Galapagos Islands: A Telling Study Site for Coral Reef Scientists
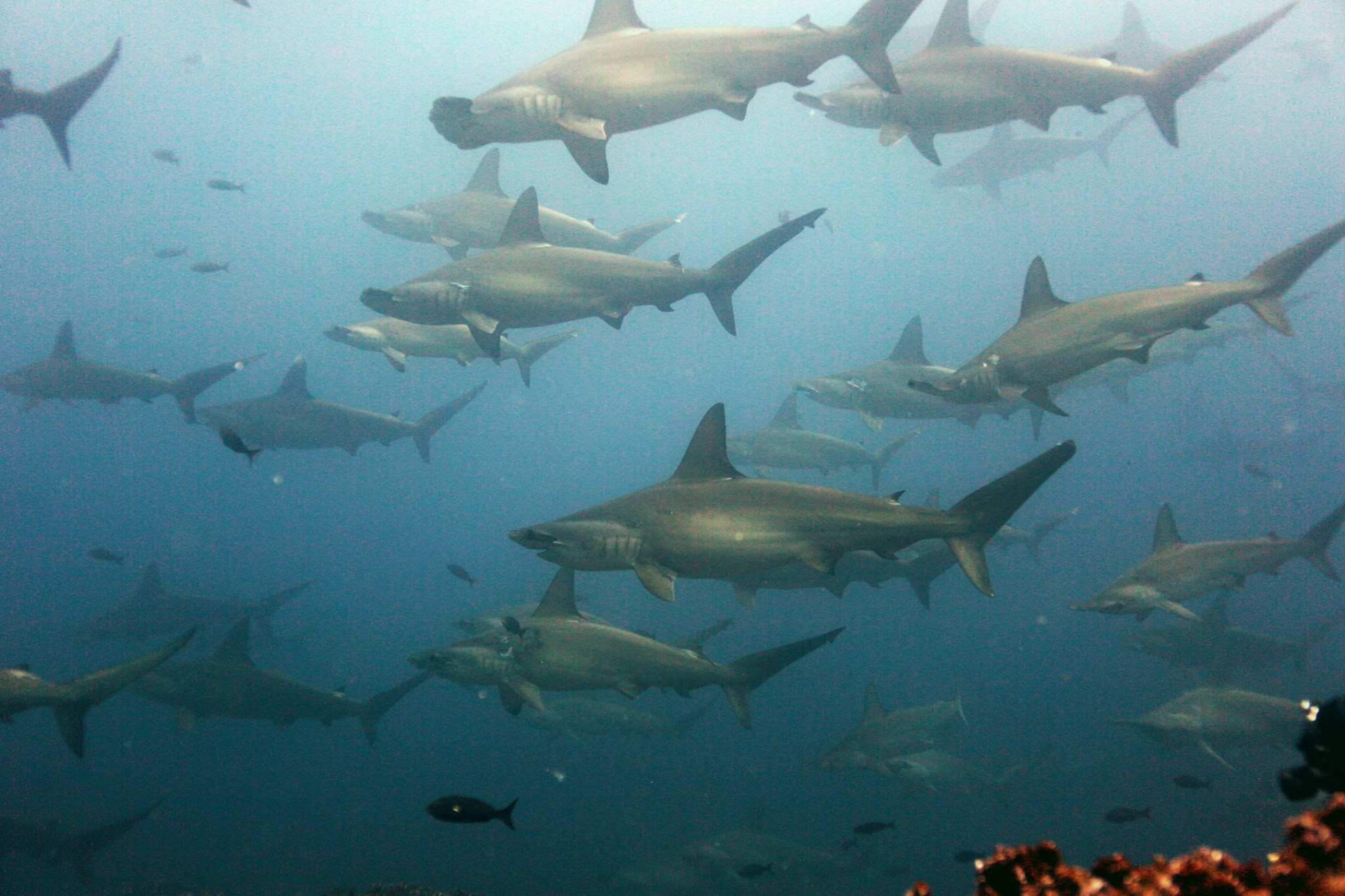
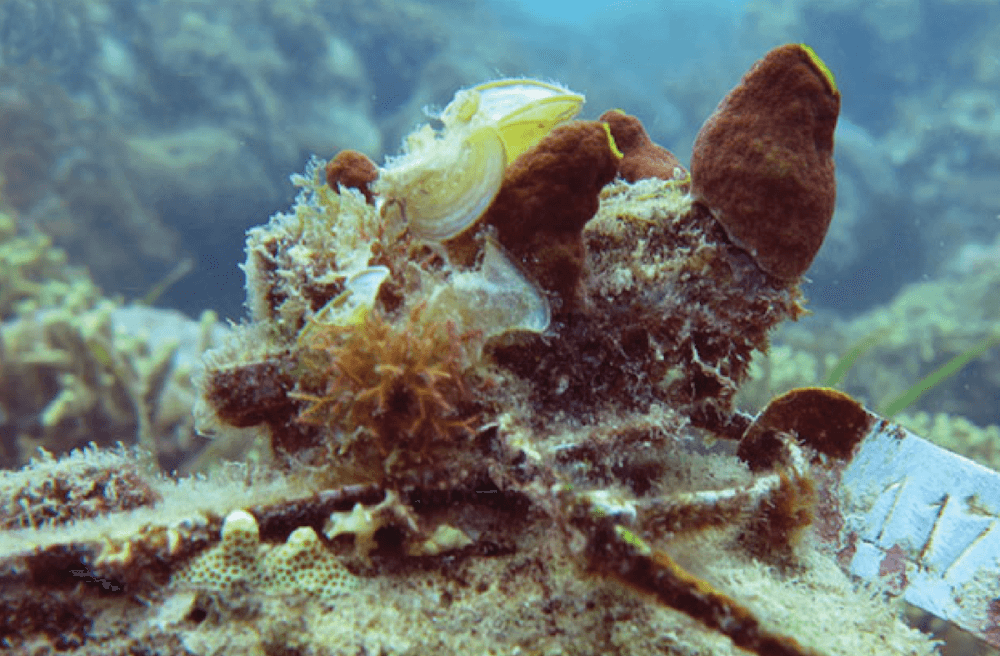
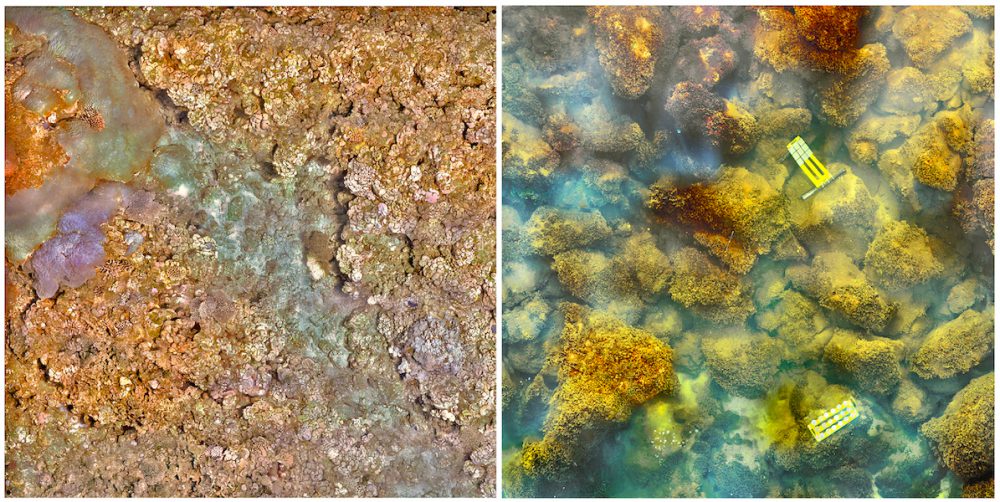
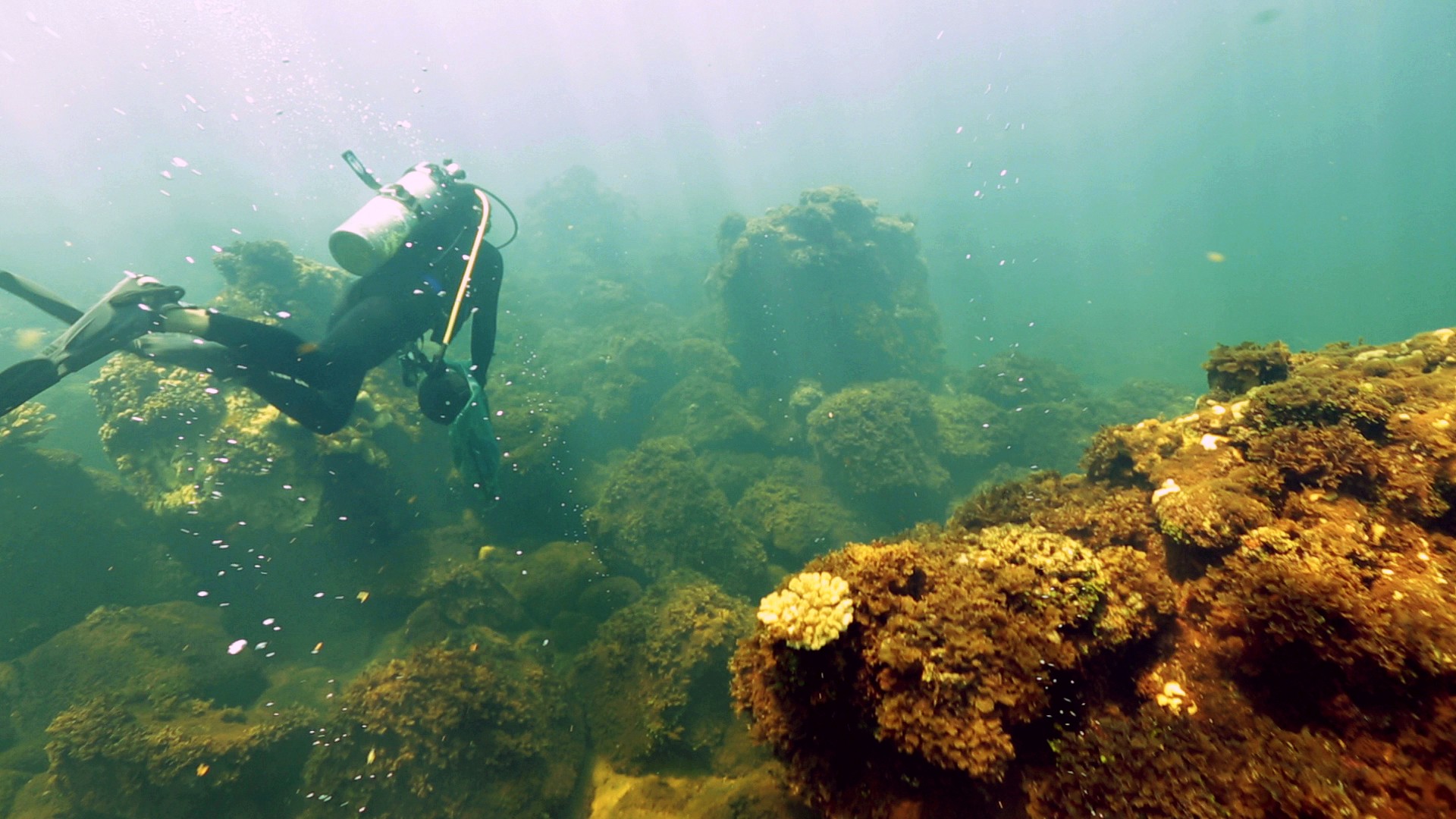
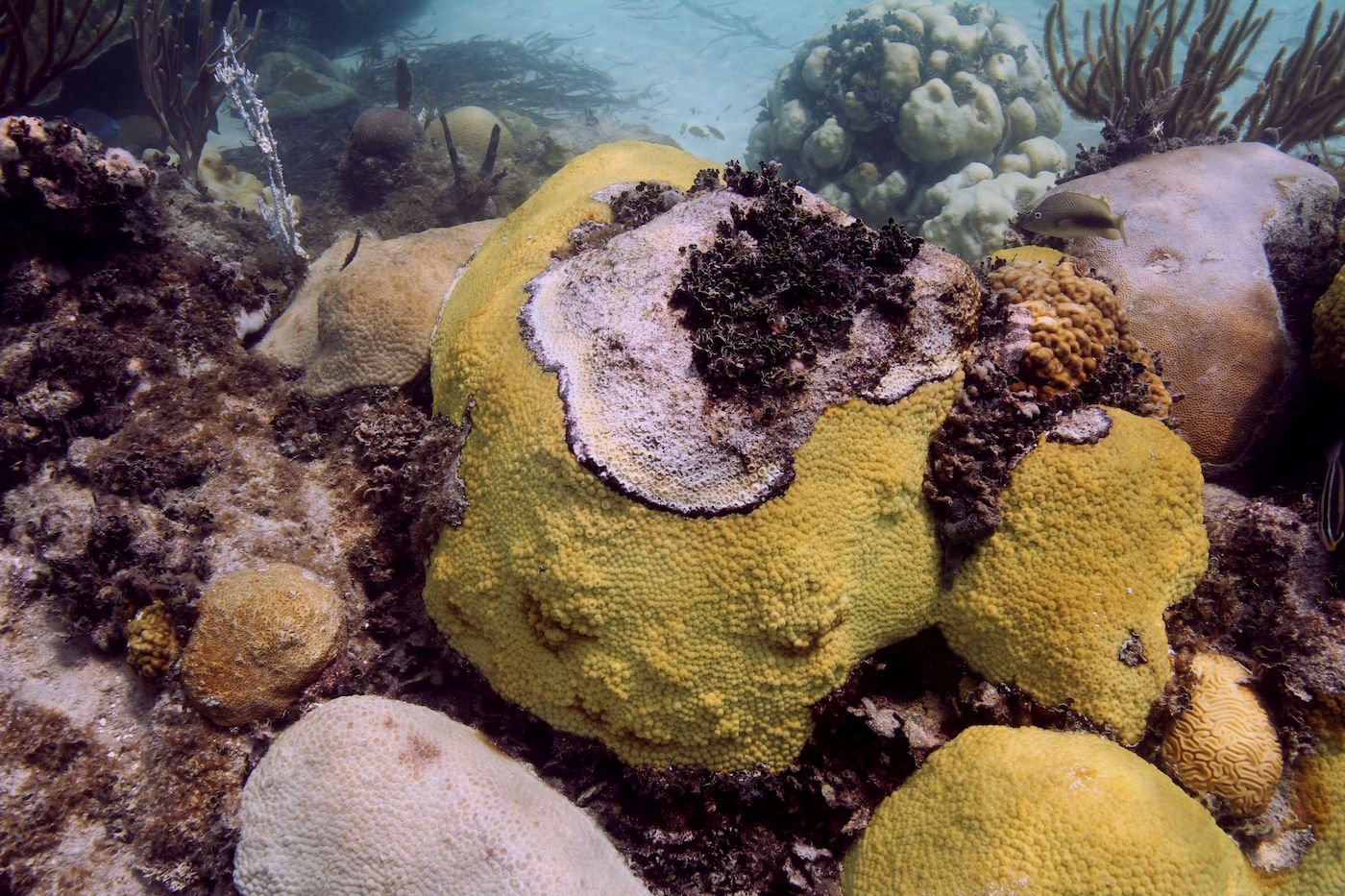
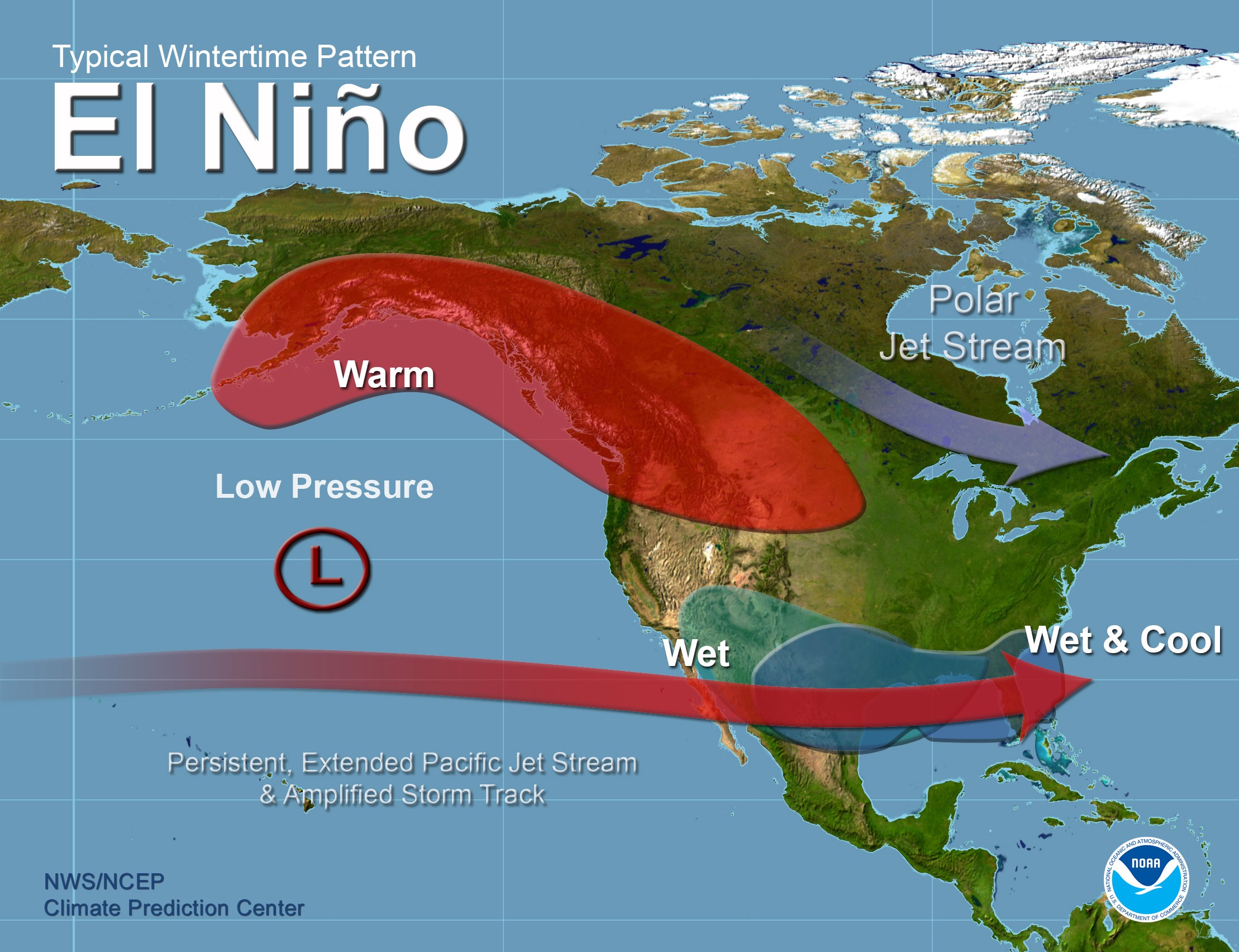
Coral scientists recently traveled to the Galapagos Islands to document coral reef health following the 2016-17 El Niño Southern Oscillation event (ENSO), which bathed the region in abnormally warm waters. Historically, these events have triggered coral bleaching and large-scale mortality, as seen in response to ENSO events of 1982-83 and 1997-98. Interestingly, these same reefs exhibited minimal bleaching in response to this most recent event. Scientists are determining whether this response is due to differing levels of heat stress, or an increased tolerance to warm water in the remnant coral communities.