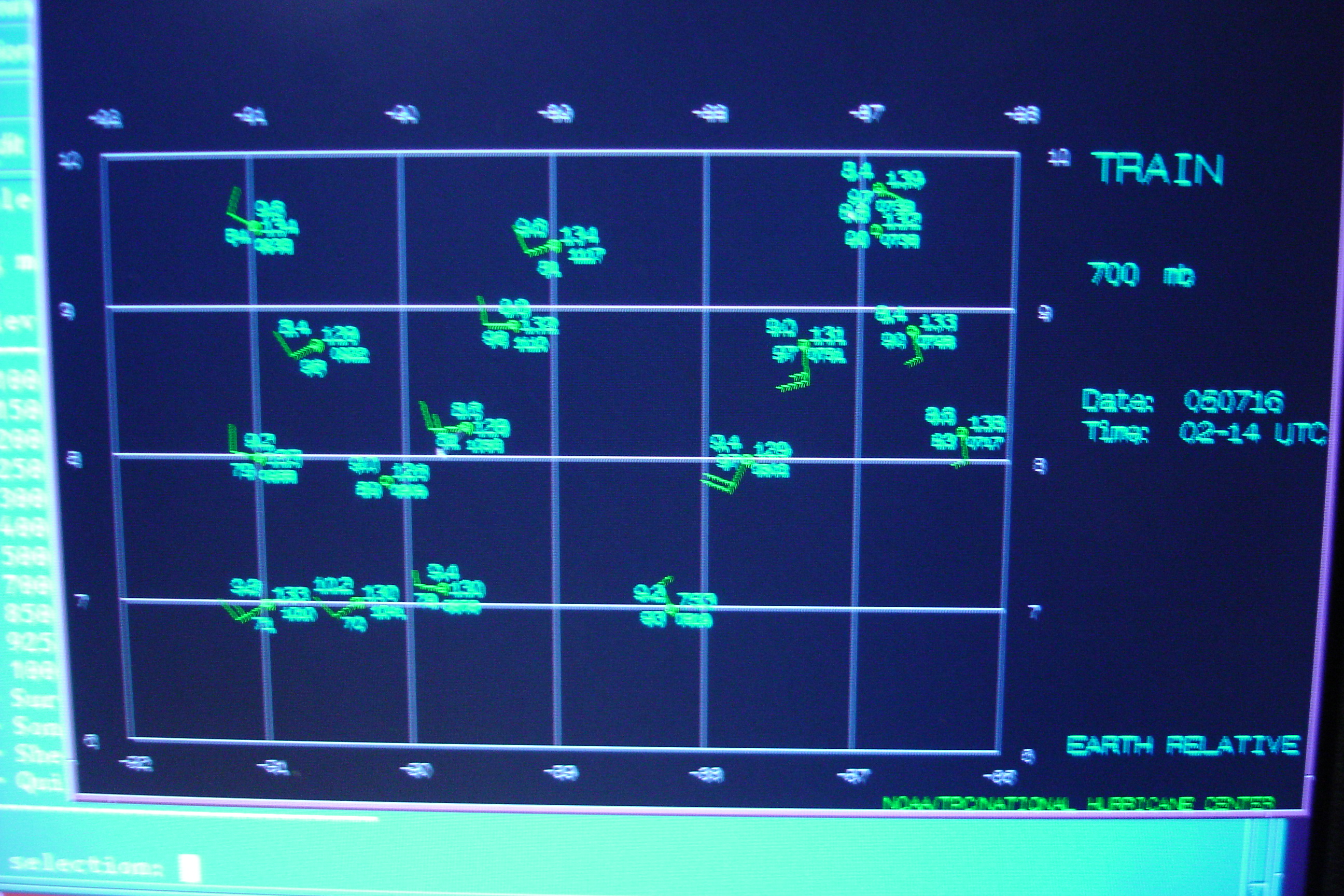
N43RF had a scheduled takeoff of 05 UTC. The flight plan called for a modified
diamond pattern similar to that flown by N42RF during the day mission. This mission
would be in conjunction with the NASA ER-2 (see 050716I mission summary for a more
complete description of this flight). During the flight there was not as much widespread
deep convection as had been expected, and N43RF had designed the pattern a bit too far
to the south initially to see the possible circulation center at flight-level. However
dropsonde measurements did show a possible shear axis or even a circulation center (Fig.
11) at about 10 N 88 W. The wind shift shows up well at 700 mb (Fig. 11a) and may be
reflected at the surface by a cyclonic wind shift (Fig. 11b). The cyclonic shear zone thus
seems to be coherent vertically.
Rob Rogers
HRD Field Program director
Return to IFEX calendar page
![[Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory]](../../hrd_top_logo7.jpg)
![[OAR/DOC/NOAA Logos]](../../oar_noaa_doc_logos3.jpg)